Prostate Gland Needle Biopsy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
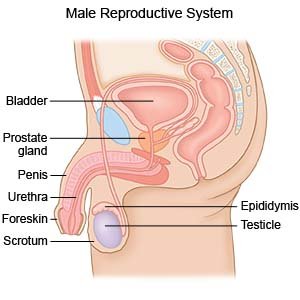
A prostate gland needle biopsy is a procedure to remove samples of tissue from your prostate gland. The prostate is a gland located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra (tube that carries urine out of the body).
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Before your procedure:
- Informed consent is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
- An IV is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
- An enema may be given to help empty your bowels.
- General anesthesia may be given to keep you asleep and free from pain during surgery. You may instead be given spinal anesthesia to numb the surgery area. You may still feel pressure or pushing during surgery, but you will not feel any pain. Numbing gel or shots of numbing medicine may also be given near your prostate to numb the area.
During your procedure:
A small tube with a camera will be put into your rectum to show pictures of your prostate on a monitor. A biopsy needle will be put in through your rectum into your prostate gland. A small sample of tissue will be removed with the needle. Your surgeon may take between 6 to 12 samples of tissue from different areas of your prostate gland. A new needle will be used to take each tissue sample. Each sample will be sent to a lab.
Related medications
After your procedure:
You will be able to rest until you are fully awake. Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Once healthcare providers see that you are not having any problems, you may be able to go home.
RISKS:
You may bleed more than expected or get an infection. Your bladder, prostate, urethra, and nearby tissues or organs may be damaged during the procedure. You may have bruises on your rectum. You may have blood in your urine, bowel movements, or semen. If you have prostate cancer, the biopsy may not show the cancer. The biopsy may show cancer when there is no cancer in your prostate gland. You may need another prostate biopsy.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
