Diabetic Neuropathy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is diabetic neuropathy (DN)?
DN is a type of nerve damage that can develop if you have diabetes. High blood sugar that is not controlled can damage nerves and slow or stop their ability to send signals. DN is most common in the legs and feet.
What increases my risk for DN?
- Blood sugar that is not controlled
- Having diabetes for a long time
- Kidney disease
- Obesity
- Tobacco and alcohol use
What are the signs and symptoms of DN?
You may have symptoms in your feet and legs first, then your hands and arms. Your symptoms may be worse at night:
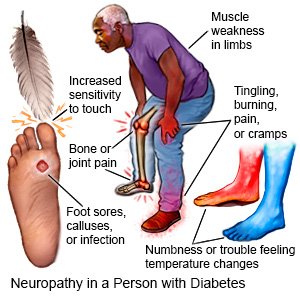
- Numbness, decreased ability to feel pain or changes in temperature
- Burning, tingling, cramping, or pain in your feet or hands
- Increased sensitivity to touch
- Serious foot problems, such as sores, infection, calluses, or bone and joint pain
- Muscle weakness or problems balancing or walking
 |
What do I need to know about DN screening?
You will be checked for DN when type 2 diabetes is diagnosed. You will need to be checked 5 years after a type 1 diabetes diagnosis. You will need yearly exams to check for symptoms of DN. Your healthcare provider will check the blood flow in your feet and look for ulcers or other problems. Nerves that control automatic functions in your body such as heartbeat and digestion will also be checked. Your provider will tell you when to get checked.
How is DN diagnosed?
- A filament test may show your sensitivity to touch. A soft nylon fiber is brushed over areas of your skin.
- Sensory testing may show how your nerves respond to touch, vibration, a pinprick, or temperature changes.
- Nerve and muscle testing may show how quickly your nerves or muscles respond to electrical signals.
Related medications
How is DN treated?
DN cannot be cured. The goal of treatment is to decrease pain, slow progression of DN, and prevent complications. You may be given medicines to help decrease nerve pain.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage DN?
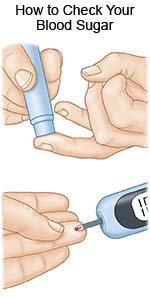
- Keep your blood sugar levels as close to your target levels as possible. Check your blood sugar levels often, as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if your levels are higher than they should be.
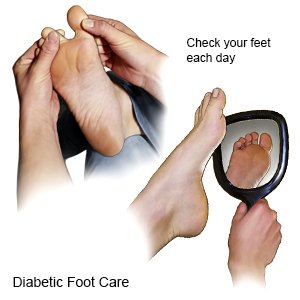
- Care for your feet. Check your feet each day for cuts, scratches, calluses, or other wounds. Look for redness and swelling, and feel for warmth. Wear shoes that fit well. Check your shoes for rocks or other objects that can hurt your feet. Do not walk barefoot or wear shoes without socks. Wear cotton socks to help keep your feet dry.
- Work with your dietitian to create a healthy meal plan. This meal plan can help you control your blood sugar and decrease your symptoms.
- Be physically active at least 30 minutes, 5 days a week. This can help keep your blood sugar level steady and help you manage your weight. Ask your care team provider about the best activity plan for you. Use caution when you exercise if you have decreased feeling in your feet.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your care team provider what a healthy weight is for you. A healthy weight can help you manage your blood sugar level.
What can I do to help prevent DN?
- Check your blood pressure as directed. High blood pressure can damage the nerves in your legs, feet, arms, or hands. This can increase your risk for DN or make your DN symptoms worse. A normal blood pressure is 119/79 or lower. Talk to your healthcare provider about your blood pressure goals. Together you can create a plan to lower your blood pressure if needed and keep it in a healthy range. The plan may include lifestyle changes or medicines to lower your blood pressure.

- Talk to your healthcare provider about your cholesterol level. Lab tests are used to measure the amount of cholesterol in your blood. High cholesterol can increase your risk for DN or make your DN symptoms worse. Your provider can help you create a plan to lower your cholesterol level if needed. You may need to make lifestyle changes or take medicines to control your cholesterol level.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine can worsen your symptoms and make it more difficult to manage your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Limit alcohol as directed. Alcohol can cause your blood sugar levels to be low if you use insulin. Alcohol can cause high blood sugar levels and weight gain if you drink too much. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor. Your healthcare provider can tell you how many drinks are okay to have within 24 hours and within 1 week.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your legs or feet start to turn blue or black.
- You have a wound that does not heal or is red, swollen, or draining fluid.
When should I call my diabetes care team provider?
- You begin to have symptoms.
- Your blood sugar level is higher or lower than care team providers have told you it should be.
- You have redness, calluses, or sores on your feet.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Diabetic Neuropathy
- Diabetes Medications and Alcohol Interactions
- FDA-Approved Weight Loss Drugs: Can They Help You?
- OneTouch Blood Glucose Meters
- Side Effects of Weight Loss Drugs
- Top 10 Diabetes Treatments You May Have Missed
- Which Drugs Cause Weight Gain?
Treatment options
- Medications for Autonomic Neuropathy
- Medications for Diabetes Mellitus
- Medications for Diabetes, Type 1
- Medications for Peripheral Neuropathy
- Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
