Cefditoren Pivoxil: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: tablet, film coated
Drug class: Third generation cephalosporins
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 25, 2025.
On This Page
Cefditoren Pivoxil Tablets 200 mg and 400 mg
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets and other antibacterial drugs, Cefditoren Pivoxil should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
Cefditoren Pivoxil Description
Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets contain cefditoren pivoxil, a semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotic for oral administration. It is a prodrug which is hydrolyzed by esterases during absorption, and the drug is distributed in the circulating blood as active cefditoren.
Chemically, cefditoren pivoxil is (-)-(6R,7R)-2,2-dimethylpropionyloxymethyl 7-[(Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-methoxy-iminoacetamido]-3-[(Z)-2-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl)ethenyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate. The empirical formula is C25H28N6O7S3 and the molecular weight is 620.73. The structural formula of cefditoren pivoxil is shown below:
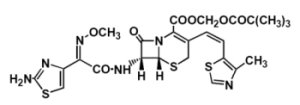
cefditoren pivoxil
The amorphous form of cefditoren pivoxil developed for clinical use is a light yellow powder. It is freely soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid and soluble at levels equal to 6.06 mg/mL in ethanol and <0.1 mg/mL in water.
Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets contain 200 mg or 400 mg of cefditoren as cefditoren pivoxil and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, mannitol, magnesium stearate, sodium caseinate (a milk protein), and sodium tripolyphosphate. The tablet coating contains carnauba wax, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide. Tablets are printed with ink containing opacode blue S-1-10533.
Cefditoren Pivoxil - Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Oral Bioavailability
Following oral administration, cefditoren pivoxil is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and hydrolyzed to cefditoren by esterases. Maximal plasma concentrations (Cmax) of cefditoren under fasting conditions average 1.8 ± 0.6 µg/mL following a single 200 mg dose and occur 1.5 to 3 hours following dosing.
Less than dose-proportional increases in Cmax and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) were observed at doses of 400 mg and above. Cefditoren does not accumulate in plasma following twice daily administration to subjects with normal renal function. Under fasting conditions, the estimated absolute bioavailability of cefditoren pivoxil is approximately 14%. The absolute bioavailability of cefditoren pivoxil administered with a low fat meal (693 cal, 14 g fat, 122 g carb, 23 g protein) is 16.1 ± 3.0%.
Food Effect
Administration of cefditoren pivoxil following a high fat meal (858 cal, 64 g fat, 43 g carb, 31 g protein) resulted in a 70% increase in mean AUC and a 50% increase in mean Cmax compared to administration of cefditoren pivoxil in the fasted state. After a high fat meal, the Cmax averaged 3.1 ± 1.0 µg/mL following a single 200 mg dose of cefditoren pivoxil and 4.4 ± 0.9 µg/mL following a 400 mg dose. Cefditoren AUC and Cmax values from studies conducted with a moderate fat meal (648 cal, 27 g fat, 73 g carb, 29 g protein) are similar to those obtained following a high fat meal.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) of cefditoren is 9.3 ± 1.6 L. Binding of cefditoren to plasma proteins averages 88% from in vitro determinations, and is concentration-independent at cefditoren concentrations ranging from 0.05 to10 µg/mL. Cefditoren is primarily bound to human serum albumin and its binding is decreased when serum albumin concentrations are reduced. Binding to α-1-acid glycoprotein ranges from 3.3 to 8.1%. Penetration into red blood cells is negligible.
Skin blister fluid
Maximal concentrations of cefditoren in suction-induced blister fluid were observed 4 to 6 hours following administration of a 400 mg dose of cefditoren pivoxil with a mean of 1.1 ± 0.42 µg/mL. Mean blister fluid AUC values were 56 ± 15% of corresponding plasma concentrations.
Tonsil tissue
In fasted patients undergoing elective tonsillectomy, the mean concentration of cefditoren in tonsil tissue 2 to 4 hours following administration of a 200 mg dose of cefditoren pivoxil was 0.18 ± 0.07 µg/g. Mean tonsil tissue concentrations of cefditoren were 12 ± 3% of the corresponding serum concentrations.
