Tilade: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: nedocromil sodium
Dosage form: aerosol
Drug class: Mast cell stabilizers
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 25, 2025.
On This Page
Tilade Description
Tilade (nedocromil sodium) is an inhaled anti-inflammatory agent for the preventive management of asthma. Nedocromil sodium is a pyranoquinoline with the chemical name 4H -Pyrano[3,2-g]quinoline-2,8-dicarboxylic acid, 9-ethyl-6,9-dihydro-4,6-dioxo-10- propyl-, disodium salt, and it has a molecular weight of 415.3. The empirical formula is C19H15NNa2O7. Nedocromil sodium, a yellow powder, is soluble in water.
The molecular structure of nedocromil sodium is:
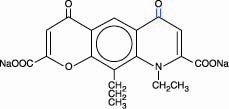
Chemical Class: Pyranoquinoline
Tilade Inhaler (nedocromil sodium inhalation aerosol) is a pressurized metered-dose aerosol suspension for oral inhalation containing micronized nedocromil sodium and sorbitan trioleate, as well as dichlorotetrafluoro ethane and dichlorodifluoromethane as propellants. Each Tilade canister contains 210 mg nedocromil sodium. Each actuation meters 2.00 mg nedocromil sodium from the valve and delivers 1.75 mg nedocromil sodium from the mouthpiece. Each 16.2 g canister provides at least 104 metered actuations. After 104 metered actuations, the amount delivered per actuation may not be consistent and the unit should be discarded.
Each Tilade Inhaler canister must be primed with 3 actuations prior to the first use. If a canister remains unused for more than 7 days, then it should be reprimed with 3 actuations.
Tilade - Clinical Pharmacology
General: Nedocromil sodium has been shown to inhibit the in vitro activation of, and mediator release from, a variety of inflammatory cell types associated with asthma, including eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages, mast cells, monocytes, and platelets. In vitro studies on cells obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage from antigen-sensitized macaque monkeys show that nedocromil sodium inhibits the release of mediators including histamine, leukotriene C4, and prostaglandin D2. Similar studies with human bronchoalveolar cells showed inhibition of histamine release from mast cells and beta-glucuronidase release from macrophages.
Nedocromil sodium has been tested in experimental models of asthma using allergic animals and shown to inhibit the development of early and late bronchoconstriction responses to inhaled antigen. The development of airway hyper-responsiveness to nonspecific bronchoconstrictors was also inhibited. Nedocromil sodium reduced antigen-induced increases in airway microvasculature leakage when administered intravenously in a model system.
In humans, nedocromil sodium has been shown to inhibit acutely the bronchoconstrictor response to several kinds of challenge. Pretreatment with single doses of nedocromil sodium inhibited the bronchoconstriction caused by sulfur dioxide, inhaled neurokinin A, various antigens, exercise, cold air, fog, and adenosine monophosphate.
Nedocromil sodium has no bronchodilator, antihistamine, or corticosteroid activity.
Nedocromil sodium, when delivered by inhalation at the recommended dose, has no known systemic activity.
Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability: Systemic bioavailability of nedocromil sodium administered as an inhaled aerosol is low. In a single dose study involving 20 healthy adult subjects who were administered a 3.5 mg dose of nedocromil sodium (2 actuations of 1.75 mg each), the mean AUC was 5.0 ng-hr/mL and the mean Cmax was 1.6 ng/mL attained about 28 minutes after dosing. The mean half-life was 3.3 hours. Urinary excretion over 12 hours averaged 3.4% of the administered dose, of which approximately 75% was excreted in the first six hours of dosing.
In a multiple dose study, six healthy adult volunteers (3 males and 3 females) received a 3.5 mg single dose followed by 3.5 mg four times a day for seven consecutive days. Accumulation of the drug was not observed. Following single and multiple dose inhalations, urinary excretion of nedocromil accounted for 5.6% and 12% of the drug administered, respectively. After intravenous administration to healthy adults, urinary excretion of nedocromil was approximately 70%. The absolute bioavailability of nedocromil was thus 8% (5.6/70) for single and 17% (12/70) for multiple inhaled doses.
Similarly, in a multiple dose study of 12 asthmatic adult patients, each given a 3.5 mg single dose followed by 3.5 mg four times a day for one month, both single dose and multiple dose inhalations gave a mean high plasma concentration of 2.8 ng/mL between 5 and 90 minutes, mean AUC of 5.6 ng-hr/mL, and a mean terminal half-life of 1.5 hours. The mean 24-hour urinary excretion after either single or multiple dose administration represented approximately 5% of the administered dose.
