Fiorinal
Generic name: aspirin, butalbital, and caffeine [ AS-pir-in, bue-TAL-bi-tal, KAF-een ]
Drug class: Analgesic combinations
What is Fiorinal?
Fiorinal contains a combination of aspirin, butalbital, and caffeine. Aspirin is a pain reliever, blood thinner, as well as an anti-inflammatory and a fever reducer. Butalbital is a barbiturate. It relaxes muscle contractions involved in a tension headache. Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant. It relaxes muscle contractions in blood vessels to improve blood flow.
Fiorinal is used to treat tension headaches. This medicine is not for treating headaches that come and go.
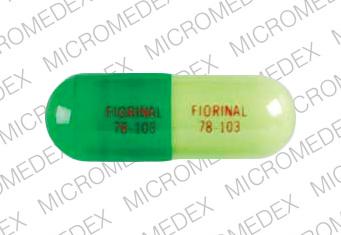
Fiorinal capsules are supplied in a two tone green capsule. Each half of capsule is imprinted with “FIORINAL 955” in red.
Warnings
You should not use Fiorinal if you have a stomach ulcer, severe liver disease, porphyria, a bleeding or blood clotting disorder, or if you are allergic to any NSAID.
Aspirin may cause stomach or intestinal bleeding, which can be fatal.
Stop using Fiorinal and call your doctor at once if you have: black, bloody, or tarry stools, and coughing up blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds.
Aspirin should not be given to a child or teenager who has a fever.
Butalbital may be habit-forming. Misuse of habit-forming medicine can cause addiction, overdose, or death.
Before taking this medicine
You should not use Fiorinal if you are allergic to aspirin, butalbital, or caffeine, or if you have:
-
a bleeding or blood clotting disorder such as hemophilia, von Willebrand's disease, low platelets;
-
severe vitamin K deficiency;
-
severe liver disease;
-
a severe allergic reaction (sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, wheezing) after taking aspirin or another NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) such as ibuprofen, celecoxib, diclofenac, indomethacin, meloxicam, naproxen, Advil, Motrin, Aleve, and others;
-
a stomach ulcer; or
-
porphyria (a genetic enzyme disorder that causes symptoms affecting the skin or nervous system).
Not approved for use by anyone younger than 18 years old. Using Fiorinal in a child or teenager with flu symptoms or chickenpox can cause a serious or fatal condition called Reye's syndrome.
To make sure Fiorinal is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have ever had:
-
liver or kidney disease;
-
bleeding problems;
-
a head injury or brain tumor;
-
a stomach or intestinal disorder;
-
an enlarged prostate or urination problems; or
-
Addison's disease (an adrenal gland disorder).
Do not use Fiorinal during pregnancy unless your doctor tells you to. Using butalbital during pregnancy may cause withdrawal symptoms in the newborn. Using aspirin in the last 20 weeks can harm the unborn baby or cause pregnancy complications.
Do not breastfeed.
How should I take Fiorinal?
Follow all directions on your prescription label and read all medication guides or instruction sheets. Use the lowest effective dose for your condition.
Butalbital may be habit-forming. Misuse can cause addiction, overdose, or death. Keep the medication where others cannot get to it. Selling or giving away Fiorinal is against the law.
Fiorinal can affect the results of certain medical tests. Tell any doctor who treats you that you are using this medicine.
Fiorinal s usually prescribed for short-term use only. You may have withdrawal symptoms if you stop using the medicine suddenly after long-term use. Ask your doctor before stopping the medicine.
Store tightly closed at room temperature, away from moisture, heat, and light. Keep your medicine in a place where no one can use it improperly.
Aspirin, butalbital, and caffeine dosing information
Usual Adult Dose for Pain:
1 or 2 capsules orally every 4 hours as needed not to exceed 6 capsules per day
Comments:
-Due to high rate of physical dependence, the extended use of this drug is not recommended.
-The safety and efficacy of treating multiple recurrent headaches with this product is not known.
Uses: For the relief of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache.
What happens if I miss a dose?
Fiorinal is used when needed. If you are on a dosing schedule, skip any missed dose. Do not use two doses at one time.
Do not take more than 6 tablets or capsules in 24 hours.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. An overdose of butalbital can be fatal.
Overdose may cause severe drowsiness, confusion, feeling restless, insomnia, tremors, fast or pounding heartbeats, vomiting, stomach pain, rapid breathing, feeling hot, ringing in your ears, weak or shallow breathing, bruising or bleeding, seizure (convulsions), fainting, or coma.
What should I avoid while taking Fiorinal?
Avoid driving or hazardous activity until you know how this medicine will affect you. Your reactions could be impaired.
Ask a doctor or pharmacist before using other medicines for pain, fever, swelling, or cold/flu symptoms. They may contain ingredients similar to aspirin (such as ibuprofen, ketoprofen, or naproxen).
Avoid drinking alcohol.
Aspirin, butalbital, and caffeine side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to Fiorinal (hives, difficult breathing, swelling in your face or throat) or a severe skin reaction (fever, sore throat, burning eyes, skin pain, red or purple skin rash with blistering and peeling).
Stop taking Fiorinal and seek medical treatment if you have a serious drug reaction that can affect many parts of your body. Symptoms may include skin rash, fever, swollen glands, muscle aches, severe weakness, unusual bruising, or yellowing of your skin or eyes.
Call your doctor at once if you have:
-
bloody or tarry stools;
-
coughing up blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds; or
-
any bleeding that will not stop.
Common Fiorinal side effects may include:
-
drowsiness; or
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Related/similar drugs
What other drugs will affect Fiorinal?
Using Fiorinal with other drugs that make you drowsy can worsen this effect. Ask your doctor before using opioid medication, a sleeping pill, a muscle relaxer, or medicine for anxiety or seizures.
Tell your doctor about all your other medicines, especially:
-
insulin or oral diabetes medicine;
-
steroid medicine such as prednisone;
-
an MAO inhibitor - isocarboxazid, linezolid, methylene blue injection, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and others; or
-
NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) - aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve), celecoxib, diclofenac, indomethacin, meloxicam, and others.
This list is not complete. Other drugs may interact with aspirin, butalbital, and caffeine, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Not all possible drug interactions are listed here.
More about Fiorinal (aspirin / butalbital / caffeine)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Reviews (77)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: analgesic combinations
Patient resources
Other brands
Professional resources
Other formulations
Related treatment guides
Further information
Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use Fiorinal only for the indication prescribed.
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Copyright 1996-2025 Cerner Multum, Inc. Version: 4.01.