Metabolism and Excretion
Cefditoren is eliminated from the plasma, with a mean terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) of 1.6 ± 0.4 hours in young healthy adults. Cefditoren is not appreciably metabolized. After absorption, cefditoren is mainly eliminated by excretion into the urine, with a renal clearance of approximately 4-5 L/h. Studies with the renal tubular transport blocking agent probenecid indicate that tubular secretion, along with glomerular filtration is involved in the renal elimination of cefditoren. Cefditoren renal clearance is reduced in patients with renal insufficiency. (See Special Populations, Renal Insufficiency and Hemodialysis.)
Hydrolysis of cefditoren pivoxil to its active component, cefditoren, results in the formation of pivalate. Following multiple doses of cefditoren pivoxil, greater than 70% of the pivalate is absorbed. Pivalate is mainly eliminated (>99%) through renal excretion, nearly exclusively as pivaloylcarnitine. Following a 200 mg BID regimen for 10 days, the mean decrease in plasma concentrations of total carnitine was 18.1 ± 7.2 nmole/mL, representing a 39% decrease in plasma carnitine concentrations. Following a 400 mg BID regimen for 14 days, the mean decrease in plasma concentrations of carnitine was 33.3 ± 9.7 nmole/mL, representing a 63% decrease in plasma carnitine concentrations. Plasma concentrations of carnitine returned to the normal control range within 7 to 10 days after discontinuation of cefditoren pivoxil. (See PRECAUTIONS, General and CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Special Populations
Geriatric
The effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of cefditoren was evaluated in 48 male and female subjects aged 25 to 75 years given 400 mg cefditoren pivoxil BID for 7 days. Physiological changes related to increasing age increased the extent of cefditoren exposure in plasma, as evidenced by a 26% higher Cmax and a 33% higher AUC for subjects aged ≥ 65 years compared with younger subjects. The rate of elimination of cefditoren from plasma was lower in subjects aged ≥ 65 years, with t1/2 values 16-26% longer than for younger subjects. Renal clearance of cefditoren in subjects aged ≥ 65 years was 20-24% lower than in younger subjects. These changes could be attributed to age-related changes in creatinine clearance. No dose adjustments are necessary for elderly patients with normal (for their age) renal function.
Gender
The effect of gender on the pharmacokinetics of cefditoren was evaluated in 24 male and 24 female subjects given 400 mg cefditoren pivoxil BID for 7 days. The extent of exposure in plasma was greater in females than in males, as evidenced by a 14% higher Cmax and a 16% higher AUC for females compared to males. Renal clearance of cefditoren in females was 13% lower than in males. These differences could be attributed to gender-related differences in lean body mass. No dose adjustments are necessary for gender.
Renal Insufficiency
Cefditoren pharmacokinetics were investigated in 24 adult subjects with varying degrees of renal function following administration of cefditoren pivoxil 400 mg BID for 7 days. Decreased creatinine clearance (CLcr) was associated with an increase in the fraction of unbound cefditoren in plasma and a decrease in the cefditoren elimination rate, resulting in greater systemic exposure in subjects with renal impairment. The unbound Cmax and AUC were similar in subjects with mild renal impairment (CLcr: 50-80 mL/min/1.73 m2) compared to subjects with normal renal function (CLcr: >80 mL/min/1.73 m2). Moderate (CLcr: 30-49 mL/min/1.73 m2) or severe (CLcr: <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment increased the extent of exposure in plasma, as evidenced by mean unbound Cmax values 90% and 114% higher and AUC values 232% and 324% higher than that for subjects with normal renal function. The rate of elimination from plasma was lower in subjects with moderate or severe renal impairment, with respective mean t1/2 values of 2.7 and 4.7 hours. No dose adjustment is necessary for patients with mild renal impairment (CLcr: 50-80 mL/min/1.73 m2). It is recommended that not more than 200 mg BID be administered to patients with moderate renal impairment (CLcr: 30-49 mL/min/1.73 m2) and 200 mg QD be administered to patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr: <30 mL/min/1.73 m2). (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Hemodialysis
Cefditoren pharmacokinetics investigated in six adult subjects with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) undergoing hemodialysis given a single 400 mg dose of cefditoren pivoxil were highly variable. The mean t1/2 was 4.7 hours and ranged from 1.5 to 15 hours. Hemodialysis (4 hours duration) removed approximately 30% of cefditoren from systemic circulation but did not change the apparent terminal elimination half-life. The appropriate dose for ESRD patients has not been determined. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Hepatic Disease
Cefditoren pharmacokinetics were evaluated in six adult subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) and six with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B). Following administration of cefditoren pivoxil 400 mg BID for 7 days in these subjects, mean Cmax and AUC values were slightly (<15%) greater than those observed in normal subjects. No dose adjustments are necessary for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A or B). The pharmacokinetics of cefditoren in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) have not been studied.