Studies involving very high oral doses of nedocromil (600 mg single dose, and subsequently 200 mg three times a day for seven days) showed an absolute bioavailability of less than 2%. In a radiolabeled (14C) nedocromil intravenous study involving two healthy adult males, urinary excretion accounted for 64% of the dose, fecal excretion for 36%.
Although minimal pharmacokinetic data are available in children between the ages of 6 and 11 years, the nedocromil sodium levels obtained at 1 hour after chronic dosing in this age group appear to be similar to those observed in adults.
Protein Binding: Nedocromil is approximately 89% protein bound in human plasma over a concentration range of 0.5 to 50µg/mL. This binding is reversible.
Metabolism: Nedocromil is not metabolized after IV administration and is excreted unchanged.
Clinical Studies
The worldwide clinical trial experience with Tilade comprises 6,469 patients, including 993 pediatric patients 6 through 11 years of age. Studies have been conducted both at twice daily and at four times daily dosage regimens. Evidence from these studies indicates that the four times daily regimen has been more effective than the twice daily regimen. Less frequent administration can be considered in patients under good control on the four times daily regimen. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Adult Studies:Tilade vs. Placebo: The effectiveness of Tilade given four times daily was examined in a 14-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial in five centers in 120 patients (60/treatment). To be eligible for entry, the asthmatic patients had to be controlled using only sustained-release theophylline (SRT) and beta2-agonists. Two weeks after the test therapies were begun the SRT was discontinued and four weeks after that oral beta2-agonists were stopped. Beta2-agonist metered dose inhalers could still be used after 6 weeks. Efficacy was assessed by symptom scores recorded on diary cards completed on a daily basis by the patients. Each morning the patient recorded nighttime asthma on a 0–2 scale, (0=slept well, no asthma; 1=woke once because of asthma; 2=woke more than once because of asthma). Before bedtime the patients recorded daytime asthma and cough on a 0–5 scale (0=no symptoms of asthma/cough today; 5=asthma/cough symptoms were noticed most of the day and caused a lot of trouble). At the end of the treatment phase, patients and clinicians were asked for their opinions on the effectiveness of the treatment based on a five point scale (1=very effective; 5=made condition worse). The results of these evaluations are shown in Table 1; Tilade was significantly superior to placebo for all measurements.
| Variable | Time Period | Tilade Mean | Placebo Mean |
| Daytime Asthma1 | Weeks 7–14 | 1.26 | 2.08 |
| Nighttime Asthma2 | Weeks 7–14 | 0.67 | 0.96 |
| Cough1 | Weeks 7–14 | 0.68 | 1.49 |
| Patient’s Opinion2 | Week 14 | 2.27 | 3.55 |
| Clinician’s Opinion2 | Week 14 | 2.13 | 3.48 |
| FEV12 (liters) | Week 2 | 2.69 | 2.18 |
| FEV12 (liters) | Week 6 | 2.65 | 2.15 |
| FEV12 (liters) | Week 10 | 2.55 | 2.15 |
| FEV12 (liters) | Week 14 | 2.59 | 2.10 |
| 1Tilade significantly better than Placebo, p<0.05 | |||
| 2Tilade significantly better than Placebo, p<0.01 | |||
The FEV1 percentage change relative to baseline is shown in Figure 1; these also favored Tilade over placebo throughout the study, with an effect seen first at the two week measurement.
Figure 1
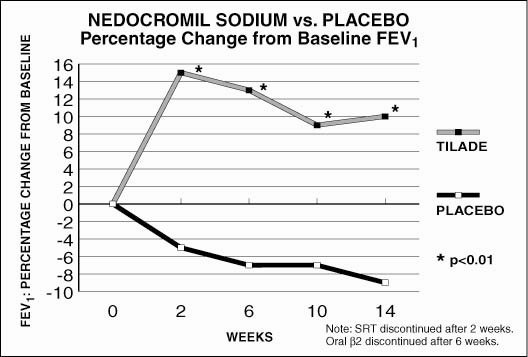
This study shows that Tilade improves symptom control and pulmonary function when it is added to an as-needed inhaled beta2-adrenergic bronchodilator regimen and that a beneficial effect could be detected within two weeks.
