Hicon Kit Dosage
Generic name: SODIUM IODIDE I-131 1000mCi in 1mL
Dosage form: oral solution, capsules
Drug classes: Antithyroid agents, Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jan 21, 2025.
Radiation Safety
- HICON® is a radioactive drug. Handle with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure to the patient and healthcare workers:
- Use only by, or under the direction of, physicians who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radioactive materials, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate governmental agency authorized to license the use of radiopharmaceuticals.
- Use waterproof gloves when handling and administering the product.
- Maintain adequate shielding during the life of the product.
- Measure patient dose with a suitable radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to administration.
Important Administration Instructions
- Do not directly administer the concentrated sodium iodide I 131 solution USP provided with HICON® to patients. The concentrated sodium iodide I 131 solution USP must be diluted and prepared prior to administration.
- Obtain a pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential prior to administration to verify the absence of pregnancy.
- Instruct patients to fast at least 2 hours before and 2 hours after administration to ensure absorption.
- Instruct patients to hydrate before and after administration of sodium iodide I 131 and to void frequently to enhance urinary elimination of the radioiodide that is not absorbed by the thyroid gland.
- Instruct patients to maintain a low-iodide diet two weeks prior to radioiodide administration and continue for several days during the uptake or imaging process.
- Instruct patients to discontinue the anti-thyroid therapy three days before administration of sodium iodide I 131.
- For patients with a history of renal impairment, evaluate renal function for therapeutic planning and consider dosimetry.
- Obtain a complete blood count within one month of therapy. If patients show leukopenia or thrombocytopenia, dosimetry should be used to determine a safe sodium iodide I 131 activity, while delivering less than 2 Gy to the bone marrow.
Recommended Dosage and Administration
Individualization of Therapy
The recommended dose for orally administered sodium iodide I 131 capsules or solution is based on the thyroid gland uptake as well as the size of the gland. Thyroidal uptake and size should be determined by the physician prior to treatment and may be useful in calculating the therapeutic dose to be administered to the individual patient.
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
The recommended dose is 148 MBq to 370 MBq (4 mCi to 10 mCi) administered orally. Toxic nodular goiter may require a larger dose.
Treatment of Thyroid Carcinoma
The recommended dose is 1,100 MBq to 3,700 MBq (30 mCi to 100 mCi) administered orally. For subsequent ablation of metastases, the recommended dose is 3,700 MBq to 7,400 MBq (100 mCi to 200 mCi) administered orally.
Dilution and Preparation Instructions
Drug Handling
- Wear waterproof gloves throughout the entire handling and administration procedure.
- Make all transfers of radioactive solutions with an adequately shielded syringe or remote handling equipment and maintain adequate shielding around the vial during the useful life of the radioactive product.
Preparation of Dilute Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution
- Using the calibration date and radionuclide concentration on the label of the product vial, calculate the required volume to produce the necessary dose in MBq or mCi.
- Using a shielded syringe, remove the required volume.
- Using the shielded syringe, transfer the required volume to a suitably shielded receiving vial.
- Add the solution diluent to the receiving vial to produce a final dose of the desired volume.
- The recommended diluent is Purified Water USP containing 0.2% sodium thiosulfate USP as a reducing agent. Acidic diluents should not be used as they may cause the pH to drop below 7.5 and stimulate the volatilization of Iodine I 131 hydriodic acid.
- Present the dose in a shielded container for administration to the patient with a straw.
Preparation of Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules
- HICON® includes one LARGE gelatin capsule and one SMALL gelatin capsule for each dose prepared. Each LARGE capsule is empty, and each SMALL capsule contains approximately 300 mg of dibasic sodium phosphate anhydrous USP as the absorbing buffer.
- Using the calibration date and radionuclide concentration on the label of the product vial, calculate the required volume to produce the necessary dose in MBq or mCi.