Microbiology
Cefditoren is a cephalosporin with antibacterial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens. The bactericidal activity of cefditoren results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis via affinity for penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs).
Cefditoren is stable in the presence of a variety of ß-lactamases, including penicillinases and some cephalosporinases. Cefditoren has been shown to be active against most strains of the following bacteria, both in vitro and in clinical infections, as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
Aerobic Gram-Positive Microorganisms
Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains, including ß-lactamase-producing strains)
Note: Cefditoren is inactive against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only)
Streptococcus pyogenes
Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms
Haemophilus influenzae (including ß-lactamase-producing strains)
Haemophilus parainfluenzae (including ß-lactamase-producing strains)
Moraxella catarrhalis (including ß-lactamase-producing strains)
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. Cefditoren exhibits in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of ≤0.125 µg/mL against most (≥90%) strains of the following bacteria; however, the safety and effectiveness of cefditoren in treating clinical infections due to these bacteria have not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Aerobic Gram-Positive Microorganisms
Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus Groups C and G
Streptococcus, viridans group (penicillin-susceptible and -intermediate strains)
Susceptibility Tests
Dilution Techniques
Quantitative methods that are used to determine MICs provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized procedure. Standardized procedures are based on dilution methods1 (broth) or equivalent with standardized inoculum concentrations and standardized concentrations of cefditoren powder. The MIC values obtained should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For testing Haemophilus spp.a and Streptococcus spp. including S. pneumoniaeb:
|
Clinical Isolates |
MIC (μg/mL) |
Interpretation |
|
S. pneumoniae |
≤0.125 0.250 ≥0.50 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
|
Haemophilus spp. |
≤0.125 0.250 ≥0.50 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
|
S. pyogenes |
≤0.125 |
Susceptible (S) |
aThis interpretive standard is applicable only to broth microdilution susceptibility tests with Haemophilus spp. using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM).1
bThese interpretive standards are applicable only to broth microdilution susceptibility tests with Streptococcus spp. using cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth with 2-5% lysed horse blood.1
Susceptibility test criteria cannot be established for S. aureus
A report of “Susceptible” indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentration usually achievable. A report of “Intermediate” indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically feasible drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug is physiologically concentrated or in situations where high dosage of drug can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone that prevents small, uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of “Resistant” indicates that the pathogen is not likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentration usually achievable and that other therapy should be selected.
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory control bacterial strains to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. Standard cefditoren powder should provide the following MICs with these quality control strains:
|
Microorganisms |
MIC Ranges(µg/mL) |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniaea ATCC 49619 Haemophilus influenzaeb ATCC 49766 Haemophilus influenzaeb ATCC 49247 |
0.016-0.12 0.004-0.016 0.06-0.25 |
aThis quality control range is applicable to only S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619 tested by a microdilution procedure using cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth with 2-5% lysed horse blood.1
bThis quality control range is applicable to only H. influenzae ATCC 49247 and ATCC 49766 tested by a microdilution procedure using HTM.1
Indications and Usage for Cefditoren Pivoxil
Cefditoren Pivoxil is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate infections in adults and adolescents (12 years of age or older) which are caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below.
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae (including ß-lactamase-producing strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae (including ß-lactamase producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin susceptible strains only), or Moraxella catarrhalis (including ß-lactamase-producing strains).
Community-Acquired Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae (including ß-lactamase-producing strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae (including ß-lactamase-producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), or Moraxella catarrhalis (including ß-lactamase producing strains).