Tilade vs. Cromolyn Sodium vs. Placebo: The effectiveness of Tilade was compared to cromolyn sodium and placebo in an eight-week, double-blind, parallel-group, 12-center trial during which medication was given four times daily. Three hundred and six patients were randomized to treatment (103/Tilade; 104/cromolyn sodium; 99/placebo). All patients were SRT dependent and this drug was stopped prior to starting the test treatment. Efficacy was assessed on the basis of diary card symptom scores and FEV1. The diary scores were the same as used in the 14-week study except that nighttime symptoms were recorded on a 0–3 scale. The primary efficacy variable was a summary symptom score derived by averaging the scores for daytime asthma, nighttime asthma, and cough. The results of the study are shown in Table 2.
| Variable | Time Period | Tilade Mean | Placebo Mean | Cromolyn Sodium Mean |
| Summary Score1 | Weeks 3–8 | 1.30 | 1.76 | 1.13 |
| Daytime Asthma1 | Weeks 3–8 | 1.59 | 2.05 | 1.41 |
| Nighttime Asthma2 | Weeks 3–8 | 0.91 | 1.23 | 0.77 |
| Cough3 | Weeks 3–8 | 1.11 | 1.58 | 0.93 |
| FEV12 | Weeks 3–8 | 2.46 | 2.23 | 2.56 |
| Patient’s Opinion1 | Week 8 | 2.54 | 3.39 | 2.22 |
| Clinician’s Opinion1 | Week 8 | 2.60 | 3.43 | 2.39 |
| 1Tilade significantly better than Placebo, p<0.001 | ||||
| 2Tilade significantly better than Placebo, p<0.01, cromolyn sodium significantly better than Tilade, p<0.05 | ||||
| 3Tilade significantly better than Placebo, p<0.05 | ||||
This study corroborates the findings of the 14-week study, showing that Tilade is effective in the management of symptoms and pulmonary function in primarily atopic mild to moderate asthmatics. Both active treatments were statistically significantly better than placebo for the primary efficacy variable (summary symptom score); Tilade and cromolyn sodium were not significantly different for this parameter. A statistically significant difference favoring cromolyn sodium was, however, seen for nighttime asthma and FEV1.
In allergic asthmatics who are well controlled on cromolyn sodium, there is no evidence that the substitution of Tilade for cromolyn sodium would confer additional benefit to the patient.
Available data on the relative efficacy of Tilade and cromolyn sodium are inconclusive and efficacy with one agent is not known to be predictive of efficacy with the other.
Pediatric Studies: Tilade vs. Placebo in Pediatric Patients: The effectiveness of Tilade in minimizing the anticipated seasonal increase in asthmatic symptoms in pediatric patients 6 through 11 years of age with mild seasonal ragweed-induced asthma was examined in an eight-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial in nine centers in 146 patients (75/Tilade ; 71/placebo). These patients had a mean baseline FEV1 that was 85% of predicted normal and a mean baseline beta2-agonist requirement of less than 2 inhalations of albuterol from a metered dose inhaler per day. Study medication was given four times a day. Efficacy was assessed on the basis of diary card symptom scores (daytime asthma, sleep disturbance, daytime cough, and morning asthma, all rated on a six point scale: 0=no symptoms; 5=severe symptoms) and as-needed bronchodilator use. The primary efficacy variable was based on both the summary symptom score (total of daytime asthma, daytime cough, and sleep disturbance) and as-needed bronchodilator usage. At the end of the treatment phase, parents and clinicians assessed treatment effectiveness on a five-point scale: 1=very effective; 5=made condition worse. After a two-week baseline, patients were randomized to eight weeks of double-blind treatment. The results of these evaluations are shown in Table 3.
| Comparison of Scores for Tilade and Placebo During the Primary Time Period of Evaluation | |||
| Variable | Time Period | Tilade Mean | Vehicle Placebo Mean |
| Summary Symptom Score1,3,4 | Weeks 3–8 | 1.38 | 1.99 |
| Bronchodilator Use2,3,4 | Weeks 3–8 | 0.43 | 0.84 |
| Parent’s Opinion4 | Week 8 | 2.13 | 2.75 |
| Clinician’s Opinion4 | Week 8 | 2.16 | 2.74 |
| 1 Daytime asthma, daytime cough, and sleep disturbance due to asthma (0–15) | |||
| 2 One unit for every two inhalations | |||
| 3 Adjusted for baseline | |||
| 4Tilade significantly better than Placebo, p<0.05 | |||
The percentage change from baseline in summary symptom score by week is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2
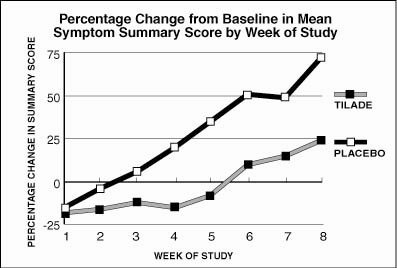
This study shows that Tilade , when used prophylactically in asthmatics with known seasonal exacerbations, can attenuate an increase in symptoms of asthma and reduce the need for rescue bronchodilator treatment.
