Metaproterenol Tablets: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: metaproterenol sulfate
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class: Adrenergic bronchodilators
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 14, 2025.
On This Page
Metaproterenol Tablets Description
Metaproterenol sulfate in tablet form is an oral bronchodilator.
Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 10 mg or 20 mg of metaproterenol sulfate. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and pregelatinized starch.
Metaproterenol sulfate, 1-(3,5 dihydroxyphenyl) -2-isopropyl-aminoethanol sulfate, is a white, crystalline, racemic mixture of two optically active isomers. It has the following structural formula:
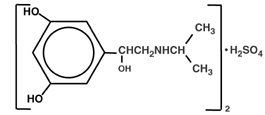
|
(C11H17NO3)2·H2SO4 |
MW 520.59 |
Metaproterenol Tablets - Clinical Pharmacology
Metaproterenol sulfate is a beta adrenergic agonist bronchodilator.
The pharmacologic effects of beta adrenergic agonist drugs, including metaproterenol, are at least in part attributable to stimulation through beta adrenergic receptors of intracellular adenyl cyclase, the enzyme which catalyzes the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate (c-AMP). Increased c-AMP levels are associated with relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle and inhibition of release mediators of immediate hypersensitivity from cells, especially from mast cells.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, biotransformation and excretion studies in humans following oral administration have indicated that an average of less than 10% of the drug is absorbed intact; it is not metabolized by catechol-O-methyltransferase nor converted to glucuronide conjugates but is excreted primarily as the polar sulfate conjugate, metaproterenol-3-O-sulfate, formed in the gut.
Pulmonary function tests performed after the administration of metaproterenol usually show improvement, e.g., an increase in the one-second forced expiratory volume (FEV1), maximum expiratory flow rate, peak expiratory flow rate, forced vital capacity, and/or a decrease in airway resistance. The resultant decrease in airway obstruction may relieve the dyspnea associated with bronchospasm.
In controlled single- and multiple-dose studies in which 319 patients were treated with metaproterenol sulfate tablets (89 patients with 10 mg and 230 patients with 20 mg), a majority (65%) demonstrated improvements in pulmonary function defined as an increase of at least 15% in the one-second forced expiratory volume (FEV1). For 54% the onset was within 30 minutes. The duration of effect persisted for at least four hours in 51% of those patients who demonstrated a response.
Recent studies in laboratory animals (minipigs, rodents and dogs) recorded the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden death (with histologic evidence of myocardial necrosis) when beta agonists and methylxanthines were administered concurrently. The significance of these findings when applied to humans is currently unknown.
Indications and Usage for Metaproterenol Tablets
Metaproterenol sulfate tablets are indicated as a bronchodilator for bronchial asthma and for reversible bronchospasm which may occur in association with bronchitis and emphysema.
Contraindications
Use in patients with cardiac arrhythmias associated with tachycardia is contraindicated.
Although rare, immediate hypersensitivity reactions can occur. Therefore, metaproterenol sulfate tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of its components.
Precautions
Extreme care must be exercised with respect to the administration of additional sympathomimetic agents.
Since metaproterenol is a sympathomimetic amine, it should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, including ischemic heart disease, hypertension or cardiac arrhythmias, in patients with hyperthyroidism or diabetes mellitus, and in patients who are unusually responsive to sympathomimetic amines or who have convulsive disorders. Significant changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure could be expected to occur in some patients after use of any beta adrenergic bronchodilator.
Information for Patients
Appropriate care should be exercised when considering the administration of additional sympathomimetic agents. A sufficient interval of time should elapse prior to administration of another sympathomimetic agent. Metaproterenol should not be used more often than prescribed. If symptoms persist, patients should consult a physician promptly.
Drug Interactions
Beta adrenergic agonists should be administered with caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, since the action of beta adrenergic agonists on the vascular system may be potentiated.
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
In an 18-month study in mice, metaproterenol produced a significant increase in benign hepatic adenomas in males and benign ovarian tumors in females at doses corresponding to 31 and 62 times the maximum recommended dose (based on a 50 kg individual). In a two-year study in rats, a non-significant incidence of benign leiomyomata of the mesovarium was noted at 62 times the maximum recommended dose. The relevance of these findings to man is not known. Mutagenicity studies with metaproterenol have not been conducted. Reproduction studies in rats revealed no evidence of impaired fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C: Metaproterenol sulfate has been shown to be teratogenic and embryotoxic in rabbits when given orally at doses of 100 mg/kg or 62 times the maximum recommended human oral dose. These effects included skeletal abnormalities, hydrocephalus and skull bone separation. Embryotoxicity has also been shown in mice when given orally at doses of 50 mg/kg or 31 times the maximum recommended human oral dose. Results of other oral reproduction studies in rats (40 mg/kg) and rabbits (50 mg/kg) have not revealed any teratogenic, embryotoxic or fetotoxic effects. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Metaproterenol sulfate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adverse reactions are similar to those noted with other sympathomimetic agents.