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. NOTE: Cefditoren Pivoxil is effective in the eradication of Streptococcus pyogenes from the oropharynx. Cefditoren Pivoxil Tablets has not been studied for the prevention of rheumatic fever following Streptococcus pyogenes pharyngitis/tonsillitis. Only intramuscular penicillin has been demonstrated to be effective for the prevention of rheumatic fever.
Uncomplicated Skin and Skin-Structure Infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including ß-lactamase-producing strains) or Streptococcus pyogenes.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefditoren Pivoxil and other antibacterial drugs, Cefditoren Pivoxil should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Contraindications
Cefditoren Pivoxil is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin class of antibiotics or any of its components.
Cefditoren Pivoxil is contraindicated in patients with carnitine deficiency or inborn errors of metabolism that may result in clinically significant carnitine deficiency, because use of Cefditoren Pivoxil causes renal excretion of carnitine. (See PRECAUTIONS, General.)
Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets contain sodium caseinate, a milk protein. Patients with milk protein hypersensitivity (not lactose intolerance) should not be administered Cefditoren Pivoxil.
Warnings
BEFORE THERAPY WITH CEFDITOREN PIVOXIL IS INSTITUTED, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE TO DETERMINE WHETHER THE PATIENT HAS HAD PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO CEFDITOREN PIVOXIL, OTHER CEPHALOSPORINS, PENICILLINS, OR OTHER DRUGS. IF CEFDITOREN PIVOXIL IS TO BE GIVEN TO PENICILLIN-SENSITIVE PATIENTS, CAUTION SHOULD BE EXERCISED BECAUSE CROSS-HYPERSENSITIVITY AMONG ß-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS HAS BEEN CLEARLY DOCUMENTED AND MAY OCCUR IN UP TO 10% OF PATIENTS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION TO CEFDITOREN PIVOXIL OCCURS, THE DRUG SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED. SERIOUS ACUTE HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS MAY REQUIRE TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE AND OTHER EMERGENCY MEASURES, INCLUDING OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS, INTRAVENOUS ANTIHISTAMINES, CORTICOSTEROIDS, PRESSOR AMINES, AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, AS CLINICALLY INDICATED.
Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefditoren pivoxil, and may range in severity from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents.
Treatment with antibacterial agents alters normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) is a primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis.
After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, appropriate therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to drug discontinuation alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation, and treatment with an antibacterial drug clinically effective against C. difficile colitis.
Precautions
General
Prescribing Cefditoren Pivoxil in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Cefditoren Pivoxil is not recommended when prolonged antibiotic treatment is necessary, since other pivalate-containing compounds have caused clinical manifestations of carnitine deficiency when used over a period of months. No clinical effects of carnitine decrease have been associated with short-term treatment. The effects on carnitine concentrations of repeat short-term courses of Cefditoren Pivoxil are not known.
In community-acquired pneumonia patients (N=192, mean age 50.3 ± 17.2 years) given a 200 mg BID regimen for 14 days, the mean decrease in serum concentrations of total carnitine while on therapy was 13.8 ± 10.8 nmole/mL, representing a 30% decrease in serum carnitine concentrations. In community-acquired pneumonia patients (N=192, mean age 51.3 ± 17.8 years) given a 400 mg BID regimen for 14 days, the mean decrease in serum concentrations of total carnitine while on therapy was 21.5 ± 13.1 mole/mL, representing a 46% decrease in serum carnitine concentrations. Plasma concentrations of carnitine returned to the normal control range within 7 days after discontinuation of cefditoren pivoxil. Comparable decreases in carnitine were observed in healthy volunteers (mean age 33.6 ± 7.4 years) following a 200 mg or 400 mg BID regimen. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY.) Community-acquired pneumonia clinical trials demonstrated no adverse events attributable to decreases in serum carnitine concentrations.
However, some sub-populations (e.g., patients with renal impairment, patients with decreased muscle mass) may be at increased risk for reductions in serum carnitine concentrations during cefditoren pivoxil therapy. Furthermore, the appropriate dose in patients with end-stage renal disease has not been determined. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Patients with Renal Insufficiency).
As with other antibiotics, prolonged treatment may result in the possible emergence and overgrowth of resistant organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate alternative therapy should be administered.
