Angiotensin II Injection: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: injection
Drug class: Vasopressors
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 9, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ANGIOTENSIN II Injection for Intravenous Infusion
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
Indications and Usage for Angiotensin II Injection
Angiotensin II Injection is a vasoconstrictor to increase blood pressure in adults with septic or other distributive shock. (1) (1)
Angiotensin II Injection Dosage and Administration
Dilute Angiotensin II Injection in 0.9% sodium chloride prior to use. See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration of injection. Diluted solution may be stored at room temperature or under refrigeration and should be discarded after 24 hours. Angiotensin II Injection must be administered as an intravenous infusion. (2.1)
• Start Angiotensin II Injection intravenously at 20 nanograms (ng)/kg/min. Titrate as frequently as every 5 minutes by increments of up to 15 ng/kg/min as needed. During the first 3 hours, the maximum dose should not exceed 80 ng/kg/min. Maintenance dose should not exceed 40 ng/kg/min. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 2.5 mg/mL in a vial. (3)
Contraindications
None (4.1) (4)
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 10% in Angiotensin II treated patients were thromboembolic events. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gland Pharma at (609)-250‐7990 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Revised: 9/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Angiotensin II Injection
Angiotensin II Injection increases blood pressure in adults with septic or other distributive shock.
2. Angiotensin II Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1. Preparation
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Angiotensin II Injection must be administered as an intravenous infusion. Angiotensin II Injection must be diluted in 0.9% sodium chloride prior to
use. Dilute the contents of one vial of Angiotensin II Injection in 0.9% saline to achieve a final concentration of 5,000 ng/mL or 10,000 ng/mL.
Discard vial and any unused portion of the drug product after use.
Table 1: Preparation of Diluted Solution
| Fluid Restricted?
| Vial Strength
| Withdraw Amount
(mL) | Infusion Bag Size (mL)
| Final Concentration (ng/mL)
|
| No | 2.5 mg/mL | 1 | 500 | 5,000 |
| Yes | 2.5 mg/mL | 1 | 250 | 10,000 |
Diluted solution may be stored at room temperature or under refrigeration. Discard prepared solution after 24 hours at room temperature or under refrigeration.
2.2. Administration
The recommended starting dosage of Angiotensin II Injection is 20 nanograms (ng)/kg/min via continuous intravenous infusion. Administration through a central venous line is recommended.
Monitor blood pressure response and titrate Angiotensin II Injection every 5 minutes by increments of up to 15 ng/kg/min as needed to achieve or maintain target blood pressure. Do not exceed 80 ng/kg/min during the first 3 hours of treatment. Maintenance doses should not exceed 40 ng/kg/min. Doses as low as 1.25 ng/kg/min may be used.
Once the underlying shock has sufficiently improved, down-titrate every 5 to 15 minutes by increments of up to 15 ng/kg/min based on blood pressure.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 2.5 mg/mL angiotensin II in a vial.
Angiotensin II Injection is a clear, aqueous solution.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk for Thrombosis
The safety of Angiotensin II was evaluated in 321 adults with septic or other distributive shock in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, ATHOS-3. There was a higher incidence of arterial and venous thrombotic and thromboembolic events in patients who received Angiotensin II compared to placebo-treated patients in the ATHOS-3 study (13% vs. 5%). The major imbalance was in deep venous thromboses. Use concurrent venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
ATHOS-3
The safety of Angiotensin II was evaluated in ATHOS-3 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Patients in ATHOS-3 were receiving other vasopressors in addition to Angiotensin II or placebo, which were titrated to effect on mean arterial pressure (MAP).