- Open one LARGE capsule supplied with HICON® by pulling apart the capsule into two pieces as illustrated below:
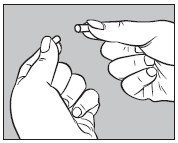
- Insert an unopened SMALL capsule supplied with HICON® into the bottom half of the empty LARGE capsule as illustrated below:
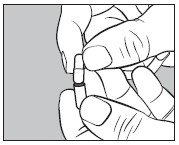
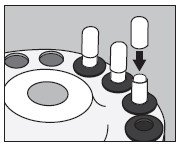
- With an appropriate syringe, withdraw the required volume of sodium iodide I 131 solution USP (maximum 150 microliters) from the vial as illustrated below:
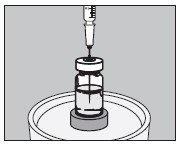
- Inject into the center of the SMALL capsule through the top as illustrated below and wait for 30 seconds to allow the solution to be absorbed by the absorbing buffer:
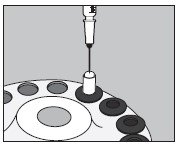
- Slip the upper half of the LARGE capsule over the bottom half to completely cover the SMALL capsule and push down gently until locked as illustrated below:
- Measure the patient dose in a suitable radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to administration.
- Prepared capsules may be stored in a suitable polypropylene container and placed inside a lead pot until use, within seven days.
Radiation Dosimetry
- The biokinetic modeling and radiation dose distributions associated with thyroid uptake of iodide I 131 depend on dietary intake of stable iodide and presume normal production of thyroid hormone. Table 1 shows a range of uptake percentages in an average adult (73.7 kg reference model). Table 1 is not intended to be used for treatment planning.
- For a thyroid blocked from iodide uptake in the production of hormones, the effective half-life of iodide I 131 is approximately 1.4 hours; for “low” to “high” uptake, the effective half-life of I 131 ranges from approximately 80 hours to 90 hours.
|
||||
| Organ |
Thyroid uptake of I 131 (% administered activity A0) 24 h after oral administration |
|||
| Blocked thyroid (0% A0) |
Low uptake† (16% A0) |
Medium uptake† (26% A0) |
High uptake† (36% A0) |
|
| Adrenals |
0.044 | 0.051 | 0.055 | 0.059 |
| Bone surfaces |
0.03 |
0.089 | 0.12 | 0.16 |
| Brain |
0.021 | 0.093 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| Breast |
0.02 | 0.038 | 0.048 | 0.058 |
| Gallbladder wall |
0.037 | 0.043 | 0.046 | 0.049 |
| Gastrointestinal tract |
||||
| Esophagus |
0.024 | 0.1 | 0.14 | 0.19 |
| Stomach wall |
0.87 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.66 |
| Small intestine wall |
0.035 | 0.033 | 0.032 | 0.032 |
| Colon wall |
0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| (Upper large intestine wall) |
0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| (Lower large intestine wall) |
0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| Heart wall |
0.062 | 0.089 | 0.1 | 0.12 |
| Kidneys |
0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| Liver |
0.05 | 0.093 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| Lungs |
0.053 | 0.1 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| Muscles |
0.026 | 0.084 | 0.12 | 0.15 |
| Ovaries |
0.038 | 0.037 | 0.036 | 0.035 |
| Pancreas |
0.06 | 0.064 | 0.066 | 0.068 |
| Red marrow |
0.031 | 0.072 | 0.095 | 0.12 |
| Salivary glands |
0.27 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.16 |
| Skin |
0.019 | 0.043 | 0.057 | 0.071 |
| Spleen |
0.064 | 0.069 | 0.072 | 0.075 |
| Testes |
0.025 | 0.024 | 0.023 | 0.22 |
| Thymus |
0.024 | 0.1 | 0.14 | 0.19 |
| Thyroid |
2.2 | 280‡ | 430‡ | 580‡ |
| Urinary bladder wall |
0.54 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.34 |
| Uterus |
0.045 | 0.042 | 0.04 | 0.038 |
| Remaining organs |
0.029 | 0.084 | 0.11 | 0.15 |
Effective dose per administered activity (mSv/MBq) |
0.28 | 14‡ | 22‡ | 29‡ |
More about Hicon (sodium iodide-i-131)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Side effects
- During pregnancy
- Generic availability
- Drug class: antithyroid agents
- Breastfeeding
Patient resources
Other brands
Professional resources
Related treatment guides
See also:
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.