Cephalosporins may be associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antimicrobial therapy, and patients previously stabilized on anticoagulant therapy. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at risk and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated. In clinical trials, there was no difference between cefditoren and comparator cephalosporins in the incidence of increased prothrombin time.
Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Cefditoren Pivoxil should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Cefditoren Pivoxil is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Cefditoren Pivoxil or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Cefditoren Pivoxil should be taken with meals to enhance absorption.
Cefditoren Pivoxil may be taken concomitantly with oral contraceptives.
It is not recommended that Cefditoren Pivoxil be taken concomitantly with antacids or other drugs taken to reduce stomach acids. (See PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions.)
Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets contain sodium caseinate, a milk protein. Patients with milk protein hypersensitivity (not lactose intolerance) should not be administered Cefditoren Pivoxil.
Drug Interactions
Oral Contraceptives
Multiple doses of cefditoren pivoxil had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of ethinyl estradiol, the estrogenic component in most oral contraceptives.
Antacids
Co-administration of a single dose of an antacid which contained both magnesium (800 mg) and aluminum (900 mg) hydroxides reduced the oral absorption of a single 400 mg dose of cefditoren pivoxil administered following a meal, as evidenced by a 14% decrease in mean Cmax and an 11% decrease in mean AUC. Although the clinical significance is not known, it is not recommended that cefditoren pivoxil be taken concomitantly with antacids.
H2-Receptor Antagonists
Co-administration of a single dose of intravenously administered famotidine (20 mg) reduced the oral absorption of a single 400 mg dose of cefditoren pivoxil administered following a meal, as evidenced by a 27% decrease in mean Cmax and a 22% decrease in mean AUC. Although the clinical significance is not known, it is not recommended that cefditoren pivoxil be taken concomitantly with H2 receptor antagonists.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Cephalosporins are known to occasionally induce a positive direct Coombs’ test. A false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine may occur with copper reduction tests (Benedict’s or Fehling’s solution or with CLINITEST® tablets), but not with enzyme-based tests for glycosuria (e.g., CLINISTIX®, TES-TAPE®). As a false-negative result may occur in the ferricyanide test, it is recommended that either the glucose oxidase or hexokinase method be used to determine blood/plasma glucose levels in patients receiving cefditoren pivoxil.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term animal carcinogenicity studies have been conducted with cefditoren pivoxil. Cefditoren pivoxil was not mutagenic in the Ames bacterial reverse mutation assay, or in the mouse lymphoma mutation assay at the hypoxanthineguanine phosphoribosyltransferase locus. In Chinese hamster lung cells, chromosomal aberrations were produced by cefditoren pivoxil, but not by cefditoren. Subsequent studies showed that the chromosome aberrations were due to the release of formaldehyde from the pivoxil ester moiety in the in vitro assay system. Neither cefditoren nor cefditoren pivoxil produced chromosomal aberrations when tested in an in vitro human peripheral blood lymphocyte assay, or in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. Cefditoren pivoxil did not induce unscheduled DNA syntheses when tested. In rats, fertility and reproduction were not affected by cefditoren pivoxil at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day, approximately 24 times a human dose of 200 mg BID based on mg/m2/day.
Pregnancy-Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category B
Cefditoren pivoxil was not teratogenic up to the highest doses tested in rats and rabbits. In rats, this dose was 1000 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 24 times a human dose of 200 mg BID based on mg/m2/day. In rabbits, the highest dose tested was 90 mg/kg/day, which is approximately four times a human dose of 200 mg BID based on mg/m2/day. This dose produced severe maternal toxicity and resulted in fetal toxicity and abortions.
In a postnatal development study in rats, cefditoren pivoxil produced no adverse effects on postnatal survival, physical and behavioral development, learning abilities, and reproductive capability at sexual maturity when tested at doses of up to 750 mg/kg/day, the highest dose tested. This is approximately 18 times a human dose of 200 mg BID based on mg/m2/day.
There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Cefditoren was detected in the breast milk of lactating rats. Because many drugs are excreted in human breast milk, caution should be exercised when cefditoren pivoxil is administered to nursing women.
