Non-Insulin Pens for People with Diabetes
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2025.
What do I need to know about pen devices?
A non-insulin pen is a device used to inject diabetes medicines. The pen contains a cartridge of diabetes medicine. The pen may be used while you are taking other diabetes medicine. Some pens are used one time and discarded. Others have several doses of medicine. These pens are used every day, sometimes more than one time each day. Your healthcare provider or pharmacist will give you information on your specific type of pen.
How do I get the medicine ready to use?
- Check the label. Confirm that you have the correct medicine and dose prescribed by your healthcare provider. Also check the expiration date. Use a new pen if the expiration date has passed.
- Check the pen. Check that the pen is not damaged.
- Check the medicine. Make sure the medicine in the cartridge is clear, not frozen, not cloudy, and has no clumps. You may need to mix the medicine before you use it. Your provider or pharmacist will show you how to mix your medicine, if needed.
How do I get the pen ready to use?
- Remove a new pen from the refrigerator 15 to 30 minutes before you use it. Inject medicine at room temperature.
- Wash your hands. Use soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. This will help decrease your risk for an infection.

- Select a new pen needle. Always use a new pen needle for each injection to help prevent an infection. Push the capped pen needle straight onto the pen. Twist the pen needle until it is tight.
- Select the correct dose on the pen as directed. You may need to pull the injection button out before you turn it. Your healthcare provider will tell you if you need to do this. Turn the dial to the dose prescribed by your provider. If you cannot turn the dial, there may not be enough medicine left in the cartridge. Use a new pen if there is not enough medicine left.
- Remove the cap from the needle. Some pens have the needle attached. These needles go back into the pen after use. Some needles need to be attached to the pens.
Related medications
Where do I inject medicine?
- You can inject medicine into your abdomen, upper arm, and the front or side of the thigh.
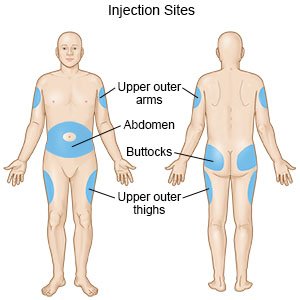
- Do not inject medicine into areas where you have a wound or bruising. Medicine injected into wounds or bruises may cause an infection or not get into your body correctly.
- Inject your medicine at least 2 inches away from where you inject insulin.
- Change the injection area within the site each time you inject medicine. For example, inject medicine into different areas in your abdomen. Injecting into the same area too many times can cause lumps, swelling, or thickened skin.
How do I inject medicine with a pen?
- Clean the skin where you will inject the medicine. Use an alcohol pad or a cotton swab dipped in alcohol. Let the area dry before you inject to help decrease pain.
- Pinch a fold of your skin. Gently hold the skin fold between your thumb and first finger.
- Insert the needle straight into your skin. Do not hold the syringe at an angle. Make sure the needle is all the way into the skin. Let go of the pinched tissue.
- Push the injection button to inject the medicine. Continue to press the injection button. Keep the needle in your skin for 10 seconds.
- Pull out the needle. Press on your injection site for 5 to 10 seconds to keep medicine from leaking out. Do not rub the injection site.
- Recap and remove the needle from the pen, if needed. Twist and remove the capped needle counter clockwise after each injection.
- Dispose of used needles and empty pens. Dispose of your needles and empty pens correctly. Do not place needles in the household trash. You may receive a hard plastic container made especially for used pens and needles. You can also use a soda bottle or other plastic bottle with a screw lid. Make sure that both the pen and needle fit into the container easily and cannot break through the sides. Check with your healthcare provider or a pharmacist about local rules for disposing of used pens and needles.
How do I store the pen?
- Follow storage directions on the label or package insert. Store your pen in a cool, dry place. Unopened pens can be stored in the refrigerator until you are ready to use them. Most pens can be opened and kept at room temperature. Ask your provider how long you can use the pen after opening it.
- Care for your pen. Wipe the inside of your pen with a clean, damp cloth, if needed. Put a pen cap on your pen as directed. Do not keep your pen in direct sunlight or in your car.
- Dispose of pens, if needed. Pens that were exposed to temperatures above 85°F (30°C) should be placed in a disposal container.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have questions or concerns about how to use the pen.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
