Peanut Allergy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
A peanut allergy
is a condition that develops because your immune system overreacts to peanuts. You may have a reaction right away, or up to 2 hours after you have peanut. A peanut allergy is usually permanent. A family history of peanut allergy may increase your risk.
Signs and symptoms
of a peanut allergy range from mild to severe (anaphylaxis). Any of the following can develop minutes to hours after you eat peanut. Your reaction may change each time you are exposed.
- Mild symptoms include a rash, hives, or itching around the eyes, mouth, or chin. You may also have a runny or stuffy nose. Your baby may have colic.
- Anaphylaxis symptoms need immediate emergency care. Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Throat tightness, trouble breathing, or wheezing
- Tingling in your hands or feet, or feeling dizzy or faint
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or blood in your bowel movements
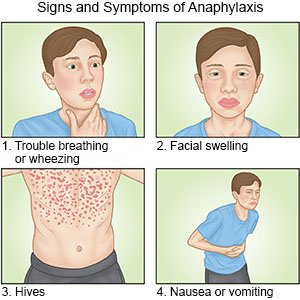
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis,
such as trouble breathing, swelling in your mouth or throat, or wheezing. You may also have itching, a rash, hives, or feel like you are going to faint.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have itching or hives that spread all over your body.
Call your doctor or allergy specialist if:
- You have new or worsening rashes, hives, or itching.
- You have an upset stomach or are vomiting.
- You have stomach cramps or diarrhea.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Steps to take for signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis:
Your healthcare provider will tell you about symptoms of an anaphylactic reaction. Give yourself epinephrine at the first sign of a severe reaction. Signs include trouble breathing or swallowing, swelling in your mouth or throat, a change in your voice, or wheezing.
- Immediately give 1 shot of epinephrine only into the outer thigh muscle. Hold the shot in place for up to 10 seconds before you remove it. This helps make sure all of the epinephrine is delivered.
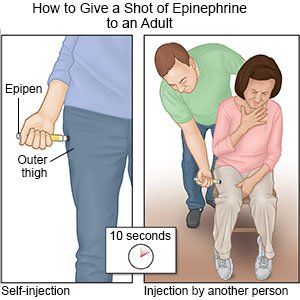
- Call 911 and go to the emergency department, even if the shot improved symptoms. Do not drive yourself. Bring the used epinephrine shot with you.
Treatment:
The main treatment for a peanut allergy is not to have any peanut products. Your healthcare provider or dietitian can help you create a meal plan that does not include peanut products. You may need any of the following:
- Antihistamines decrease mild symptoms such as itching or a rash.
- Epinephrine is used to treat severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Manage a peanut allergy:
- Read all food labels. Read the label each time you buy the food to make sure the ingredients have not changed. Look for peanuts in the list of ingredients. Also check the label for warnings that peanuts were processed in the same place where the food was made.
- Be careful with baked foods. Many baked foods, such as cookies and cakes, contain peanuts. Ask about foods you buy at a bakery that are not packaged.
- Do not try to remove peanuts from a food. For example, do not eat bread after peanut butter was scraped off. Do not eat trail mix even after peanuts are removed. Once peanut touches a food, it can cause an allergic reaction if you eat it.
- Prevent cross-contamination. Do not use kitchen items that have touched peanut. For example, do not use a knife to cut a food after it was used to spread peanut butter. This is called cross-contamination, and it can still cause an allergic reaction. Keep all utensils, cutting boards, and dishes that touched peanut separate from other equipment. Use hot, soapy water to wash all kitchen items that touch food. Wash the items after each time they touch food as you cook.
- Do not eat tree nuts unless your healthcare provider says it is okay. Peanuts are not the same as tree nuts such as cashews and almonds. Peanuts are legumes, similar to dried beans. Your healthcare provider may tell you not to eat tree nuts. Tree nuts and peanuts are also often processed in the same facilities.
Safety precautions to take if you are at risk for anaphylaxis:
- Tell others about your allergy. Tell family members, friends, and coworkers. Tell your child's school officials, teachers, and babysitters. Your child's school or daycare center can help make sure your child is not exposed to peanut. This includes making sure your child does not eat baked foods brought into the classroom to celebrate a holiday or birthday. Ask if your child should carry epinephrine at all times. Some schools keep epinephrine in a medical office. Make sure others know what to do in case of an anaphylactic reaction.
- Keep 2 shots of epinephrine with you at all times. You may need a second shot if the first dose of epinephrine does not help you or if your symptoms return. Your healthcare provider can show you and family members how to give the shot. Check the expiration date every month and replace it before it expires.
- Create an action plan. Your healthcare provider can help you create a written plan that explains the allergy and an emergency plan to treat a reaction. The plan explains when to give a second epinephrine shot if symptoms return or do not improve after the first. Give copies of the action plan and emergency instructions to family members, work and school staff, and daycare providers. Show them how to give a shot of epinephrine. Update the plan as the allergy changes.
- Be careful when you exercise. If you have had exercise-induced anaphylaxis, do not exercise right after you eat. Stop exercising right away if you start to develop any signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis. You may first feel tired, warm, or have itchy skin. Hives, swelling, and severe breathing problems may develop if you continue to exercise.
- Carry medical alert identification. Wear jewelry or carry a card that says you have a peanut allergy. Ask your healthcare provider where to get these items.
- Talk to servers or managers at restaurants when you eat out. Tell the server or manager about the peanut allergy before you order. Ask about ingredients in the dish you want to order. Ask how food is prepared. The restaurant may use equipment to cook your dish that has also touched peanut. Ask if the dish comes with a peanut sauce or if peanuts are used to thicken the food.
- Be careful with food and eating utensils. Do not share utensils or food. Wash your hands before and after meals. An allergic reaction usually will not happen if you only touch peanuts. You may have a reaction if you kiss a person who has recently eaten peanut protein.
Follow up with your doctor or allergy specialist as directed:
You may need to see specialists for ongoing care. Your healthcare provider may want to test you regularly to see if the food allergy changes. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during follow-up visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Peanut Allergy
- Allergies, Cough/Cold Medications & Alcohol Interactions
- Benadryl Dosage Charts for Infants and Children
- Claritin Dosage Charts for Infants and Children
- EpiPen Costs and Alternatives: What Are Your Best Options?
- Low Salicylate Diet
- Zyrtec Dosage Charts for Infants and Children
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
