Fiorinal: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: butalbital, aspirin, and caffeine
Dosage form: capsule
Drug class: Analgesic combinations
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 2, 2025.
On This Page
Fiorinal Description
FIORINAL (Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules, USP) is supplied in capsule form for oral administration.
Each capsule contains the following active ingredients:
| butalbital, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . | 50 mg |
| aspirin, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | 325 mg |
| caffeine, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | 40 mg |
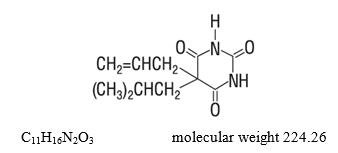
Butalbital (5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid) is a short- to intermediate-acting barbiturate. It has the following structural formula:
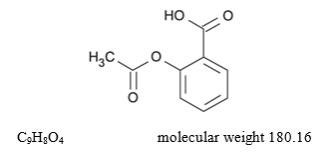
Aspirin (benzoic acid, 2-(acetyloxy)-) is an analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory. It has the following structural formula:
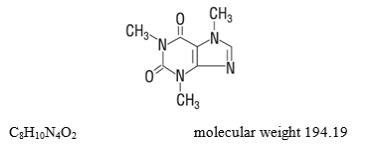
Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) is a central nervous system stimulant. It has the following structural formula:
Inactive Ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, and talc. Gelatin capsules contain D&C Yellow No. 10, FD&C Green No. 3, and gelatin. The capsules are printed with edible ink containing red iron oxide.
Fiorinal - Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacologically, FIORINAL combines the analgesic properties of aspirin with the anxiolytic and muscle relaxant properties of butalbital.
The clinical effectiveness of FIORINAL in tension headache has been established in double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-clinic trials. A factorial design study compared FIORINAL with each of its major components. This study demonstrated that each component contributes to the efficacy of FIORINAL in the treatment of the target symptoms of tension headache (headache pain, psychic tension, and muscle contraction in the head, neck, and shoulder region). For each symptom and the symptom complex as a whole, FIORINAL was shown to have significantly superior clinical effects to either component alone.
Pharmacokinetics
The behavior of the individual components is described below.
Aspirin
The systemic availability of aspirin after an oral dose is highly dependent on the dosage form, the presence of food, the gastric emptying time, gastric pH, antacids, buffering agents, and particle size. These factors affect not necessarily the extent of absorption of total salicylates but more the stability of aspirin prior to absorption.
During the absorption process and after absorption, aspirin is mainly hydrolyzed to salicylic acid and distributed to all body tissues and fluids, including fetal tissues, breast milk, and the central nervous system (CNS). Highest concentrations are found in plasma, liver, renal cortex, heart, and lung. In plasma, about 50%-80% of the salicylic acid and its metabolites are loosely bound to plasma proteins.
The clearance of total salicylates is subject to saturable kinetics; however, first-order elimination kinetics are still a good approximation for doses up to 650 mg. The plasma half-life for aspirin is about 12 minutes and for salicylic acid and/or total salicylates is about 3 hours.
The elimination of therapeutic doses is through the kidneys either as salicylic acid or other biotransformation products. The renal clearance is greatly augmented by an alkaline urine as is produced by concurrent administration of sodium bicarbonate or potassium citrate.
The biotransformation of aspirin occurs primarily in the hepatocytes. The major metabolites are salicyluric acid (75%), the phenolic and acyl glucuronides of salicylate (15%), and gentisic and gentisuric acid (1%). The bioavailability of the aspirin component of FIORINAL is equivalent to that of a solution except for a slower rate of absorption. A peak concentration of 8.8 mcg/mL was obtained at 40 minutes after a 650 mg dose.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Butalbital
Butalbital is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is expected to distribute to most of the tissues in the body. Barbiturates, in general, may appear in breast milk and readily cross the placental barrier. They are bound to plasma and tissue proteins to a varying degree and binding increases directly as a function of lipid solubility.