Indications and Usage for Tilade
Tilade Inhaler is indicated for maintenance therapy in the management of adult and pediatric patients 6 years and older with mild to moderate asthma.
Tilade is not indicated for the reversal of acute bronchospasm.
Contraindications
Tilade Inhaler is contraindicated in patients who have shown hypersensitivity to nedocromil sodium or other ingredients in this preparation.
Warnings
Tilade® Inhaler (nedocromil sodium inhalation aerosol) is not a bronchodilator and, therefore, should not be used for the reversal of acute bronchospasm, particularly status asthmaticus. Tilade should ordinarily be continued during acute exacerbations, unless the patient becomes intolerant to the use of inhaled dosage forms.
As with other inhaled asthma medications, bronchospasm, which can be life-threatening, may occur immediately after administration. If this occurs, Tilade should be discontinued and alternative therapy instituted.
Precautions
General: The role of Tilade as a corticosteroid-sparing agent in patients receiving oral or inhaled corticosteroids remains to be defined. If systemic or inhaled corticosteroid therapy is reduced in patients receiving Tilade, careful monitoring is necessary.
Information for Patients: Patients should be told that:
-
Tilade must be taken regularly to achieve benefit, even during symptom-free periods.
-
Tilade is not meant to relieve acute asthma symptoms. If symptoms do not improve or the patient’s condition worsens, the patient should not increase the dosage but should notify the physician immediately.
-
They should not decrease the dose without the physician’s knowledge. The recommended dose should not be exceeded.
-
The full therapeutic effect of Tilade may not be obtained for 1 week or longer after initiating treatment.
-
Because the therapeutic effect depends upon local delivery to the lungs, it is essential that patients be properly instructed in the correct method of use (see Patient Instructions for Use).
-
An illustrated leaflet for the patient is included in each Tilade Inhaler pack.
Drug Interactions: In clinical studies, Tilade has been co-administered with other anti-asthma medications, including inhaled and oral bronchodilators, and inhaled corticosteroids, with no evidence of increased frequency of adverse events or laboratory abnormalities. No formal drug-drug interaction studies, however, have been conducted.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility: A two-year inhalation carcinogenicity study of nedocromil sodium at a dose of 24 mg/kg/day (approximately 8 times the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis) in Wistar rats showed no carcinogenic potential. A 21-month oral dietary carcinogenicity study of nedocromil sodium performed in B6C3F1 mice with doses up to 180 mg/kg/day (approximately 30 times the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis) showed no carcinogenic potential.
Nedocromil sodium showed no mutagenic potential in the Ames Salmonella/microsome plate assay, mitotic gene conversion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, mouse lymphoma forward mutation, and mouse micronucleus assays.
Reproduction and fertility studies in mice and rats showed no effects on male and female fertility at a subcutaneous dose of 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 30 times and 60 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis).
Pregnancy:Pregnancy Category B: Reproduction studies performed in mice, rats, and rabbits using a subcutaneous dose of 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 30 times, 60 times, and 116 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis) revealed no evidence of teratogenicity or harm to the fetus due to nedocromil sodium. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers: It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Tilade is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use: Safety data in normal volunteers and asthmatic patients between the ages of 6 and 11 years are available on a total of 311 children from U.S. clinical trials and 192 children from foreign clinical trials (total = 503) of 4–12 weeks duration. An additional 225 children received Tilade for 40 weeks and 24 received Tilade for 52 weeks.
The safety and effectiveness of Tilade in children ages 6 through 11 have been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials. (See CLINICAL STUDIES: Pediatric Studies.) Use of Tilade in children ages 6 through 11 years is also supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of Tilade in adults. The safety and effectiveness of Tilade in patients below the age of 6 years have not been established.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Tilade is generally well tolerated. Adverse event information was derived from 6,469 patients receiving Tilade in controlled and open-label clinical trials of 1–52 weeks in duration. A total of 4,400 patients received two inhalations four times a day. An additional 2,069 patients received two inhalations twice daily or another dose regimen. Seventy-seven percent of patients were treated with Tilade for eight weeks or longer.
