Bromax Tablets: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: brompheniramine maleate
Dosage form: tablet, extended release
Drug class: Antihistamines
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 24, 2025.
On This Page
Bromax Tablets Description
Each white, dye free, Bromax Tablet for oral administration contains:
Brompheniramine Maleate ..... 11 mg
Formulated in a specially prepared base which provides prolonged activity suitable for B.I.D. dosing.
Bromax Tablets contain ingredients of the following therapeutic class: Antihistamine.
Brompheniramine Maleate is 2-Pyridinepropanamine, γ-(4- bromophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-, (±)-, (Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) and has the following structural formula:
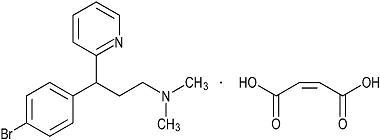
C16H19BrN2 • C4H4O4 M.W. 435.31
INACTIVE INGREDIENTS
Colloidal silicon dioxide, Eudragit, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate (veg.), methylcellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, silicified microcrystalline cellulose and stearic acid.
Bromax Tablets - Clinical Pharmacology
Brompheniramine maleate is classified as an alkylamine antihistamine. This class is among the most active histamine antagonists and is generally effective in relatively low doses. Alkylamines cause a lesser degree of drowsiness and sedation than the phenothiazine and ethanolamine antihistamines and hence may be more suitable for daytime use. It should be noted however that patients taking alkylamine antihistamines may experience some degree of drowsiness and should be cautioned accordingly.
Indications and Usage for Bromax Tablets
Bromax is indicated for the temporary relief of symptoms associated with seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis and vasomotor rhinitis.
Contraindications
This product is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to antihistamines, in nursing mothers, in patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) therapy (see Drug Interactions section), or in patients with narrow angle glaucoma, urinary retention, peptic ulcer and in patients during an asthmatic attack.
Warnings
Caution should be exercised in patients with hyperthyroidism, increased intraocular pressure and prostatic hypertrophy.
Patients sixty (60) years and older may demonstrate an increased response to this drug, both in therapeutic effect and in the incidence of adverse reactions. A reduction in dosage may be more appropriate for these patients. Antihistamines may cause drowsiness or excitability, particularly in children. At doses higher than the recommended dose, nervousness, dizziness or sleeplessness may occur.
Precautions
General
Antihistamines have an atropine-like action and therefore should be used with caution in patients with a history of bronchial asthma, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, cardiovascular disease and hypertension.
Information for Patients
Patient consultation should include the following information regarding proper use of this medication:
• Do not take more medication than the amount recommended.
• Take medication with food, water, or milk to minimize gastric irritation.
• Swallow sustained release dosages whole; do not crush tablets.
• Do not drive or operate machinery if drowsiness or dizziness occurs.
• Do not ingest alcoholic beverages, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), or CNS depression-producing medications (hypnotics, sedatives, tranquilizers) while taking this medication.
• If a dose is missed, the medication should be taken as soon as possible unless it is almost time for the next dose; do not double doses.
• This medication should be stored in a tight, light-resistant container as described in the USP/NF, with a child resistant closure, and at temperatures between 20°- 25°C (68°- 77°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature.
• Keep all medications out of the reach of children. In case of accidental overdose, seek professional assistance or contact a poison control center immediately.
Caution patients about the signs of potential side effects, especially:
• Anticholinergic effects clumsiness or unsteadiness; severe drowsiness; severe dry mouth, nose, or throat; flushing or redness of face; shortness of breath or troubled breathing;
• Blood dyscrasias – sore throat and fever, unusual bleeding or bruising, unusual tiredness or weakness;
• Fast or irregular heart beat;
• Psychotic episodes;
• Tightness in chest.
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
Antihistamines may interfere with diagnostic test results for skin tests using allergen extracts.
Drug Interactions
• MAOIs and Tricyclic Antidepressants - may prolong and intensify the anticholinergic (drying) effects of antihistamines.
• CNS Depressants - concomitant use of antihistamines with alcohol, tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates and other CNS depressants may have an additive effect.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No data are available on the long-term potential of the components of this product for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility in animals and humans.
Pregnancy
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. However, certain antihistamines are known to be excreted in human milk. Because of the higher risks of antihistamines for infants generally and for newborns and prematures in particular, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Do not give this product to children under 12 years of age except under the advice and supervision of a physician.
Geriatric Use
Confusion, dizziness, sedation, hypotension, hyperexcitability, and anticholinergic side effects, such as dryness of mouth and urinary retention (especially in males), may be more likely to occur in geriatric patients taking antihistamines. Demonstrate safe use of a short-acting antihistamine before use of a sustained action formulation in elderly patients.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The physician should be alert to the possibility of any of the adverse reactions which have been observed with antihistaminic drugs. These include: drowsiness; confusion; restlessness; nausea; vomiting; drug rash; vertigo; palpitation; anorexia; dizziness; dysuria due to vesicle sphincter spasm; headache, insomnia; anxiety; tension; weakness; tachycardia; angina; sweating; blood pressure elevation; mydriasis; gastric distress; abdominal cramps; central nervous system stimulation; circulatory collapse.
Related/similar drugs
Overdosage
Signs and Symptoms:
Overdosage with antihistamines may cause hallucinations, convulsions or possible death, especially in infants and children. Antihistamines are more likely to cause dizziness, sedation, and hypotension in elderly patients.
Recommended General Treatment:
In the event of overdosage, emergency treatment should be started immediately. Since the action of sustained release products may continue for as long as 12 hours, treatment of overdosage should be directed toward reducing further absorption and supporting the patient for at least that length of time.
Since there is no specific antidote for antihistamine overdose, treatment is symptomatic and supportive with possible utilization of the following:
• Induction of emesis (syrup of ipecac recommended); however, precaution against aspiration is necessary, especially in infants and children.
• Gastric lavage (isotonic or 0.45% sodium chloride solution) if patient is unable to vomit within three hours of ingestion.
• Saline cathartics (milk of magnesia) are sometimes used.
• Vasopressors to treat hypotension. However, epinephrine should not be used since it may further lower blood pressure.
• Oxygen and intravenous fluids.
• Precaution against the use of stimulants (analeptic agents) is recommended because they may cause seizures.
• Short-acting barbiturates, diazepam, or paraldehyde, may be administered to control seizures.
• Hyperpyrexia, especially in children, may require treatment with tepid water sponge bath or a hypothermic blanket.
• Apnea is treated with ventilatory support.
Bromax Tablets Dosage and Administration
Adults and children over 12 years of age: One tablet twice daily (B.I.D.).
Not recommended for children under 12 years of age.
How is Bromax Tablets supplied
Bromax is supplied as white, capsule shaped tablets debossed "POLY / 911" on one side, and “plain” on the opposite side. Available in bottles of 100 tablets, NDC 50991-911-01
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATION OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN. IN CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSE, SEEK PROFESSIONAL ASSISTANCE OR CONTACT A POISON CONTROL CENTER IMMEDIATELY.
| BROMAX
brompheniramine maleate tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Poly Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (198449894) |
| Registrant - Poly Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (198449894) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sovereign Pharmaceuticals, LLC | 623168267 | MANUFACTURE | |
More about Bromax (brompheniramine)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Imprints, shape & color data
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: antihistamines
- Breastfeeding