Elimination of butalbital is primarily via the kidney (59%-88% of the dose) as unchanged drug or metabolites. The plasma half-life is about 35 hours. Urinary excretion products included parent drug (about 3.6% of the dose), 5-isobutyl-5-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) barbituric acid (about 24% of the dose), 5-allyl-5(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-propyl) barbituric acid (about 4.8% of the dose), products with the barbituric acid ring hydrolyzed with excretion of urea (about 14% of the dose), as well as unidentified materials. Of the material excreted in the urine, 32% was conjugated.
The bioavailability of the butalbital component of FIORINAL is equivalent to that of a solution except for a decrease in the rate of absorption. A peak concentration of 2,020 ng/mL is obtained at about 1.5 hours after a 100 mg dose.
The in vitro plasma protein binding of butalbital is 45% over the concentration range of 0.5-20 mcg/mL. This falls within the range of plasma protein binding (20%-45%) reported with other barbiturates such as phenobarbital, pentobarbital, and secobarbital sodium. The plasma-to-blood concentration ratio was almost unity indicating that there is no preferential distribution of butalbital into either plasma or blood cells.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Caffeine
Like most xanthines, caffeine is rapidly absorbed and distributed in all body tissues and fluids, including the CNS, fetal tissues, and breast milk.
Caffeine is cleared rapidly through metabolism and excretion in the urine. The plasma half-life is about 3 hours. Hepatic biotransformation prior to excretion results in about equal amounts of 1-methylxanthine and 1-methyluric acid. Of the 70% of the dose that has been recovered in the urine, only 3% was unchanged drug.
The bioavailability of the caffeine component for FIORINAL is equivalent to that of a solution except for a slightly longer time to peak. A peak concentration of 1,660 ng/mL was obtained in less than an hour for an 80 mg dose.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Indications and Usage for Fiorinal
FIORINAL is indicated for the relief of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache. Evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of FIORINAL in the treatment of multiple recurrent headaches is unavailable. Caution in this regard is required because butalbital is habit-forming and potentially abusable.
Contraindications
FIORINAL is contraindicated under the following conditions:
- Hypersensitivity or intolerance to aspirin, caffeine, or butalbital.
- Patients with a hemorrhagic diathesis (e.g., hemophilia, hypoprothrombinemia, von Willebrand’s disease, the thrombocytopenias, thrombasthenia and other ill-defined hereditary platelet dysfunctions, severe vitamin K deficiency and severe liver damage).
- Patients with the syndrome of nasal polyps, angioedema and bronchospastic reactivity to aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anaphylactoid reactions have occurred in such patients.
- Peptic ulcer or other serious gastrointestinal lesions.
- Patients with porphyria.
Warnings
Therapeutic doses of aspirin can cause anaphylactic shock and other severe allergic reactions. It should be ascertained if the patient is allergic to aspirin, although a specific history of allergy may be lacking.
Significant bleeding can result from aspirin therapy in patients with peptic ulcer or other gastrointestinal lesions, and in patients with bleeding disorders. Aspirin administered preoperatively may prolong the bleeding time. Butalbital is habit-forming and potentially abusable. Consequently, the extended use of FIORINAL is not recommended. Results from epidemiologic studies indicate an association between aspirin and Reye’s Syndrome. Caution should be used in administering this product to children, including teenagers, with chicken pox or flu.
Fetal Toxicity
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Avoid use of NSAIDs, including FIORINAL, in pregnant women at about 30 weeks gestation and later. NSAIDs including FIORINAL, increase the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus at approximately this gestational age.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
Use of NSAIDs, including FIORINAL, at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy may cause fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. Oligohydramnios is often, but not always, reversible with treatment discontinuation. Complications of prolonged oligohydramnios may, for example, include limb contractures and delayed lung maturation. In some post-marketing cases of impaired neonatal renal function, invasive procedures such as exchange transfusion or dialysis were required.
If NSAID treatment is necessary between about 20 weeks and 30 weeks gestation, limit FIORINAL use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. Consider ultrasound monitoring of amniotic fluid if FIORINAL treatment extends beyond 48 hours. Discontinue FIORINAL if oligohydramnios occurs and follow up according to clinical practice [see PRECAUTIONS; Pregnancy].
