GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
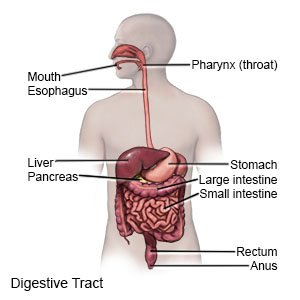
GERD is reflux that happens more than 2 times a week for a few weeks. Reflux means acid and food in your stomach back up into your esophagus. GERD can cause other health problems over time if it is not treated.
 |
What causes GERD?
GERD often happens because the lower muscle (sphincter) of the esophagus does not close properly. The sphincter normally opens to let food into the stomach. It then closes to keep food and stomach acid in the stomach. If the sphincter does not close properly, stomach acid and food back up (reflux) into the esophagus. The following may increase your risk for GERD:
- Certain foods such as spicy foods, chocolate, foods that contain caffeine, peppermint, and fried foods
- Hiatal hernia
- Certain medicines such as calcium channel blockers (used to treat high blood pressure), allergy medicines, sedatives, or antidepressants
- Pregnancy, obesity, or scleroderma
- Lying down after a meal
- Drinking alcohol or smoking cigarettes
What are the signs and symptoms of GERD?
- Heartburn (burning pain in your chest)
- Pain after meals that spreads to your neck, jaw, or shoulder
- Pain that gets better when you change positions
- Bitter or acid taste in your mouth
- A dry cough
- Trouble swallowing or pain with swallowing
- Hoarseness or a sore throat
- Burping or hiccups
- Feeling full soon after you start eating
How is GERD diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and when they started. Tell your provider about other medical conditions you have, your eating habits, and your activities. You may also need any of the following:
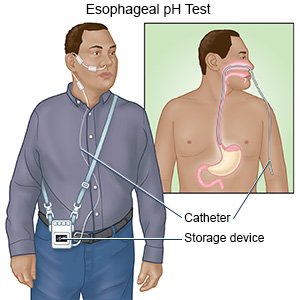
- An esophageal pH test measures the amount of stomach acid that reaches your esophagus. A small probe is used to check the amount. The probe may stay attached to the catheter. If so, the catheter is taped to your nose to hold it in place. Sometimes the probe is wireless, so the catheter is removed after the probe is placed.
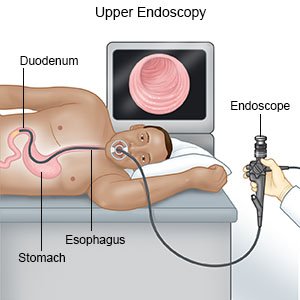
- An endoscopy is a procedure used to look at the inside of your esophagus and stomach. An endoscope is a bendable tube with a light and camera on the end. Your healthcare provider may remove a small sample of tissue and send it to a lab for tests.
- X-ray pictures may be taken of your stomach and intestines (bowel). You may be given a chalky liquid to drink before the pictures are taken. This liquid helps your stomach and intestines show up better on the x-rays.
- Pressure and function tests of your esophagus can help find problems such as a hiatal hernia.
Related medications
How is GERD treated?
- Medicines are used to decrease stomach acid. Medicine may also be used to help your lower esophageal sphincter and stomach contract (tighten) more.
- Surgery is done to wrap the upper part of the stomach around the esophageal sphincter. This will strengthen the sphincter and prevent reflux.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage GERD?
 |
- Do not have foods or drinks that may increase heartburn. These include chocolate, peppermint, fried or fatty foods, drinks that contain caffeine, or carbonated drinks (soda). Other foods include spicy foods, onions, tomatoes, and tomato-based foods. Do not have foods or drinks that can irritate your esophagus, such as citrus fruits, juices, and alcohol.
- Do not eat large meals. When you eat a lot of food at one time, your stomach needs more acid to digest it. Eat 6 small meals each day instead of 3 large ones, and eat slowly. Do not eat meals 2 to 3 hours before bedtime.
- Elevate the head of your bed. Place 6-inch blocks under the head of your bed frame. You may also use more than one pillow under your head and shoulders while you sleep.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If you are overweight, weight loss may help relieve symptoms of GERD.
- Do not smoke. Smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter and increases the risk of GERD. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Do not put pressure on your abdomen. Pressure pushes acid up into your esophagus. Do not wear clothing that is tight around your waist. Do not bend over. Bend at the knees if you need to pick something up.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have severe chest pain and sudden trouble breathing.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have trouble breathing after you vomit.
- You have trouble swallowing, or pain with swallowing.
- Your bowel movements are black, bloody, or tarry-looking.
- Your vomit looks like coffee grounds or has blood in it.
When should I call my doctor?
- You feel full and cannot burp or vomit.
- You vomit large amounts, or you vomit often.
- You are losing weight without trying.
- Your symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about GERD
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
