Difluprednate Eye Drops: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: ophthalmic emulsion
Drug class: Ophthalmic steroids
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 25, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
DIFLUPREDNATE ophthalmic emulsion 0.05%
Initial U.S. approval: 2008
Indications and Usage for Difluprednate Eye Drops
Difluprednate Eye Drops Dosage and Administration
- For the treatment of inflammation and pain associated with ocular surgery instill one drop into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye 4 times daily beginning 24 hours after surgery and continuing throughout the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period, followed by 2 times daily for a week and then a taper based on the response. ( 2.1)
- For the treatment of endogenous anterior uveitis instill one drop into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye 4 times daily for 14 days followed by tapering as clinically indicated. ( 2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion contains 0.05% difluprednate, as a sterile preserved ophthalmic emulsion for topical ophthalmic use only. ( 3)
Contraindications
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion, as with other ophthalmic corticosteroids, is contraindicated in most active viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, and varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye and fungal diseases of ocular structures. ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Intraocular pressure (IOP) increase – Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision. If this product is used for 10 days or longer, IOP should be monitored. ( 5.1)
- Cataracts – Use of corticosteroids may result in posterior subcapsular cataract formation. ( 5.2)
- Delayed healing – The use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical steroids. The initial prescription and renewal of the medication order beyond 28 days should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining. ( 5.3)
- Bacterial infections – Prolonged use of corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In acute purulent conditions, steroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection. If signs and symptoms fail to improve after 2 days, the patient should be re-evaluated. ( 5.4)
- Viral infections – Employment of a corticosteroid medication in the treatment of patients with a history of herpes simplex requires great caution. Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex). ( 5.5)
- Fungal infections – Fungal infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term local steroid application. Fungus invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where a steroid has been used or is in use. ( 5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Upsher-Smith Laboratories, LLC at 1-855-899-9180 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Difluprednate Eye Drops
1.1 Ocular Surgery
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion 0.05%, a topical corticosteroid, is indicated for the treatment of inflammation and pain associated with ocular surgery.
2. Difluprednate Eye Drops Dosage and Administration
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion contains 0.05% difluprednate as a sterile preserved emulsion for topical ophthalmic administration.
4. Contraindications
The use of difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion, as with other ophthalmic corticosteroids, is contraindicated in most active viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, and varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye and fungal disease of ocular structures.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 IOP Increase
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision. Steroids should be used with caution in the presence of glaucoma. If this product is used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be monitored.
5.3 Delayed Healing
The use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical steroids. The initial prescription and renewal of the medication order beyond 28 days should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining.
5.4 Bacterial Infections
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In acute purulent conditions, steroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection. If signs and symptoms fail to improve after 2 days, the patient should be re-evaluated.
5.5 Viral Infections
Employment of a corticosteroid medication in the treatment of patients with a history of herpes simplex requires great caution. Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex).
5.6 Fungal Infections
Fungal infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term local steroid application. Fungus invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where a steroid has been used or is in use. Fungal culture should be taken when appropriate.
5.7 Topical Ophthalmic Use Only
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion is not indicated for intraocular administration.
5.8 Contact Lens Wear
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion should not be instilled while wearing contact lenses. Remove contact lenses prior to instillation of difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion. The preservative in difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Lenses may be reinserted after 10 minutes following administration of difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious reactions are found elsewhere in the labeling:
- Elevated intraocular pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Posterior subcapsular cataract formation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Secondary ocular infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Perforation of the globe [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Ocular Surgery
Ocular adverse reactions occurring in 5% to 15% of subjects in clinical studies with difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion included corneal edema, ciliary and conjunctival hyperemia, eye pain, photophobia, posterior capsule opacification, anterior chamber cells, anterior chamber flare, conjunctival edema, and blepharitis. Other ocular adverse reactions occurring in 1% to 5% of subjects included reduced visual acuity, punctate keratitis, eye inflammation, and iritis. Ocular adverse reactions occurring in < 1% of subjects included application site discomfort or irritation, corneal pigmentation and striae, episcleritis, eye pruritis, eyelid irritation and crusting, foreign body sensation, increased lacrimation, macular edema, sclera hyperemia, and uveitis. Most of these reactions may have been the consequence of the surgical procedure.