Table 2 summarizes adverse reactions with an incidence of at least 4% among patients treated with Angiotensin II and with a rate of at least 1.5% higher with Angiotensin II than with placebo.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 4% of Patients Treated with Angiotensin II and ≥ 1.5% More Often than in Placebo-treated Patients in ATHOS-3
| Adverse Event
| Angiotensin II N=163
| Placebo
N=158 |
| Thromboembolic eventsa
| 21 (12.9%) | 8 (5.1%) |
| Deep vein thrombosis | 7 (4.3%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Thrombocytopenia | 16 (9.8%) | 11 (7.0%) |
| Tachycardia | 14 (8.6%) | 9 (5.7%) |
| Fungal infection | 10 (6.1%) | 2 (1.3%) |
| Delirium | 9 (5.5%) | 1 (0.6%) |
| Acidosis | 9 (5.5%) | 1 (0.6%) |
| Hyperglycemia | 7 (4.3%) | 4 (2.5%) |
| Peripheral ischemia | 7 (4.3%) | 4 (2.5%) |
a Including arterial and venous thrombotic events
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The published data on angiotensin II use in pregnant women are not sufficient to determine a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Angiotensin II.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Septic or other distributive shock is a medical emergency that can be fatal if left untreated. Delaying treatment in pregnant women with hypotension associated with septic or other distributive shock is likely to increase the risk of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality.
8.2. Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether Angiotensin II is present in human milk. No data are available on the effects of angiotensin II on the breastfed child or the effects on milk production.
10. Overdosage
Overdose of Angiotensin II would be expected to result in hypertension, necessitating close monitoring and supportive care. Effects are expected to be brief because the half-life of angiotensin II is less than one minute.
11. Angiotensin II Injection Description
Angiotensin II is a naturally occurring peptide hormone of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. Angiotensin II Injection is a sterile, aqueous solution of synthetic human angiotensin II for intravenous administration by infusion. Each 1 mL of Angiotensin II Injection contains 2.5 mg angiotensin II equivalent to an average of 2.9 mg angiotensin II acetate, 25 mg mannitol, and Water for Injection adjusted with sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid to pH of 5.5.
The chemical name of the synthetic angiotensin II acetate is L-Aspartyl-L-arginyl-L-valyl-L-tyrosyl-L-isoleucyl-L-histidyl-L-prolyl-L-phenylalanine, acetate salt. The counter ion acetate is present in a non-stoichiometric ratio. It is a white to off-white powder, soluble in water.
The structure of angiotensin II acetate is shown below.
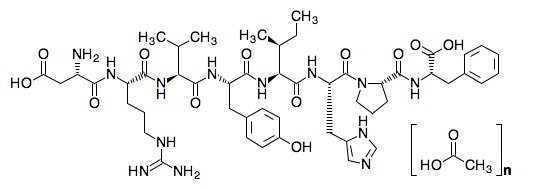
Molecular formula: C50H71N13O12 • (C2H4O2) n; (n= number of acetate molecules; theoretical n= 3)
Average molecular weight: 1046.2 (as free base).
12. Angiotensin II Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Angiotensin II raises blood pressure by vasoconstriction and increased aldosterone release.
Direct action of angiotensin II on the vessel wall is mediated by binding to the G-protein coupled-angiotensin II receptor type 1 on vascular smooth muscle cells, which stimulates Ca2+ /calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of myosin and causes smooth muscle contraction.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
For the 114 (70%) patients in the Angiotensin II arm who reached the target MAP at Hour 3, the median time to reach the target MAP endpoint was approximately 5 minutes. Angiotensin II is titrated to effect for each individual patient.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following intravenous infusion of angiotensin II in adults with septic or other distributive shock, serum levels of angiotensin II are similar at Baseline and Hour 3 after intravenous infusion. After 3 hours of treatment, however, the serum level of angiotensin I (the angiotensin II precursor peptide) is reduced by approximately 40%.
Distribution:
No specific studies were conducted that examined the distribution of Angiotensin II.
Metabolism and Excretion:
No specific studies were conducted that examined the metabolism and excretion of Angiotensin II.
The plasma half-life of IV administered angiotensin II is less than one minute. It is metabolized by aminopeptidase A and angiotensin converting enzyme 2 to angiotensin-(2-8) [angiotensin III] and angiotensin-(1-7), respectively in plasma, erythrocytes and many of the major organs (i.e., intestine, kidney, liver and lung). Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1) mediated activity of angiotensin III is approximately 40% of angiotensin II; however, aldosterone synthesis activity is similar to angiotensin II. Angiotensin-(1-7) exerts the opposite effects of angiotensin II on AT1 receptors and causes vasodilation.