Pediatric Use
Use of cefditoren pivoxil is not recommended for pediatric patients less than 12 years of age. The safety and efficacy of cefditoren pivoxil tablets in this population, including any effects of altered carnitine concentration, have not been established. (See PRECAUTIONS, General.)
Geriatric Use
Of the 2675 patients in clinical studies who received cefditoren pivoxil 200 mg BID, 308 (12%) were >65 years of age. Of the 2159 patients in clinical studies who received cefditoren pivoxil 400 mg BID, 307 (14%) were >65 years of age. No clinically significant differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between older and younger patients. No dose adjustments are necessary in geriatric patients with normal (for their age) renal function. This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Clinical Trials – Cefditoren Pivoxil Tablets (Adults and Adolescent Patients ≥12 Years of Age)
In clinical trials, 4834 adult and adolescent patients have been treated with the recommended doses of cefditoren pivoxil tablets (200 mg or 400 mg BID). Most adverse events were mild and self-limiting. No deaths or permanent disabilities have been attributed to cefditoren.
The following adverse events were thought by the investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely related to cefditoren tablets in multiple-dose clinical trials:
| Cefditoren Pivoxil | Comparatorsa | |||
| 200 mg BID | 400 mg BID | |||
| N=2675 | N=2159 | N=2648 | ||
| Incidence ≥ | Diarhea | 11% | 15% | 8% |
| 1% | Nausea | 4% | 6% | 5% |
| Headache | 3% | 2% | 2% | |
| Abdominal Pain | 2% | 2% | 1% | |
| Vaginal Moniliasis | 3%b | 6%c | 6%d | |
| Dyspepsia | 1% | 2% | 2% | |
| Vomiting | 1% | 1% | 2% | |
aincludes amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefadroxil monohydrate, cefuroxime axetil, cefpodoxime proxetil, clarithromycin, and penicillin
b1428 females
c1135 females
d1461 females
The overall incidence of adverse events, and in particular diarrhea, increased with the higher recommended dose of Cefditoren Pivoxil.
Treatment related adverse events experienced by <1% but >0.1% of patients who received 200 mg or 400 mg BID of cefditoren pivoxil were abnormal dreams, allergic reaction, anorexia, asthenia, asthma, coagulation time increased, constipation, dizziness, dry mouth, eructation, face edema, fever, flatulence, fungal infection, gastrointestinal disorder, hyperglycemia, increased appetite, insomnia, leukopenia, leukorrhea, liver function test abnormal, myalgia, nervousness, oral moniliasis, pain, peripheral edema, pharyngitis, pseudomembranous colitis, pruritus, rash, rhinitis, sinusitis, somnolence, stomatitis, sweating, taste perversion, thirst, thrombocythemia, urticaria, and vaginitis. Pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may begin during or after antibiotic treatment. (See WARNINGS.)
Sixty-one of 2675 (2%) patients who received 200 mg BID and 69 of 2159 (3%) patients who received 400 mg BID of cefditoren pivoxil discontinued medication due to adverse events thought by the investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely associated with cefditoren therapy. The discontinuations were primarily for gastrointestinal disturbances, usually diarrhea or nausea. Diarrhea was the reason for discontinuation in 19 of 2675 (0.7%) patients who received 200 mg BID and in 31 of 2159 (1.4%) patients who received 400 mg BID of cefditoren pivoxil.
Changes in laboratory parameters of possible clinical significance, without regard to drug relationship and which occurred in ≥1% of patients who received cefditoren pivoxil 200 mg or 400 mg BID, were hematuria (3.0% and 3.1%), increased urine white blood cells (2.3% and 2.3%), decreased hematocrit (2.1% and 2.2%), and increased glucose (1.8% and 1.1%). Those events which occurred in <1% but >0.1% of patients included the following: increased/decreased white blood cells, increased eosinophils, decreased neutrophils, increased lymphocytes, increased platelet count, decreased hemoglobin, decreased sodium, increased potassium, decreased chloride, decreased inorganic phosphorus, decreased calcium, increased SGPT/ALT, increased SGOT/AST, increased cholesterol, decreased albumin, proteinuria, and increased BUN. It is not known if these abnormalities were caused by the drug or the underlying condition being treated.