6.2 Endogenous Anterior Uveitis
A total of 200 subjects participated in the clinical trials for endogenous anterior uveitis, of which 106 were exposed to difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion. The most common adverse reactions of those exposed to difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion occurring in 5% to 10% of subjects included blurred vision, eye irritation, eye pain, headache, increased IOP, iritis, limbal and conjunctival hyperemia, punctate keratitis, and uveitis. Adverse reactions occurring in 2% to 5% of subjects included anterior chamber flare, corneal edema, dry eye, iridocyclitis, photophobia, and reduced visual acuity.
Related/similar drugs
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C. Difluprednate has been shown to be embryotoxic (decrease in embryonic body weight and a delay in embryonic ossification) and teratogenic (cleft palate and skeletal anomalies) when administered subcutaneously to rabbits during organogenesis at a dose of 1 to 10 mcg/kg/day. The no-observed-effect-level (NOEL) for these effects was 1 mcg/kg/day, and 10 mcg/kg/day was considered to be a teratogenic dose that was concurrently found in the toxic dose range for fetuses and pregnant females. Treatment of rats with 10 mcg/kg/day subcutaneously during organogenesis did not result in any reproductive toxicity, nor was it maternally toxic. At 100 mcg/kg/day after subcutaneous administration in rats, there was a decrease in fetal weights and delay in ossification, and effects on weight gain in the pregnant females. It is difficult to extrapolate these doses of difluprednate to maximum daily human doses of difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion, since difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion is administered topically with minimal systemic absorption, and difluprednate blood levels were not measured in the reproductive animal studies. However, since use of difluprednate during human pregnancy has not been evaluated and cannot rule out the possibility of harm, difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the embryo or fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether topical ophthalmic administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in breast milk. Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. Caution should be exercised when difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion was evaluated in a 3-month, multicenter, double-masked trial in 79 pediatric patients (39 difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion; 40 prednisolone acetate) 0 to 3 years of age for the treatment of inflammation following cataract surgery. A similar safety profile was observed in pediatric patients comparing difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion to prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension, 1%.
11. Difluprednate Eye Drops Description
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion 0.05% is a sterile, topical anti-inflammatory corticosteroid for ophthalmic use. The chemical name is 6α,9difluoro-11β,17,21trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 21-acetate 17-butyrate (CAS number 23674-86-4). Difluprednate is represented by the following structural formula:
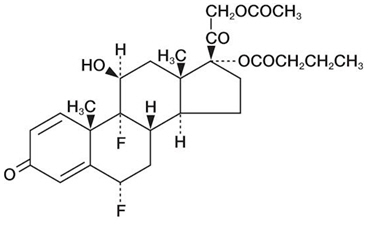
Difluprednate has a molecular weight of 508.56, and the empirical formula is C 27H 34F 2O 7.
Each mL contains: ACTIVE: difluprednate 0.5 mg (0.05%); INACTIVE: boric acid, castor oil, edetate disodium, glycerin, polysorbate 80, sodium acetate, sodium hydroxide (to adjust the pH to 5.2 to 5.8), and water for injection. The emulsion is essentially isotonic with a tonicity of 304 to 411 mOsm/kg. PRESERVATIVE: sorbic acid 0.1%.