Of the 4,400 patients who received two inhalations of Tilade four times a day, 2,632 were in placebo-controlled, parallel trials and of these 6.0% withdrew from the trials due to adverse events, compared to 5.7% of the 2,446 patients who received placebo.
The reasons for withdrawal were generally similar in the Tilade and placebo-treated groups, except that patients withdrew due to bad taste statistically more frequently on Tilade than on placebo. Headache reported as severe or very severe, some with nausea and ill feeling, was experienced by 1.0% of Tilade patients and 0.7% of placebo patients.
The events reported with a frequency of 1% or greater across all placebo-controlled studies are displayed for all patients ages 6 years and older who received Tilade or placebo at two inhalations four times daily.
The adverse event profile observed in children ages 6 through 11 was similar to that observed in adults.
| % Experiencing AE | % Withdrawing | |||
| ADVERSE EVENT (AE) | Tilade (N=2632) | Placebo (N=2402) | Tilade | Placebo |
| Special Senses | ||||
| Unpleasant Taste* | 11.6% | 3.1% | 1.6% | 0.0% |
| Respiratory System Disorders | ||||
| Coughing | 8.9% | 10.2% | 1.1% | 1.2% |
| Pharyngitis | 7.6% | 7.5% | 0.5% | 0.4% |
| Rhinitis* | 7.3% | 6.0% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Upper Respiratory Infection | 6.7% | 6.3% | 0.1% | 0.2% |
| Sputum Increased | 1.5% | 1.4% | 0.1% | 0.2% |
| Bronchitis | 1.1% | 1.5% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Dyspnea | 2.5% | 3.3% | 0.8% | 1.0% |
| Bronchospasm** | 8.4% | 11.8% | 1.4% | 2.0% |
| Sinusitis | 3.3% | 4.1% | 1.1% | 0.0% |
| Respiratory Disorder | 0.8% | 1.1% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | ||||
| Nausea* | 3.9% | 2.3% | 1.1% | 0.5% |
| Vomiting* | 2.5% | 1.6% | 0.2% | 0.3% |
| Dyspepsia | 1.5% | 1.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Diarrhea | 1.3% | 1.2% | 0.1% | 0.0% |
| Abdominal Pain* | 1.9% | 1.3% | 0.2% | 0.1% |
| Central and Peripheral Nervous System | ||||
| Dizziness | 0.8% | 1.3% | 0.1% | 0.2% |
| Body as a Whole | ||||
| Headache | 8.1% | 7.5% | 0.4% | 0.2% |
| Chest Pain | 3.6% | 3.8% | 0.7% | 0.5% |
| Fatigue | 1.0% | 0.8% | 0.2% | 0.0% |
| Fever | 3.1% | 3.7% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Resistance Mechanism Disorders | ||||
| Infection Viral | 2.4% | 3.2% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Vision Disorder | ||||
| Conjunctivitis | 1.1% | 0.7% | 0.0% | 0.1% |
| Skin and Appendages Disorders | ||||
| Rash** | 0.5% | 1.2% | 0.1% | 0.0% |
| * Statistically significant higher frequency on Tilade , p<0.05 | ||||
| **Statistically significant higher frequency on Placebo, p<0.05 | ||||
Other adverse events present at less than the 1% level of occurrence, but that might be related to Tilade administration, include arthritis, tremor, and a sensation of warmth.
In clinical trials with 2,632 patients receiving Tilade , 2 patients (0.08%) developed neutropenia and 3 patients (0.11%) developed leukopenia. Although it is unclear if these reactions were caused by Tilade, in several cases these abnormal laboratory tests returned to normal when Tilade was discontinued.
There have been reports of clinically significant elevation of hepatic transaminases (ALT and AST greater than 10 times the upper limit of the normal reference range in one patient) associated with the administration of Tilade . It is unclear if these abnormal laboratory tests in asymptomatic patients were caused by Tilade.
Cases of bronchospasm immediately following dosing with Tilade have been reported from postmarketing experience. (See WARNINGS.) Isolated cases of pneumonitis with eosinophilia (PIE syndrome) and anaphylaxis have also been reported in which a relationship to drug is undetermined.
