Electroencephalogram
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about an EEG:
An EEG is a test that measures the electrical activity in your brain. It can help healthcare providers decide what treatments you need. An EEG can also help diagnose or monitor any of the following:
- Seizures
- Sleep disorders
- Brain infection, disease, or injury
- Brain activity during brain surgery or a coma
How to prepare for an EEG:
Your healthcare provider will talk to you about how to prepare for an EEG. The provider will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of your test. Do not drink or eat foods with caffeine on the day of your test. Do not put oils or lotions on your scalp or hair for 24 hours before your test. This includes conditioner, hair spray, hair cream, or hair gel. Your provider may tell you to sleep less than usual the night before your test.
What will happen during an EEG:
- You will not feel pain during the test. Healthcare providers will ask you to lie still, and not talk during the test. A provider will put gel or cream on your scalp. Small discs will be placed in different places on your head. The discs will be connected to wires and a monitor. The monitor will show healthcare providers your brain's electrical activity.
- During the test you may be asked to change how fast you breathe. You may also be asked to look at pictures or a flashing light. You may also hear loud noises.
- Bright lights or loud noises may cause you to have a seizure during the test. Healthcare providers may give you medicine to control or stop your seizure. They will also protect you from injury.
- You may be given medicine to help you sleep during the test. You may also be videotaped during the test. The videotape will help providers look for signs of a seizure.
Call 911 or have someone else call for any of the following:
- Your seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes.
- You cannot be woken after a seizure.
- You have more than 1 seizure before you are fully awake or aware.
- You have trouble breathing.
- You have a seizure in water.
Related medications
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a second seizure that happens within 24 hours of your first.
- You are injured during a seizure.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- You have seizures even with treatment.
- Your seizures happen more often.
- After your seizures you are confused longer than you usually are.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
How others can keep you safe during a seizure:
Give the following instructions to family, friends, and coworkers:
- Do not panic.
- Gently guide me to the floor or a soft surface.
- Do not hold me down or put anything in my mouth.
- Place me on my side to help prevent me from swallowing saliva or vomit.
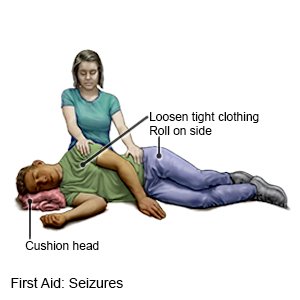
- Protect me from injury. Remove sharp or hard objects from the area surrounding me, or cushion my head.
- Loosen my clothing around the head and neck.
- Time how long my seizure lasts. Call 911 if my seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes or if I have a second seizure.
- Stay with me until my seizure ends. Let me rest until I am fully awake.
- Perform CPR if I stops breathing or you cannot feel my pulse.
- Do not give me anything to eat or drink until I am fully awake.
Take your medicine as directed:
Call your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell him or her if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Electroencephalogram
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
