Meal Planning with the Plate Method
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is meal planning with the plate method?
Meal planning with the plate method is a way for people with diabetes to plan meals. The plate method can help you eat the right amount of carbohydrates and keep your blood sugar levels under control. Carbohydrates naturally raise your blood sugar level. Your blood sugar level can rise too high if you eat too much carbohydrate at one time. Carbohydrates are found in starches (bread, cereal, starchy vegetables, and beans), fruit, milk, yogurt, and sweets.
How do I use the plate method to plan my meals?
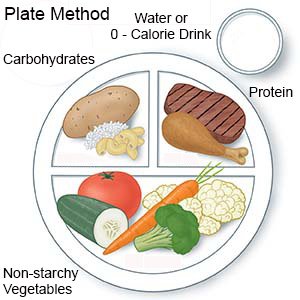
- Draw an imaginary line down the middle of a 9-inch dinner plate. On one side, draw another line to divide that section in half. Your plate will have 3 sections.
- Fill the largest section of your plate with non-starchy vegetables. Examples are broccoli, spinach, cucumbers, peppers, cauliflower, and tomatoes.
- Add a carbohydrate to 1 of the small sections of your plate. Examples are pasta, rice, whole-grain bread, tortillas, corn, potatoes, and beans. Your plan may allow a serving of low-fat dairy or fruit for a carbohydrate.
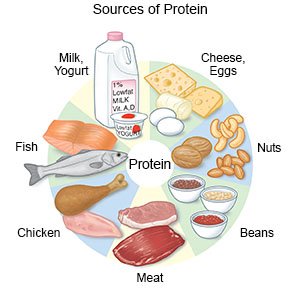
- Add meat or another source of protein to the other small section of your plate. Examples are chicken or turkey without skin, fish, lean beef or pork, low-fat cheese, tofu, or eggs.
- Add a low-calorie or calorie-free drink. Examples include water or unsweetened tea or coffee.
 |
Related medications
What are serving sizes of foods?
- Non-starchy vegetables:
- ½ cup of cooked vegetables or 1 cup of raw vegetables
- ½ cup of vegetable juice
- Starches:
- 1 ounce of whole-wheat bread or 1 small (6 inch) flour or corn tortilla
- 1 small (4 inch) pancake (about ¼ inch thick)
- ¾ cup of dry, unsweetened, whole-grain ready-to-eat cereal or ¼ cup of low-fat granola
- ½ cup of cooked cereal or oatmeal
- ⅓ cup of rice or pasta
- ½ cup of corn, green peas, sweet potatoes, or mashed potatoes
- ½ cup of cooked beans and peas (garbanzo, pinto, kidney, white, split, black-eyed)
- Meat and other protein sources:
- 3 to 4 ounces of any lean meat, fish, or poultry
- ½ cup of tofu or tempeh
- 1 large egg
- 1½ ounces (about 2 tablespoons) of nuts or 2 tablespoons of peanut butter
- Fruit:
- 1 small piece of fresh fruit
- ½ cup of canned or fresh fruit or unsweetened fruit juice
- ¼ cup of dried fruit
- Milk and yogurt:
- 1 cup (8 ounces) of skim or 1% milk
- ¾ cup (6 ounces) of plain, non-fat yogurt
What are some other healthy nutrition tips?
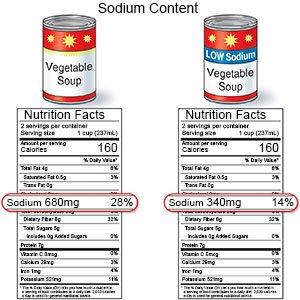
- Limit salt and sugar. Choose and prepare foods and drinks with less salt and added sugars. Use the nutrition information on food labels to help you make healthy choices. The percent daily value listed on the food label tells you whether a food is low or high in certain nutrients. A percent daily value of 5% or less means that the food is low in a nutrient. A percent daily value of 20% or more means that the food is high in a nutrient.
- Choose healthy fats. Choose healthy fats such as polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats in place of unhealthy fats. Healthy fats are found in vegetable oils such as soybean, corn, canola, olive, and sunflower oil. Unhealthy fats are saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. Unhealthy fats are found in shortening, butter, stick margarine, and animal fat.

- Ask your healthcare provider if alcohol is okay for you. Generally, men 65 or older and women should limit alcohol to 1 drink within 24 hours and 7 within 1 week. Men 21 to 64 years should limit alcohol to 2 drinks a day and 14 within 1 week. Your healthcare provider can tell you how many drinks are okay for you within 24 hours or within 1 week. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor. Always have food when you drink alcohol. Your blood sugar may fall to a low level if you drink when your stomach is empty.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