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) has been reported in patients taking NSAIDs such as FIORINAL. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling. Other clinical manifestations may include hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis. Sometimes symptoms of DRESS may resemble an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its presentation, other organ systems not noted here may be involved.
It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, discontinue FIORINAL and evaluate the patient immediately.
Precautions
General
FIORINAL should be prescribed with caution for certain special-risk patients such as the elderly or debilitated, and those with severe impairment of renal or hepatic function, coagulation disorders, head injuries, elevated intracranial pressure, acute abdominal conditions, hypothyroidism, urethral stricture, Addison’s disease, or prostatic hypertrophy.
Aspirin should be used with caution in patients on anticoagulant therapy and in patients with underlying hemostatic defects, and extreme caution in the presence of peptic ulcer.
Precautions should be taken when administering salicylates to persons with known allergies. Hypersensitivity to aspirin is particularly likely in patients with nasal polyps, and relatively common in those with asthma.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed that FIORINAL contains aspirin and should not be taken by patients with an aspirin allergy.
Serious Skin Reactions, including DRESS
Advise patients to stop taking FIORINAL immediately if they develop any type of rash or fever and to contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible [see WARNINGS].
FIORINAL may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. Such tasks should be avoided while taking FIORINAL.
Alcohol and other CNS depressants may produce an additive CNS depression when taken with FIORINAL and should be avoided.
Butalbital may be habit-forming. Patients should take the drug only for as long as it is prescribed, in the amounts prescribed, and no more frequently than prescribed.
Pregnancy
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Inform pregnant women to avoid use of aspirin and other NSAIDs starting at 30 weeks gestation because of the risk of the premature closing of the fetal ductus arteriosus. If treatment with FIORINAL is needed for a pregnant woman between about 20 to 30 weeks gestation, advise her that she may need to be monitored for oligohydramnios, if treatment continues for longer than 48 hours [see WARNINGS; Fetal Toxicity, PRECAUTIONS; Pregnancy].
Laboratory Tests
In patients with severe hepatic or renal disease, effects of therapy should be monitored with serial liver and/or renal function tests.
Drug Interactions
The CNS effects of butalbital may be enhanced by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
In patients receiving concomitant corticosteroids and chronic use of aspirin, withdrawal of corticosteroids may result in salicylism because corticosteroids enhance renal clearance of salicylates and their withdrawal is followed by return to normal rates of renal clearance.
FIORINAL may enhance the effects of:
- Oral anticoagulants, causing bleeding by inhibiting prothrombin formation in the liver and displacing anticoagulants from plasma protein binding sites.
- Oral antidiabetic agents and insulin, causing hypoglycemia by contributing an additive effect, if dosage of FIORINAL exceeds maximum recommended daily dosage.
- 6-mercaptopurine and methotrexate, causing bone marrow toxicity and blood dyscrasias by displacing these drugs from secondary binding sites, and, in the case of methotrexate, also reducing its excretion.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, increasing the risk of peptic ulceration and bleeding by contributing additive effects.
- Other narcotic analgesics, alcohol, general anesthetics, tranquilizers such as chlordiazepoxide, sedative-hypnotics, or other CNS depressants, causing increased CNS depression.
FIORINAL may diminish the effects of:
Uricosuric agents such as probenecid and sulfinpyrazone, reducing their effectiveness in the treatment of gout. Aspirin competes with these agents for protein binding sites.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Aspirin: Aspirin may interfere with the following laboratory determinations in blood: serum amylase, fasting blood glucose, cholesterol, protein, serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), uric acid, prothrombin time and bleeding time. Aspirin may interfere with the following laboratory determinations in urine: glucose, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, Gerhardt ketone, vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), uric acid, diacetic acid, and spectrophotometric detection of barbiturates.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Adequate long-term studies have been conducted in mice and rats with aspirin, alone or in combination with other drugs, in which no evidence of carcinogenesis was seen. No adequate studies have been conducted in animals to determine whether aspirin has a potential for mutagenesis or impairment of fertility. No adequate studies have been conducted in animals to determine whether butalbital has a potential for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Withdrawal seizures were reported in a two-day-old male infant whose mother had taken a butalbital-containing drug during the last 2 months of pregnancy. Butalbital was found in the infant’s serum. The infant was given phenobarbital 5 mg/kg, which was tapered without further seizure or other withdrawal symptoms.