Related/similar drugs
Overdosage
There is no experience to date with overdose of Tilade in humans. There were no deaths in rodents at an oral dose of 4,000 mg/kg (approximately 690 times [for mice] and 1,370 times [for rats] the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis). The subcutaneous or intravenous lethal dose in rats was between 2,000 and 4,000 mg/kg (approximately 690 and 1,370 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis). No deaths occurred in mice at a subcutaneous dose of 4,000 mg/kg (approximately 690 times the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis), and the intravenous lethal dose in mice was between 2,000 and 4,000 mg/kg (approximately 345 and 690 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis). An intravenous dose of 240 mg/kg (approximately 110 times the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis) did not produce any deaths in cats. Head shaking/tremor and salivation were observed in beagle dogs following daily inhalation doses of 5 mg/kg (approximately 6 times the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis) and transient hypotension was detected following daily subcutaneous doses of 8 mg/kg (approximately 9 times the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose on a mg/m2 basis). In addition, clonic convulsions were observed in dogs following daily inhalation doses of 20 mg/kg plus subcutaneous doses of 20 mg/kg giving peak plasma nedocromil levels of 7.6 µg/mL, some three orders of magnitude greater than peak plasma levels (2.5 ng/mL) of the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose. Specific tests designed to evaluate CNS activity demonstrated no effects due to nedocromil sodium, and nedocromil sodium does not pass the blood brain barrier. Therefore, overdosage is unlikely to result in clinical manifestations requiring more than observation and discontinuation of the drug where appropriate.
Tilade Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage for adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is two inhalations four times a day at regular intervals, which provides a dose of 14 mg per day. In patients whose asthma is well controlled on this dosage (e.g., patients who only need occasional inhaled or oral beta2-agonists and who are not experiencing serious exacerbations), less frequent administration may be effective.
Each Tilade Inhaler canister must be primed with 3 actuations prior to the first use. If a canister remains unused for more than 7 days, then it should be reprimed with 3 actuations.
Tilade Inhaler may be added to the patient’s existing treatment regimen (e.g., bronchodilators). When a clinical response to Tilade Inhaler is evident and if the patient’s asthma is under good control, an attempt may be made to decrease concomitant medication usage gradually.
Proper inhalational technique is essential (see Patient Instructions for Use).
Patientsshould be advised that the optimal effect of Tilade therapy depends upon its administration at regular intervals, even during symptom-free periods.
How is Tilade supplied
Tilade Inhaler is available in 16.2 g canisters providing at least 104 metered inhalations. Each Tilade canister contains 210 mg nedocromil sodium. Each pack is supplied with patient instructions, a tan-colored rubber valve cover, and white plastic mouthpiece and cover, bearing the Tilade logo. The Tilade mouthpiece should not be used with other aerosol medications and the Tilade canister should not be used with other mouthpieces. Each actuation meters 2.00 mg nedocromil sodium from the valve and delivers 1.75 mg nedocromil sodium from the mouthpiece.
NDC 60793-120-01 ..... One 16.2 g Canister (104 Metered Inhalations)
The canister should be discarded after the labeled number of actuations have been used. The amount of medication in each actuation cannot be assured after this point.
Store between 2° to 30°C (36° to 86°F). Do not freeze. Avoid spraying in eyes. Contents under pressure. Do not puncture, incinerate, place near sources of heat, or use with other mouthpieces. Exposure to temperatures above 120°F may cause bursting. Never throw canister into fire or incinerator. Keep out of the reach of children. For best results, the canister should be at room temperature before use.
Shake well before using.
Note: The indented statement below is required by the Federal government’s Clean Air Act for all products containing or manufactured with chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
WARNING: Contains CFC-12 and CFC-114, substances which harm public health and the environment by destroying ozone in the upper atmosphere.
A notice similar to the above WARNING has been placed in the “Patient Instructions for Use” portion of this package insert under the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) regulations. The patient’s warning states that the patient should consult his or her physician if there are questions about alternatives.
Rx only
Prescribing Information as of September 2005.
Distributed by: King Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Bristol, TN 37620
Manufactured by: Aventis Pharma LTD, Holmes Chapel CW48BE, United Kingdom
Made in United Kingdom
Patient Instructions for Use
Tilade® Inhaler (NEDOCROMIL SODIUM INHALATION AEROSOL)
Metered-Dose Inhaler
Rx Only
This leaflet does not contain the complete information about your medication. If you have any further questions, or are not sure about something, you should ask your doctor or pharmacist.
You may want to read this leaflet again. Please DO NOT THROW IT AWAY until you have finished this canister.
TELL YOUR DOCTOR BEFORE STARTING TO TAKE THIS MEDICINE:
-
if you are pregnant (or intending to become pregnant),
-
if you are breast-feeding a baby,
-
if you are allergic to Tilade, or any other components of the drug product.
In some circumstances, this medication may not be suitable and your doctor may wish to give you a different medicine. Make sure that your doctor knows what other medicines you are taking.
