Diabetes and Exercise
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
How will exercise help me manage diabetes?
Physical activity, such as exercise, can help keep your blood sugar stable or make your body use insulin better. Activity can also lower your chance of getting heart disease and help you lose weight, if needed. Exercise can also lower your A1c or help keep it at a healthy level. Your diabetes care team will help you make an exercise plan. The plan will be based on the type of diabetes you have and your fitness level.
What are some tips to help me create and meet my exercise goals?
Your diabetes care provider may recommend counseling to help you meet these or other exercise goals:
- Set a goal to get at least 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of moderate to vigorous aerobic activity each week. Spread aerobic activity over at least 3 days, with no more than 2 days off in a row. Aerobic activity helps keep your heart healthy and strong. You can walk, bike, dance, swim, or garden for aerobic exercise. Try to do at least 10 minutes at a time, aiming for 30 minutes each day. Any activity is better than no activity at all. You can work up to your goals as your fitness improves. Your diabetes care team can help you make a step-by-step plan to reach your goals.

- Set a goal for strength training 2 to 3 times a week. Take at least 1 day off between sessions. Strength training helps you keep and build muscles.

- Older adults should also set a goal to do flexibility and balance training 2 to 3 times a week. In addition to strength training, yoga and tai chi can help improve strength, balance, and flexibility.


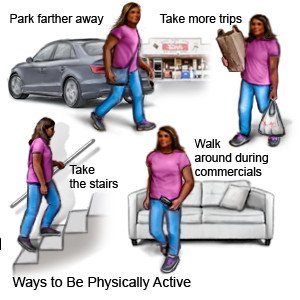
What are some other healthy activity tips?
- Do not sit for more than 30 minutes at a time. If you cannot walk around, at least stand up. This helps keep you active and your blood circulating. Try to stay active throughout the day.
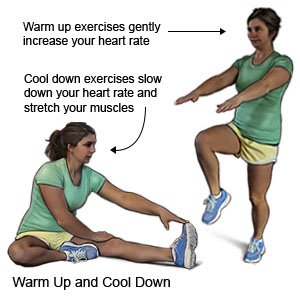
- Stretch before and after you exercise to help prevent injuries.
- Drink water or sugar-free liquids before, during, and after exercise. Ask your dietitian or provider which liquids are best for you.
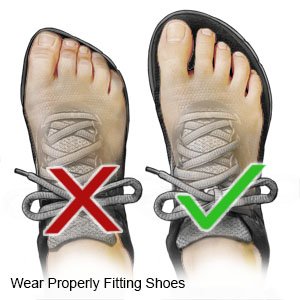
- Wear cotton socks and athletic shoes that fit well to protect your feet.
Related medications
What do I need to know about exercise and my blood sugar levels?
Check your blood sugar before and after exercise if you use insulin. Your provider may adjust your insulin or meal plan.
- If your blood sugar is high, check for ketones in your blood or urine before you exercise. Do not exercise if your blood sugar is high and you have ketones.
- If your blood sugar is less than 100 mg/dL, eat a small carbohydrate snack before you exercise. Examples are 4 to 6 crackers, ½ banana, 8 ounces (1 cup) of milk, or 4 ounces (½ cup) of juice.

Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have chest pain or shortness of breath.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have low blood sugar, and it doesn't improve with treatment. You may have trouble thinking, a pounding heartbeat, and sweating.
- You have high blood sugar above 240 mg/dL, and it does not go down within 15 minutes of treatment.
- You have blurred or double vision.
- You have fruity, sweet-smelling breath, or your breathing is shallow.
When should I call my doctor or diabetes care team?
- You have ketones in your blood or urine.
- You have a fever.
- Your blood sugar levels are higher than your target goals.
- You often have low blood sugar levels.
- Your skin is red, dry, warm, or swollen.
- You have a wound that does not heal.
- You have trouble coping with diabetes or feel anxious or depressed.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
