Adenoidectomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
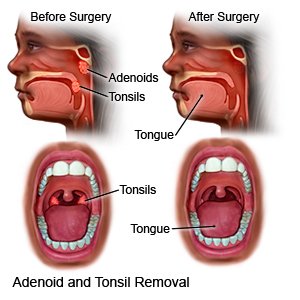
An adenoidectomy
is surgery to remove your adenoids. Adenoids are located at the back of your nasal passage. They may need to be removed if they are enlarged or if they cause frequent infections.
 |
How to prepare for an adenoidectomy:
- Your surgeon will talk to you about how to prepare for surgery. He or she may tell you not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of your surgery.
- Your surgeon will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of your surgery. He or she will tell you to stop taking aspirin 2 weeks before your surgery. You may be given an antibiotic through your IV to help prevent a bacterial infection.
- Arrange to have someone drive you home and stay with you after surgery.
What will happen during an adenoidectomy:
- You will be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and free from pain during surgery.
- Your healthcare provider will remove your adenoids through your mouth or nose. You will not have incisions or stitches.
What to expect after an adenoidectomy:
- You may be able to go home the same day of your surgery.
- You may have a low-grade fever for 1 to 2 days after your surgery.
- You may snore or breathe through your mouth because of the swelling in your throat. Your breathing will return to normal after the swelling goes down.
- You should not bleed from your mouth or nose after you go home. If you start to bleed from your mouth or nose, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
- You may have bad breath that is caused by scabs that form where your adenoids were removed.
- The thick, white scabs will fall off in small pieces 5 to 10 days after surgery.
Risks of an adenoidectomy:
You may have swallowing problems, vomiting, fever, throat pain, and ear pain. You may get an infection.
Related medications
Seek care immediately if:
- You see bright red blood in your saliva or coming from your nose.
- You have trouble breathing.
Call your surgeon or doctor if:
- You are vomiting.
- You have a fever higher than 102°F (39°C), or a low-grade fever for longer than 2 days.
- You have signs of dehydration, such as dark yellow urine, little or no urine, dry eyes or mouth, or increased thirst.
- You have severe pain, even after you take your medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Do not blow your nose for 1 week after surgery, or as directed. You may have heavy bleeding if scabs fall off when you blow your nose.
- Drink liquids as directed to prevent dehydration. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Eat soft, bland foods. Soft foods may be easier for you to eat when you have throat pain. Soft foods include applesauce, ice cream, scrambled eggs, or soups with soft vegetables, pasta, or rice. Do not eat spicy or citrus foods. These may irritate your throat and cause pain.
- Increase your activities slowly. Ask your healthcare provider when you can return to your daily activities.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause prevent healing after surgery. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
Follow up with your surgeon or doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Adenoidectomy
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