The following table of adverse experiences is derived from 26 controlled clinical trials with 496 patients treated with metaproterenol sulfate tablets:
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | INCIDENCE |
|
|
| Number of Patients | % |
| Cardiovascular | ||
| Chest Pain | 1 | 0.2 |
| Edema | 1 | 0.2 |
| Hypertension | 2 | 0.4 |
| Palpitations | 19 | 3.8 |
| Tachycardia | 85 | 17.1 |
| Central Nervous System | ||
| Dizziness | 12 | 2.4 |
| Drowsiness | 3 | 0.6 |
| Fatigue | 7 | 1.4 |
| Headache | 35 | 7.0 |
| Insomnia | 9 | 1.8 |
| Nervousness | 100 | 20.2 |
| Sensory disturbances | 1 | 0.2 |
| Syncope | 2 | 0.4 |
| Weakness | 1 | 0.2 |
| Dermatological | ||
| Diaphoresis | 1 | 0.2 |
| Hives | 1 | 0.2 |
| Pruritus | 2 | 0.4 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Appetite changes | 2 | 0.4 |
| Diarrhea | 6 | 1.2 |
| Gastrointestinal distress | 15 | 3.0 |
| Nausea | 18 | 3.6 |
| Vomiting | 4 | 0.8 |
| Musculoskeletal | ||
| Pain | 1 | 0.2 |
| Spasms | 1 | 0.2 |
| Tremor | 84 | 16.9 |
| Ophthalmological | ||
| Blurred vision | 1 | 0.2 |
| Oro-Otolaryngeal | ||
| Dry mouth/throat | 2 | 0.4 |
| Laryngeal changes | 1 | 0.2 |
| Bad taste | 4 | 0.8 |
| Respiratory | ||
| Asthma exacerbation | 10 | 2.0 |
| Coughing | 1 | 0.2 |
| Other | ||
| Chatty | 1 | 0.2 |
| Chills | 1 | 0.2 |
| Clonus noted on flexing foot | 1 | 0.2 |
| Feverish | 2 | 0.4 |
| Flu Symptoms | 1 | 0.2 |
| Facial and finger puffiness | 1 | 0.2 |
Related/similar drugs
Overdosage
The expected symptoms with overdosage are those of excessive beta stimulation and/or any of the symptoms listed under ADVERSE REACTIONS, e.g., angina, hypertension or hypotension, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, dry mouth, palpitation, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise and insomnia.
Treatment consists of discontinuation of metaproterenol together with appropriate symptomatic therapy.
Metaproterenol Tablets Dosage and Administration
Adults: The usual dose is 20 mg three or four times a day.
Children: Aged six to nine years or weight under 60 lbs - 10 mg three or four times a day. Over nine years or weight over 60 lbs - 20 mg three or four times a day. Metaproterenol sulfate tablets are not recommended for use in children under six years at this time. (Please refer to the CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY section for further information on clinical experience with this product.)
It is recommended that the physician titrate the dosage according to each individual patient's response to therapy.
How is Metaproterenol Tablets supplied
Metaproterenol sulfate tablets are supplied as follows:
10 mg: white, compressed, round, scored tablets, debossed "PAR 258" available in bottles of 100 (NDC #49884-258-01).
20 mg: white, compressed, round, scored tablets, debossed "PAR 259" available in bottles of 100 (NDC #49884-259-01).
Store at controlled room temperature 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). Protect from light and moisture.
Manufactured by:
PAR PHARMACEUTICAL
Chestnut Ridge, New York 10977
Revised: 04/2016
OS258-01-1-08
| METAPROTERENOL SULFATE
metaproterenol sulfate tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| METAPROTERENOL SULFATE
metaproterenol sulfate tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Par Pharmaceutical, Inc. (092733690) |
More about metaproterenol
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Reviews (2)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: adrenergic bronchodilators
- Breastfeeding
- En español