Specific Populations
No formal pharmacokinetic studies were conducted with Angiotensin II in the following specific populations.
Renal Impairment
The clearance of angiotensin II is not dependent on renal function. Therefore, the pharmacokinetics of Angiotensin II are not expected to be influenced by renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
The clearance of angiotensin II is not dependent on hepatic function. Therefore, the pharmacokinetics of Angiotensin II are not expected to be influenced by hepatic impairment.
Age
The effect of age was analyzed in the 163 patients receiving Angiotensin II in ATHOS-3. There were no significant differences in pharmacokinetics between age groups (< 65 years / ≥ 65 years).
Male and Female Patients
The effect of sex was analyzed in the 163 patients receiving Angiotensin II in ATHOS-3. There were no significant differences in pharmacokinetics between male and female patients.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No genetic toxicity studies have been conducted with Angiotensin II. No carcinogenicity or fertility studies with Angiotensin II have been conducted in animals.
13.2. Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
No animal toxicology studies were conducted with Angiotensin II.
13.3. Safety Pharmacology
In a cardiovascular safety pharmacology study in normotensive dogs, Angiotensin II doses of 150, 450, and 1800 ng/kg (5, 15 and 60 ng/kg/min) were infused intravenously for 30 minutes each. At ≥ 450 ng/kg, Angiotensin II caused significantly elevated MAP and systemic vascular resistance, as expected. The 1800 ng/kg dose also caused increased heart rate, increased systemic vascular resistance, increased left ventricular systolic and end-diastolic pressures, and PR interval prolongation. Angiotensin II did not significantly alter respiratory rate or cause electrocardiographic changes in QRS duration or QTc.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1. ATHOS-3
The Angiotensin II for the Treatment of High-Output Shock (ATHOS-3) trial was a double-blind study in which 321 adults with septic or other distributive shock who remained hypotensive despite fluid and vasopressor therapy were randomized 1:1 to Angiotensin II or placebo. Doses of Angiotensin II or placebo were titrated to a target mean arterial pressure (MAP) of ≥ 75 mmHg during the first 3 hours of treatment while doses of other vasopressors were maintained. From Hour 3 to Hour 48, Angiotensin II or placebo were titrated to maintain MAP between 65 and 70 mmHg while reducing doses of other vasopressors. The primary endpoint was the percentage of subjects who achieved either a MAP ≥ 75 mmHg or a ≥ 10 mmHg increase in MAP without an increase in baseline vasopressor therapy at 3 hours.
91% of subjects had septic shock; the remaining subjects had other forms of distributive shock such as neurogenic shock. At the time of study drug administration, 97% of subjects were receiving norepinephrine, 67% vasopressin, 15% phenylephrine, 13% epinephrine, and 2% dopamine. 83% of subjects had received two or more vasopressors and 47% three or more vasopressors prior to study drug administration. 61% of subjects were male, 80% were White, 10% were Black, and 10% were other races. The median age of subjects was 64 years (range: 22-89 years). Patients requiring high doses of steroids, patients with a history of asthma or bronchospasm, and patients with Raynaud’s syndrome were not included.
The primary endpoint was achieved by 70% of patients randomized to Angiotensin II compared to 23% of placebo subjects; p < 0.0001 (a treatment effect of 47%). Figure 1 shows the results in all patients and in selected subgroups.