Use of NSAIDs, including FIORINAL, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus and fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. Because of these risks, limit dose and duration of FIORINAL use between about 20 and 30 weeks of gestation, and avoid FIORINAL use at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy [see WARNINGS; Fetal Toxicity].
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Use of NSAIDs, including FIORINAL, at about 30 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
Use of NSAIDs at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy has been associated with cases of fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with FIORINAL. It is also not known whether FIORINAL can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. FIORINAL should be given to a pregnant woman only when clearly needed.
Based on animal data, prostaglandins have been shown to have an important role in endometrial vascular permeability, blastocyst implantation, and decidualization. In animal studies, administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors such as aspirin, resulted in increased pre- and post-implantation loss. Prostaglandins also have been shown to have an important role in fetal kidney development. In published animal studies, prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors have been reported to impair kidney development when administered at clinically relevant doses.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy, because NSAIDs, including FIORINAL, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus [see WARNINGS; Fetal Toxicity].
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
If an NSAID is necessary at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy, limit the use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. If FIORINAL treatment extends beyond 48 hours, consider monitoring with ultrasound for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, discontinue FIORINAL and follow up according to clinical practice [see WARNINGS; Fetal Toxicity].
Data
Human Data
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Published literature reports that the use of NSAIDs at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
Published studies and post-marketing reports describe maternal NSAID use at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy associated with fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. In many cases, but not all, the decrease in amniotic fluid was transient and reversible with cessation of the drug. There have been a limited number of case reports of maternal NSAID use and neonatal renal dysfunction without oligohydramnios, some of which were irreversible. Some cases of neonatal renal dysfunction required treatment with invasive procedures, such as exchange transfusion or dialysis.
Methodological limitations of these post-marketing studies and reports include lack of a control group; limited information regarding dose, duration, and timing of drug exposure; and concomitant use of other medications. These limitations preclude establishing a reliable estimate of the risk of adverse fetal and neonatal outcomes with maternal NSAID use. Because the published safety data on neonatal outcomes involved mostly preterm infants, the generalizability of certain reported risks to the full-term infant exposed to NSAIDs through maternal use is uncertain.
Labor and Delivery
Ingestion of aspirin prior to delivery may prolong delivery or lead to bleeding in the mother or neonate.
Nursing Mothers
Aspirin, caffeine, and barbiturates are excreted in breast milk in small amounts, but the significance of their effects on nursing infants is not known. Because of potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from FIORINAL, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most frequent adverse reactions are drowsiness and dizziness. Less frequent adverse reactions are lightheadedness and gastrointestinal disturbances including nausea, vomiting, and flatulence. A single incidence of bone marrow suppression has been reported with the use of FIORINAL. Several cases of dermatological reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme have been reported.
Related/similar drugs
Drug Abuse and Dependence
Controlled Substance
FIORINAL is controlled by the Drug Enforcement Administration and is classified under Schedule III.
Abuse and Dependence
Butalbital
Barbiturates may be habit-forming: Tolerance, psychological dependence, and physical dependence may occur especially following prolonged use of high doses of barbiturates. The average daily dose for the barbiturate addict is usually about 1,500 mg. As tolerance to barbiturates develops, the amount needed to maintain the same level of intoxication increases; tolerance to a fatal dosage, however, does not increase more than two-fold. As this occurs, the margin between an intoxication dosage and fatal dosage becomes smaller. The lethal dose of a barbiturate is far less if alcohol is also ingested. Major withdrawal symptoms (convulsions and delirium) may occur within 16 hours and last up to 5 days after abrupt cessation of these drugs. Intensity of withdrawal symptoms gradually declines over a period of approximately 15 days. Treatment of barbiturate dependence consists of cautious and gradual withdrawal of the drug. Barbiturate-dependent patients can be withdrawn by using a number of different withdrawal regimens. One method involves initiating treatment at the patient’s regular dosage level and gradually decreasing the daily dosage as tolerated by the patient.
