Uterine Fibroids
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
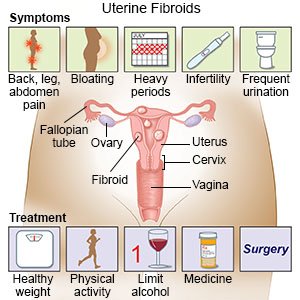
Uterine fibroids are growths found inside your uterus. Uterine fibroids are benign (not cancer) and may also be called myomas or leiomyomas. Uterine fibroids often appear in groups, or you may have only one. They can be small or large, and they can grow. Fibroids likely will not spread to other parts of your body. They may grow when you are pregnant and shrink after you no longer have a monthly period.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- Your heart begins to race, and you feel faint.
- You begin to pass large blood clots from your vagina.
Call your doctor or gynecologist if:
- Your symptoms do not go away, or they get worse.
- You feel weak and are more tired than usual.
- You do not feel like your bladder is empty after you urinate. You also may urinate small amounts more often.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Medicines that decrease hormones may help shrink your fibroids and decrease menstrual bleeding.
- Oral contraceptives can help control menstrual bleeding.
- NSAIDs help decrease swelling and pain or fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Prevent uterine fibroids:
- Maintain a healthy weight. Extra weight can increase your risk for fibroids. Talk to your healthcare provider about a healthy weight for you. Your provider can help you create a healthy weight loss plan, if needed.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Fruits and vegetables are especially important to help lower the risk for fibroid. Other healthy foods include whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Your healthcare provider or a dietitian can help you create a healthy meal plan.

- Limit or do not drink alcohol, as directed. Alcohol can increase your risk for fibroids. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 1½ ounces of liquor, or 5 ounces of wine. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you need help to quit drinking alcohol.
Follow up with your doctor or gynecologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Uterine Fibroids
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
