Moderate and Severe Persistent Asthma
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
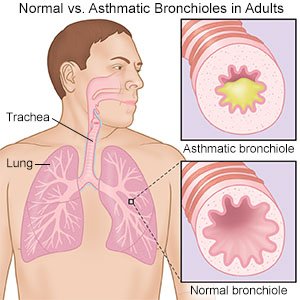
Moderate or severe persistent asthma means you have asthma symptoms every day. You may also need to use your rescue inhaler daily to treat shortness of breath. Your normal activities are affected by wheezing, shortness of breath, or chest tightness. You have frequent flare-ups when your symptoms become worse. Flare-ups at night can affect your sleep and happen at least 1 time each week.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Medicines:
- Bronchodilators help open your airways. The short-acting bronchodilators start to work right away and are used to relieve sudden, severe symptoms. The long-acting bronchodilators are used for long-term management of your asthma.
- Steroids help decrease swelling and open your airways to help you breathe easier. They may be given as an injection, pills, or in an inhaler. After an asthma attack, you may need to take steroid pills for several days. Inhaled steroids are used for long-term control.
- Medicines may be used to help your body prevent allergic reactions that trigger your asthma.
- Antibiotics are sometimes used to help control asthma.
Monitoring:
Pulse oximetry measures the amount of oxygen in your blood. A cord with a clip or sticky strip is placed on your finger, ear, or toe. The other end of the cord is hooked to a machine that measures the oxygen levels. Never turn off the machine. An alarm will sound if your oxygen level is low or cannot be read.
Related medications
Tests:
- Blood tests are done to check oxygen levels. They may also be used to check for infections.
- Lung function tests , such as spirometry and peak flow expiratory flow rates, show how well your lungs are working. These tests may be done more than 1 time.
- A chest x-ray may be done to look for signs of infection, such as swelling and fluid.
Treatment:
- Oxygen may be needed if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils. Ask your doctor before you take off the mask or tubing.
- A nebulizer is a long tube that goes from a machine to a container that holds liquid asthma medicine. The liquid medicine turns into a mist when the machine is turned on. You breathe in this mist through a mouthpiece.
- A ventilator may be needed to give you oxygen and breathe for you when you cannot breathe on your own.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
You may have decreased lung function if persistent asthma is not controlled. You may also have an increased risk of a collapsed lung, pneumonia, or other lung problems. These conditions can be life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Moderate and Severe Persistent Asthma
Treatment options
Care guides
- Asthma
- Asthma in Children
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
- Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction
- Moderate and Severe Persistent Asthma
- Reactive Airways Disease
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