12. Difluprednate Eye Drops - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Corticosteroids inhibit the inflammatory response to a variety of inciting agents and may delay or slow healing. They inhibit edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilation, leukocyte migration, capillary proliferation, fibroblast proliferation, deposition of collagen, and scar formation associated with inflammation. There is no generally accepted explanation for the mechanism of action of ocular corticosteroids. However, corticosteroids are thought to act by the induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins, collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotreines by inhibiting the release of their common precursor arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2. Difluprednate is structurally similar to other corticosteroids.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Difluprednate undergoes deacetylation in vivoto 6α, 9-difluoroprednisolone 17-butyrate (DFB), an active metabolite of difluprednate. Clinical pharmacokinetic studies of difluprednate after repeat ocular instillation of 2 drops of difluprednate (0.01% or 0.05%) four times per day for 7 days showed that DFB levels in blood were below the quantification limit (50 ng/mL) at all time points for all subjects, indicating the systemic absorption of difluprednate after ocular instillation of difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion is limited.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Difluprednate was not genotoxic in vitroin the Ames test, and in cultured mammalian cells CHL/IU (a fibroblastic cell line derived from the lungs of newborn female Chinese hamsters). An in vivomicronucleus test of difluprednate in mice was also negative. Treatment of male and female rats with subcutaneous difluprednate up to 10 mcg/kg/day prior to and during mating did not impair fertility in either gender. Long term studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of difluprednate.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In multiple studies performed in rodents and non-rodents, subchronic and chronic toxicity tests of difluprednate showed systemic effects such as suppression of body weight gain; a decrease in lymphocyte count; atrophy of the lymphatic glands and adrenal gland; and for local effects, thinning of the skin; all of which were due to the pharmacologic action of the molecule and are well known glucocorticosteroid effects. Most, if not all of these effects were reversible after drug withdrawal. The NOEL for the subchronic and chronic toxicity tests were consistent between species and ranged from 1 to 1.25 mcg/kg/day.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Ocular Surgery
Clinical efficacy was evaluated in 2 randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled trials in which subjects with an anterior chamber cell grade ≥ "2" (a cell count of 11 or higher) after cataract surgery were assigned to difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion or placebo (vehicle) following surgery. One drop of difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion or vehicle was self-instilled either 2 times per day or 4 times per day for 14 days, beginning the day after surgery. The presence of complete clearing (a cell count of 0) was assessed 3, 8 and 15 days post-surgery using a slit lamp binocular microscope. In the intent-to-treat analyses of both studies, a significant benefit was seen in the 4 times per day (QID) difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion-treated group in ocular inflammation, at days 8 and 15, and reduction of pain, at days 3, 8 and 15, when compared with placebo. The consolidated clinical trial results are provided below.
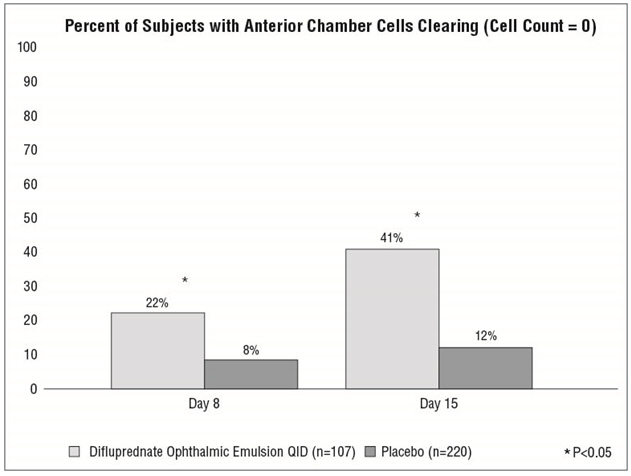
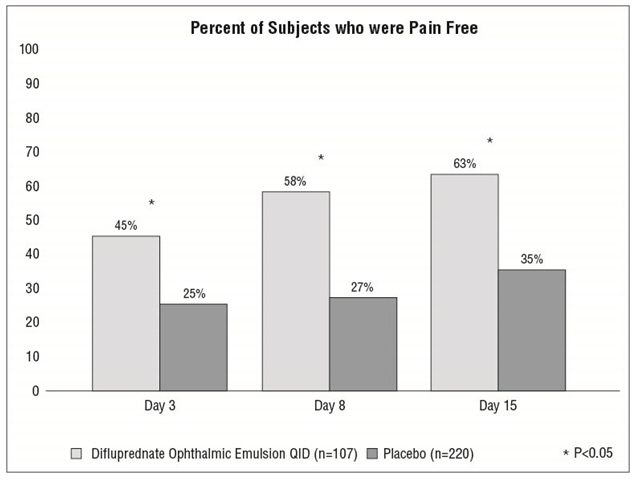
14.2 Endogenous Anterior Uveitis
Clinical efficacy was evaluated in two randomized, double masked active controlled trials in which patients who presented with endogenous anterior uveitis were treated with either difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion 4 times daily or prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension, 1%, 8 times daily for 14 days. Both studies demonstrated that difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion was equally effective as prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension, 1% in treating subjects with endogenous anterior uveitis.
