Intravenous Pyelogram
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW:
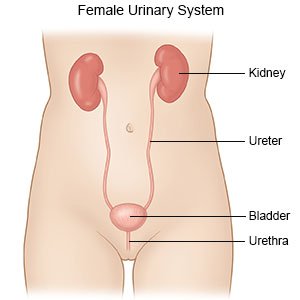
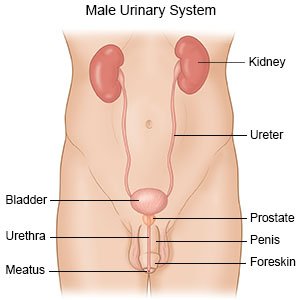
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is an x-ray of your urinary system. The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. Ureters carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder. The urethra carries urine out of your bladder when you urinate.
 |
 |
HOW TO PREPARE:
The week before your procedure:
- Arrange to have someone drive you home after the procedure.
- Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines you currently take. He or she will tell you if you need to stop any medicine for the procedure. He or she will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of the procedure.
- You will be given contrast liquid before the x-rays are taken to help your provider see your urinary tract better. Tell him or her if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- You may need blood tests, urine tests, or other x-rays before your procedure.
The night before your procedure:
You may be told not to eat or drink anything after midnight.
The day of your procedure:
- You or a close family member will be asked to sign a legal document called a consent form. It gives healthcare providers permission to do the procedure or surgery. It also explains the problems that may happen, and your choices. Make sure all your questions are answered before you sign this form.
- Take only the medicines your healthcare provider told you to take.
- An IV will be put into a vein. You may be given liquids or medicine through the IV.
WHAT WILL HAPPEN:
What will happen:
Contrast liquid will be injected into your IV. A band may be put around your stomach. This band can be tightened to help keep the liquid in your kidneys for a short time. Several x-rays will taken. Your healthcare provider may push on your stomach and ask you to change positions. You will be asked to go to the bathroom and empty your bladder. More x-rays will then be taken.
After your procedure:
You may need to drink liquids to help your body get rid of the contrast liquid. When your healthcare provider sees that you are okay, you will be able to go home. If you are staying in the hospital, you will be taken to your hospital room.
CONTACT YOUR HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IF:
- You have a fever.
- You get a cold or the flu.
- You have questions or concerns about your procedure.
Seek Care Immediately if
- Your symptoms get worse.
- You are not able to eat or drink.
- You are urinating less or not at all.
- You are vomiting.
- You have blood in your urine.
Risks
The contrast liquid may cause a headache, upset stomach, or vomiting. It can also cause you to feel itchy or hot. The liquid can damage your kidneys.
Related medications
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