Figure 1: ATHOS-3: Primary Endpoint – Overall Result and Results in Selected Subgroups
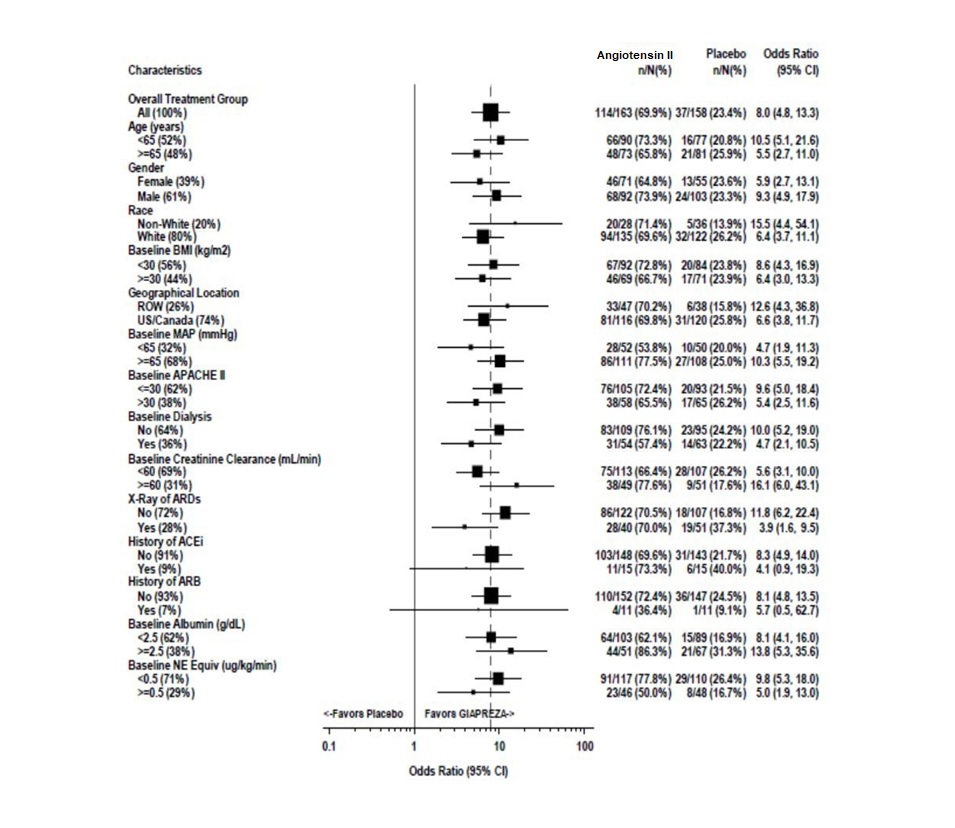
NE Equiv = norepinephrine equivalent dose: the sum of all vasopressors doses with each vasopressor dose converted to the clinically equivalent norepinephrine dose
Note: The figure above presents effects in various subgroups, all of which are baseline characteristics. The 95% confidence limits that are shown do not take into account the number of comparisons made, and may not reflect the effect of a particular factor after adjustment for all other factors. Apparent homogeneity or heterogeneity among groups should not be over-interpreted.
In the Angiotensin II -treated group, the median time to reach the target MAP endpoint was 5 minutes. The effect on MAP was sustained for at least the first three hours of treatment. The median dose of Angiotensin II was 10 ng/kg/min at 30 minutes. Of the 114 responders at Hour 3, only 2 (1.8%) received more than 80 ng/kg/min.
Patients were not necessarily on maximum doses of other vasopressors at the time of randomization. The effect of Angiotensin II when added to maximum doses of other vasopressors is unknown.
Mortality through Day 28 was 46% on Angiotensin II and 54% on placebo (hazard ratio 0.78; 95% confidence interval 0.57 – 1.07).
16. How is Angiotensin II Injection supplied
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Carton label
NDC 68083-553-01
1 x 1 mL single-dose vial
Angiotensin II
Injection
2.5 mg/mL
Must dilute prior to
intravenous infusion.
Rx Only
Single-dose vial
Discard unused portion

Container label
1 mL single-dose vial
NDC 68083-553-01
Angiotensin II
Injection
2.5 mg/mL
Must dilute prior to
intravenous infusion.
Discard unused portion
Rx Only
| ANGIOTENSIN II
angiotensin ii injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gland Pharma Limited (918601238) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLAND PHARMA LIMITED | 858971074 | ANALYSIS(68083-553) , LABEL(68083-553) , MANUFACTURE(68083-553) , PACK(68083-553) | |
More about angiotensin II
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: vasopressors