Cephalosporin Class Adverse Reactions
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above which have been observed in patients treated with cefditoren pivoxil, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory test results have been reported for cephalosporin class antibiotics:
Adverse Reactions: Allergic reactions, anaphylaxis, drug fever, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, serum sickness-like reaction, erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, colitis, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, reversible hyperactivity, hypertonia, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, and superinfection.
Altered Laboratory Tests: Prolonged prothrombin time, positive direct Coombs’ test, false-positive test for urinary glucose, elevated alkaline phosphatase, elevated bilirubin, levated LDH, increased creatinine, pancytopenia, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis.
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse experiences, regardless of their relationship to cefditoren pivoxil, have been reported during extensive postmarketing experience, beginning with approval in Japan in 1994: pneumonia interstitial, eosinophilic pneumonia acute, acute renal failure, arthralgia, thrombocytopenia, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis and anaphylactoid reactions which may be accompanied by hypotension.
Related/similar drugs
Overdosage
Information on cefditoren pivoxil overdosage in humans is not available. However, with other ß-lactam antibiotics, adverse effects following overdosage have included nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, diarrhea, and convulsions. Hemodialysis may aid in the removal of cefditoren from the body, particularly if renal function is compromised (30% reduction of plasma concentrations following 4 hours of hemodialysis). Treat overdosage symptomatically and institute supportive measures as required.
In acute animal toxicity studies, cefditoren pivoxil when tested at the limit oral doses of 5100 mg/kg in rats and up to 2000 mg/kg in dogs did not exhibit any health effects of concern. Certain effects, such as diarrhea and soft stool lasting for a few days were observed in some animals as expected with most oral antibiotics due to inhibition of intestinal microflora.
Cefditoren Pivoxil Dosage and Administration
(See INDICATIONS AND USAGE for Indicated Pathogens.)
|
Cefditoren Pivoxil Dosage and Administration* Adults and Adolescents (≥12 Years) |
||
|
Type of Infection |
Dosage |
Duration (Days) |
|
Community-Acquired Pneumonia |
400 mg BID |
14 |
|
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis |
400 mg BID |
10 |
|
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis |
200mg BID |
|
|
Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections |
||
*Should be taken with meals
Patients with Renal Insufficiency
No dose adjustment is necessary for patients with mild renal impairment (CLcr: 50-80 mL/min/1.73 m2). It is recommended that not more than 200 mg BID be administered to patients with moderate renal impairment (CLcr: 30-49 mL/min/1.73 m2) and 200 mg QD be administered to patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr: <30 mL/min/1.73 m2). The appropriate dose in patients with end-stage renal disease has not been determined.
How is Cefditoren Pivoxil supplied
Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets containing cefditoren pivoxil equivalent to 200 mg or 400 mg of cefditoren are available as white, elliptical, film-coated tablets imprinted with “CBP 200” or “CBP 400” in blue. These tablets are available in blister packages, as follows:
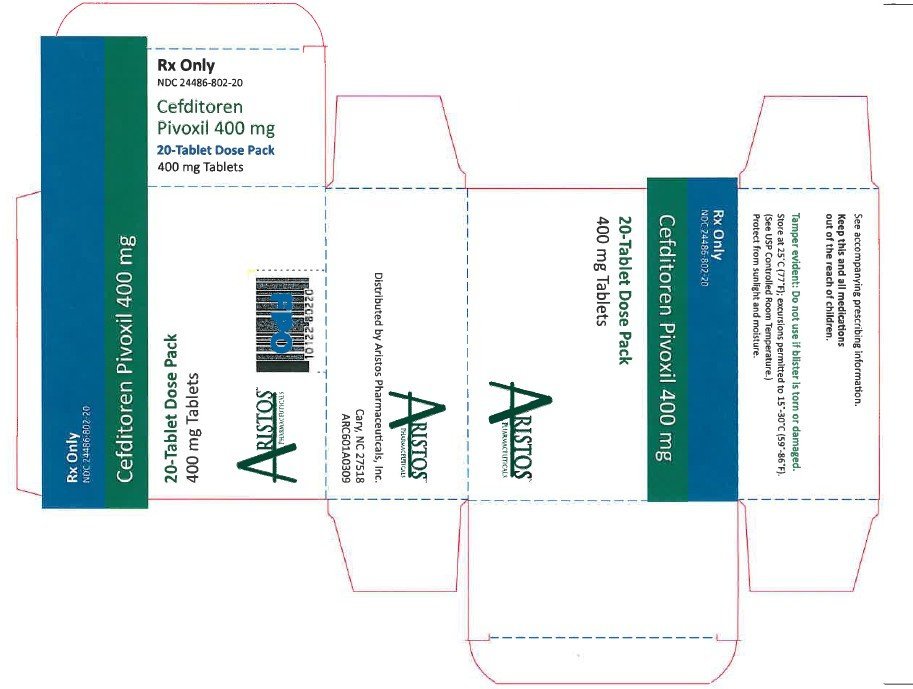
- NDC 24486-802-20: 400 mg 20 count blister. Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets containing cefditoren pivoxil equivalent to 400 mg of cefditoren are available as white, elliptical, film-coated tablets imprinted with “CBP 400” in blue.