| Study 1 time point | Difluprednate Ophthalmic Emulsion | Prednisolone Acetate | Difference † |
| N=57 | N=53 | (95% CI) | |
| Baseline | 2.6 | 2.5 | 0.0 (-0.22, 0.28) |
| Day 3 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -0.1 (-0.35, 0.25) |
| Day 7 | -1.6 | -1.5 | -0.0 (-0.31, 0.25) |
| Day 14 | -2.0 | -1.8 | -0.2 (-0.46, 0.10) |
| Day 21 | -2.2 | -1.9 | -0.3 (-0.53, 0.01) |
| Day 28 | -2.2 | -2.1 | -0.1 (-0.37, 0.18) |
| Day 35 | -2.1 | -2.0 | -0.1 (-0.39, 0.20) |
| Day 42 | -2.1 | -2.1 | 0.0 (-0.27, 0.34) |
| Study 2 time point | Difluprednate Ophthalmic Emulsion | Prednisolone Acetate | Difference † |
| N=50 | N=40 | (95% CI) | |
| Baseline | 2.4 | 2.4 | 0.0 (-0.21, 0.29) |
| Day 3 | -0.9 | -0.9 | -0.0 (-0.34, 0.25) |
| Day 7 | -1.7 | -1.6 | -0.1 (-0.35, 0.21) |
| Day 14 | -1.9 | -1.8 | -0.1 (-0.34, 0.20) |
| Day 21 | -2.0 | -2.0 | 0.0 (-0.25, 0.28) |
| Day 28 | -2.0 | -2.0 | 0.0 (-0.21, 0.26) |
| Day 35 | -2.1 | -2.0 | -0.1 (-0.32, 0.16) |
| Day 42 | -2.0 | -1.9 | -0.1 (-0.36, 0.24) |
16. How is Difluprednate Eye Drops supplied
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion 0.05% is a sterile, aqueous topical ophthalmic emulsion supplied in an opaque plastic bottle with a controlled drop tip and a pink cap in the following sizes:
| 5 mL in a 5 mL bottle (NDC 0832-6054-05) |
17. Patient Counseling Information
17.1 Risk of Contamination
This product is sterile when packaged. Advise patients not to allow the dropper tip to touch any surface, as this may contaminate the emulsion.
Use of the same bottle for both eyes is not recommended with topical eye drops that are used in association with surgery.
17.2 Risk of Secondary Infection
If pain develops, or if redness, itching, or inflammation becomes aggravated, advise patients to consult a physician.
17.3 Contact Lens Wear
Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion should not be instilled while wearing contact lenses. Advise patients to remove contact lenses prior to instillation of difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion. The preservative in difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Lenses may be reinserted after 10 minutes following administration of difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion.
| DIFLUPREDNATE
difluprednate emulsion |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Upsher-Smith Laboratories, LLC (047251004) |
More about difluprednate ophthalmic
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (24)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: ophthalmic steroids
- Breastfeeding
- En español

