Ozempic: Uses, How It Works, and Common Side Effects
Ozempic is used in adults for type 2 diabetes to improve blood sugar levels and also to lower the risk of stroke or heart attacks in adults with type 2 diabetes and who have heart disease. It should be used together with diet and exercise.
Video transcript
The Ozempic pen is an injection that you can administer to yourself once a week.
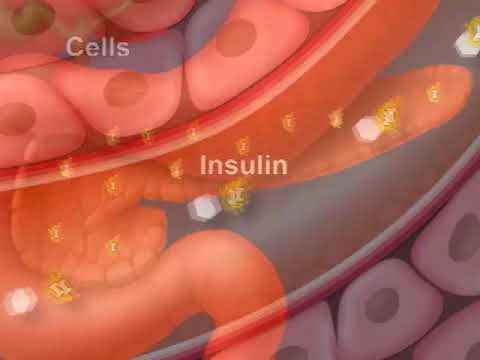
Ozempic works by helping the pancreas make more insulin, decreasing the amount of sugar your liver makes, and slowing the rate food passes through your body, making you feel full longer. This helps to lower blood sugar levels and lowers the risk of a major cardiovascular event. It may also reduce your appetite but it is not an FDA-approved weight loss medicine.
This medicine should not be used for type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Common side effects include low blood sugar (in people with type 2 diabetes), upset stomach, heartburn, burping, gas, bloating, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, loss of appetite, diarrhea, constipation, runny nose or sore throat, stomach flu symptoms or headache, dizziness and tiredness.
This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your healthcare provider.
More about Ozempic (semaglutide)
- Ozempic consumer information
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (1,604)
- Drug images
- Latest FDA alerts (5)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- Patient tips
- During pregnancy
- Support group
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: GLP-1 Agonists (Incretin Mimetics)
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Related treatment guides
Recommended videos
How to use an Ozempic Pen
Ozempic is a GLP-1 receptor agonist used to manage blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes in addition to diet and exercise.
How diabetes affects your blood sugar
See how diabetes, blood sugar and insulin are related.
Start at the Store: Prevent Foodborne Illness
By starting at the store with safe food handling practice, consumers can play a major role in preventing foodborne illness. In this new Consumer Update video, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides tips for keeping food safe while guiding viewers through a grocery store.
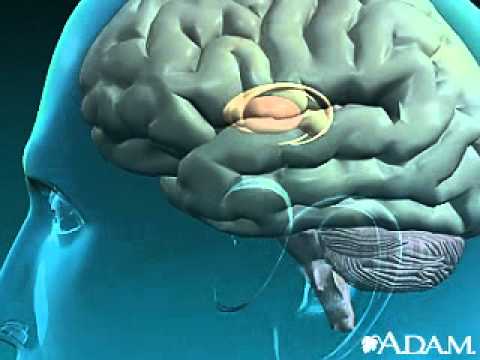
Athetosis resulting from basal ganglia injury
This animation illustrates the location of basal ganglia in the brain. Injury to the basal ganglia may result in athetosis (constant writhing movements of the body).
Simple squat and reach exercises with fitness ball
You can do many exercises with a fitness ball. See the simple squat and reach.
Browse by category
- ADHD
- Allergy
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Asthma
- Back Pain
- Beauty
- Birth Control
- Cancer
- Children's Health
- Diabetes
- Exercise & Fitness
- Fibromyalgia
- Foot Health
- Gout
- Headache
- Hearing
- Heart Disease
- Hypertension
- Injury
- Joint Pain
- Men's Health
- Pain
- Parkinson's Disease
- Pregnancy
- Psoriasis
- Sleep Disorders
- Stroke
- UTI
- Vision
- Women's Health
By medication
- Aimovig
- Ambien
- Amoxicillin
- Austedo
- Biktarvy
- Botox
- Breztri Aerosphere
- Caplyta
- Celebrex
- Cobenfy
- Cosentyx
- Dovato
- Ella
- Emgality
- Entyvio
- Evenity
- Gemtesa
- Humira
- Ibuprofen
- Intuniv
- Jaypirca
- Jornay PM
- Journavx
- Kesimpta
- Keytruda
- Kisunla
- Leqvio
- Lisinopril
- Lyrica
- Mounjaro
- Narcan
- Next Choice One Dose
- Nurtec ODT
- Olumiant
- Omvoh
- Opdivo
- Otezla
- Ozempic
- Padcev
- Plan B One-Step
- Prednisone
- Qulipta
- Quviviq
- Repatha
- Rexulti
- Skyrizi
- Syfovre
- Tagrisso
- Taltz
- Tepezza
- Tramadol
- Trelegy Ellipta
- Trintellix
- Ubrelvy
- Ultomiris
- Verzenio
- Victoza
- Vraylar
- Vumerity
- Vyepti
- Vyvanse
- Xcopri
- Xolair
- Zepbound
- Zoloft