- NDC 24486-802-28: 400 mg 28 count blister. Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets containing cefditoren pivoxil equivalent to 400 mg of cefditoren are available as white, elliptical, film-coated tablets imprinted with “CBP 400” in blue.
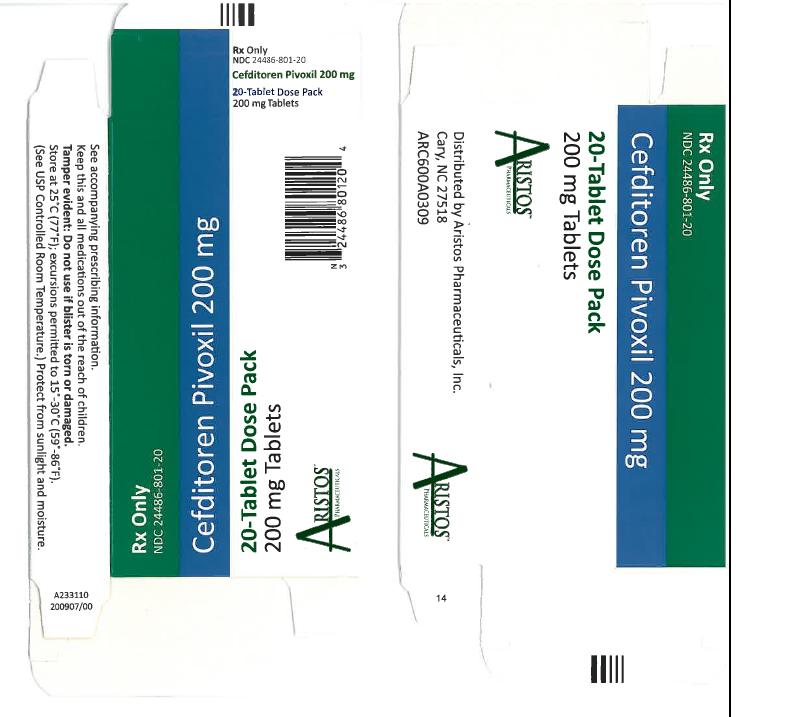
- NDC 24486-801-20: 20 count blister. Cefditoren Pivoxil tablets containing cefditoren pivoxil equivalent to 200 mg of cefditoren are available as white, elliptical, film-coated tablets imprinted with “CBP 200” in blue.
STORAGE
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Protect from light and moisture. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
Healthcare professionals can telephone Aristos Pharmaceuticals Information Line (1-866-280-5755) for information on this product.
References
1. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically – Fifth Edition; Approved Standard, NCCLS Document M7-A5, Vol. 20, No. 2, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January, 2000.
Rx Only
Manufactured by:
Tedec-Meiji Farma, S.A
Madrid, Spain
Distributed by:
Aristos Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Cary, NC 27518
CTS-002-1211-00-SPL
A233140-201111/01
| CEFDITOREN PIVOXIL
cefditoren pivoxil tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CEFDITOREN PIVOXIL
cefditoren pivoxil tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Aristos Phamaceuticals, Inc. (010201166) |
Frequently asked questions
More about cefditoren
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Reviews (4)
- Imprints, shape & color data
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: third generation cephalosporins
- Breastfeeding