Overdosage
The toxic effects of acute overdosage of FIORINAL are attributable mainly to its barbiturate component, and, to a lesser extent, aspirin. Because toxic effects of caffeine occur in very high dosages only, the possibility of significant caffeine toxicity from FIORINAL overdosage is unlikely.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms attributable to acute barbiturate poisoning include drowsiness, confusion, and coma; respiratory depression; hypotension; hypovolemic shock. Symptoms attributable to acute aspirin poisoning include hyperpnea; acid-base disturbances with development of metabolic acidosis; vomiting and abdominal pain; tinnitus; hyperthermia; hypoprothrombinemia; restlessness; delirium; convulsions. Acute caffeine poisoning may cause insomnia, restlessness, tremor, and delirium; tachycardia and extrasystoles.
Treatment
Treatment consists primarily of management of barbiturate intoxication and the correction of the acid-base imbalance due to salicylism. Vomiting should be induced mechanically or with emetics in the conscious patient. Gastric lavage may be used if the pharyngeal and laryngeal reflexes are present and if less than 4 hours have elapsed since ingestion. A cuffed endotracheal tube should be inserted before gastric lavage of the unconscious patient and when necessary to provide assisted respiration. Diuresis, alkalinization of the urine, and correction of electrolyte disturbances should be accomplished through administration of intravenous fluids such as 1% sodium bicarbonate in 5% dextrose in water. Meticulous attention should be given to maintaining adequate pulmonary ventilation. The value of vasopressor agents such as Norepinephrine or Phenylephrine Hydrochloride in treating hypotension is questionable since they increase vasoconstriction and decrease blood flow. However, if prolonged support of blood pressure is required, Norepinephrine Bitartrate (Levophed®) may be given I.V. with the usual precautions and serial blood pressure monitoring. In severe cases of intoxication, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, or exchange transfusion may be lifesaving. Hypoprothrombinemia should be treated with Vitamin K, intravenously.
Up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose can often be obtained from a Certified Regional Poison Control Center. Telephone numbers of Certified Regional Poison Control Centers are listed in the Physicians’ Desk Reference®.
Toxic and Lethal Doses (for adults)
Butalbital: toxic dose 1 g (20 capsules)
Aspirin: toxic blood level greater than 30 mg/100 mL; lethal dose 10-30 g
Caffeine: toxic dose 1 g (25 capsules)
Fiorinal Dosage and Administration
One or 2 capsules every 4 hours. Total daily dose should not exceed 6 capsules. Extended and repeated use of this product is not recommended because of the potential for physical dependence.
How is Fiorinal supplied
FIORINAL (Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules, USP)
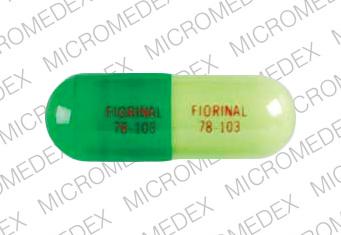
Bright kelly green cap with a bright lime green body. Each half of capsule is imprinted with “FIORINAL 955” in red.
Bottles of 100 are supplied with child-resistant closures. (NDC 0023-6146-01)
Store and Dispense
Below 25°C (77°F); tight container. Protect from moisture.
Rx only
For all medical inquiries contact:
Allergan
Medical Communications
1-800-678-1605
Distributed by:
Allergan USA, Inc.
Madison, NJ 07940
© 2021 Allergan. All rights reserved.
FIORINAL® is a registered trademark of Allergan Sales, LLC.
Allergan® and its design are trademarks of Allergan, Inc.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.

Content Updated: April 2021
v2.0USPI6146
| FIORINAL
butalbital, aspirin, and caffeine capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |
More about Fiorinal (aspirin / butalbital / caffeine)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Reviews (77)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: analgesic combinations