DO NOT use after the date shown as “EXP” on the label or box.
Instructions for Use
The following is one of several acceptable inhalation techniques. If your physician has suggested another method, you should use that method.
-
To use the Tilade Inhaler, remove the Mouthpiece Cover and make sure the metal Canister is fully and firmly inserted into the plastic Mouthpiece. Do not remove the Valve Cover from the metal Canister (Figures 1a & 1b).
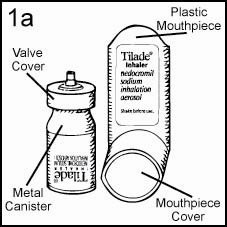
Inhaler Components
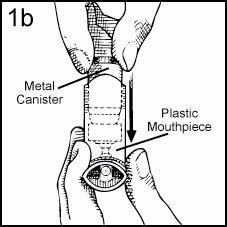
Assembly of Inhaler
-
To prepare your Tilade Inhaler for use, the Inhaler must be primed prior to the first use. To prime, hold the Inhaler upright, with the Mouthpiece facing away from you. Shake the Inhaler, then press firmly downward on the Canister. Repeat this procedure again until a total of three (3) sprays are released. Your Tilade Inhaler is now ready for use. Repriming is only necessary when your Inhaler remains unused for more than 7 days. To reprime, shake the Inhaler and release one spray. Repeat this procedure until a total of three (3) sprays are released.
-
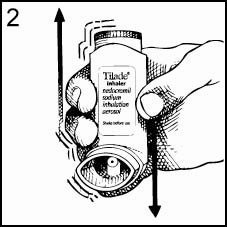
Hold the Inhaler (as illustrated in Figure 2) and shake well before each use. The Mouthpiece should be inspected for the presence of foreign objects before use. For optimal results, the Canister should be at room temperature before use.
-
Avoid spraying in eyes.
-
Hold the Inhaler away from your mouth, as shown, and exhale slowly. Do not breathe into the Inhaler as moisture could cause it to clog (Figure 3).
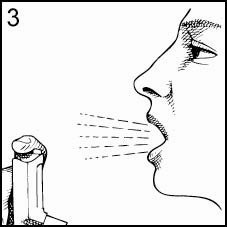
-
Place the Mouthpiece in your mouth and close your lips around it. Tilt your head back, keeping your tongue below the opening of the Inhaler (Figure 4).
-
Press the top of the Canister down firmly at exactly the same time as you begin to inhale. Keep the Canister depressed as you continue to inhale slowly through your mouth until you have taken a full breath (Figure 5). After you have finished your full breath, release the pressure of your finger from the top of the Canister.
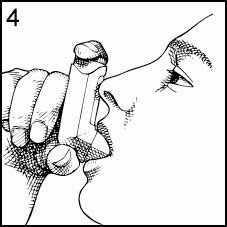
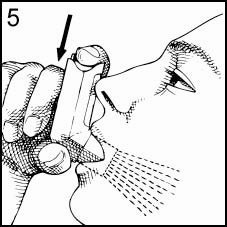
-
Remove the Inhaler from your mouth, and hold your breath as long as comfortably possible before breathing out slowly. This step is very important because it allows the medication to spread throughout your lungs.
-
Repeat Steps 3-8; then replace the Mouthpiece Cover.
-
Keeping the plastic Mouthpiece clean is extremely important to prevent medication buildup and blockage. To clean, simply remove the Canister and Mouthpiece Cover, and wash the Mouthpiece through the top and bottom in HOT water (Figures 6 & 7). Never immerse the metal Canister in water. The Mouthpiece can be washed every day, and should be washed at least twice a week. To dry, shake off excess water and let the Mouthpiece air dry in a warm place overnight. When the Mouthpiece is completely dry, replace the Canister and Mouthpiece Cover.
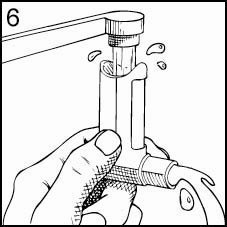
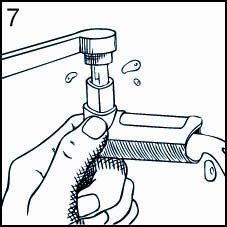
For Best Results
-
Use the Inhaler every day, as directed by your physician. Do not stop the treatment, or even reduce the dosage during symptom-free periods, without your physician’s permission.
-
Remember, your Tilade Inhaler must be primed prior to the first use. Repriming is only necessary when the Inhaler remains unused for more than 7 days. Do not reprime between more frequent usage. (See Step 2 under INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE.) Note: The Valve Cover should not be removed from the Canister (see Step 1 under INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE).
