Induced Thyroid Disorders
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
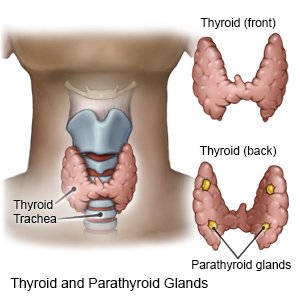
Induced thyroid disorders (ITD) are conditions that occur when certain medicines or treatments change the amount of hormone your thyroid makes. Your thyroid is a gland located at the front of your neck. Thyroid hormones regulate body temperature, heart rate, and weight gain or loss.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Medicines:
- Thyroid medicines replace, increase, or decrease your thyroid hormone levels. They may also help control your signs and symptoms. You may need other medicines to treat fast heartbeats, nervousness, or trembling.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
You may need to have regular blood tests if you take thyroid medicine. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Eat a variety of healthy foods:
If you have hyperthyroidism, you may need to eat more to give your body the extra energy it needs. If you have hypothyroidism, you may need to eat foods rich in iodine. Ask which foods are best for you and if you need to be on a special diet.
Drink liquids as directed:
Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- You have a fever.
- Your signs and symptoms return or become worse.
- You have pain, redness, and swelling in your muscles and joints.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have sudden chest pain or trouble breathing.
- Your heart is fluttering and you feel restless.
- You have slurred speech, problems with balance or walking, or cannot think clearly.
- You have swelling in your legs, ankles, or feet.
- You feel faint or had a seizure.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Induced Thyroid Disorders
Treatment options
Care guides
- Acquired Hypothyroidism in Children
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism in Pregnancy
- Hypothyroidism
- Induced Thyroid Disorders
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