-
It is essential that the Canister be pressed at exactly the same time as you inhale. It is well worth your time to review this technique with your physician.
-
The dose delivered from the Inhaler can be seen as a fine mist. If you notice this mist escaping from your mouth or nose, you may not be breathing in at the exact moment the Canister is being pressed (see Steps 6 & 7 under INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE).
-
Keep the Mouthpiece Cover on the Inhaler when not in use so that dirt can’t get into it.
-
Keep a record of the number of sprays used and discard the Canister after 104 sprays.The amount of medication in each spray cannot be assured after 104 sprays. Please note that the Canister has been filled with extra suspension to accommodate the initial priming activity.
-
The Tilade Canister is to be used only with the Tilade Inhaler Mouthpiece and should not be used with other mouthpieces. In addition, the Tilade Mouthpiece should not be used with canisters of other inhaled medications.
-
While taking Tilade Inhaler, other inhaled drugs should be taken only as directed by your physician.
Product Utilization
For the treatment of mild to moderate asthma in patients 6 years of age and older, the recommended dosage is two (2) inhalations four times a day at regular intervals. For maintenance therapy, daily dosing frequency will depend upon your physician’s assessment of your asthma and may be four times a day or less at regular intervals.
With regular use, Tilade will decrease asthma symptoms. However, Tilade will not relieve the symptoms of an asthma attack once the attack has started.
It is important that you follow your physician’s daily dosing instructions– even during symptom-free periods – to achieve optimal benefit from this medication. Please note that Tilade is not a steroid medication.
Benefits which may be achieved from regular use of Tilade include:
-
Prevention or reduction of asthma symptoms such as wheezing, chest tightness, cough, and shortness of breath.
-
Treatment of the bronchial inflammation that causes asthma.
Tilade Canisters should only be used with the Tilade Inhaler Mouthpiece. The Tilade Mouthpiece should not be used with canisters of other inhaled medications.
Tilade Inhaler will provide at least 104 metered sprays. However, after 104 sprays, the amount of drug delivered per spray may not be consistent. You should keep track of the number of sprays used from each Canister of Tilade Inhaler and discard the Canister after 104 sprays.
HOW TO CHECK CONTENTS OF YOUR CANISTER
Shaking the Canister will NOT give you a good estimate of how much medication is left. We have included a convenient check-off chart to assist you in keeping track of medication inhalations used. This will help assure that you receive the labeled number of inhalations present. Please note that the Canister has been filled with extra suspension to accommodate the initial priming activity.
Each 16.2 gram inhaler delivers 104 metered inhalations. Tilade® Inhaler Check-Off Chart
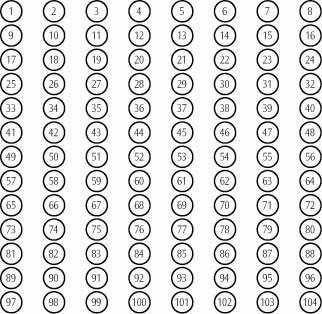
-
Retain with medication or affix to convenient location.
-
Starting with inhalation #1, check off one circle for each inhalation used.
-
DISCARD MEDICATION AFTER THE LABELED NUMBER OF INHALATIONS HAVE BEEN USED.
-
NEVER IMMERSE THE METAL CANISTER IN WATER.
Storage and Handling
The contents of Tilade Inhaler are under pressure. Do not puncture. Do not use or store near heat or open flame. Exposure to temperatures over 120°F may cause bursting. Never throw the Canister into a fire or incinerator.
Keep out of the reach of children. Store at room temperature. Avoid excessive humidity.
Note: The indented statement below is required by the Federal government’s Clean Air Act for all products containing or manufactured with chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
This product contains CFC-12 and CFC-114, substances which harm the environment by destroying ozone in the upper atmosphere.
Your physician has determined that this product is likely to help your personal health. USE THIS PRODUCT AS DIRECTED, UNLESS INSTRUCTED TO DO OTHERWISE BY YOUR PHYSICIAN. If you have any questions about alternatives, consult with your physician.
Prescribing Information as of September 2005.
Distributed by: King Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Bristol, TN 37620
Manufactured by: Aventis Pharma LTD, Holmes Chapel CW48BE, United Kingdom
Made in United Kingdom
| TILADE
nedocromil sodium aerosol, metered |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - King Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
More about Tilade (nedocromil)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: mast cell stabilizers
- Breastfeeding
