Diabetic Hyperglycemia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Diabetic hyperglycemia
is a blood sugar level that is higher than your diabetes care team provider recommends. You may not have any signs and symptoms. You may have more thirst and urinate more often than usual.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have a seizure.
- You begin to breathe fast or are short of breath.
- You become weak and confused.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your blood sugar level is over 240 mg/dL and you have ketones in your urine.
- Your breath smells fruity.
- You have nausea and are vomiting.
- You have symptoms of dehydration, such as dark yellow urine, dry mouth and lips, and dry skin.
Call your diabetes care team provider if:
- You continue to have higher blood sugar levels than your provider recommends.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Why it is important to manage diabetic hyperglycemia:
Over time, hyperglycemia can damage your nerves, blood vessels, tissues, and organs. Damage to arteries may increase your risk for heart attack and stroke. Nerve damage may also lead to other heart, stomach, and nerve problems. If diabetic hyperglycemia is not controlled, it can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS). These are serious conditions that can become life-threatening.
Manage diabetic hyperglycemia:
- Take diabetes medicine or insulin as directed. Missed or wrong doses can cause your blood sugar level to go up.
- Tell your diabetes care team provider if you continue to have trouble managing your blood sugar level. Your provider may change the type, amount, or timing of your diabetes medicine or insulin. If you do not take diabetes medicine or insulin, you may need to start.
- Work with your provider to develop a sick day plan. Illness can cause your blood sugar to rise. A sick day plan helps you control your blood sugar level when you are sick.
Prevent diabetic hyperglycemia:
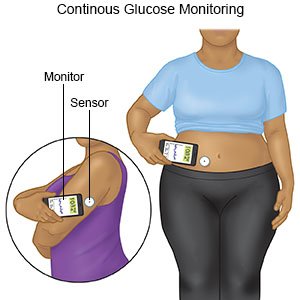
- Check your blood sugar levels regularly. Ask your diabetes care team provider how often to check your blood sugar and what your levels should be. Your healthcare provider will help you create a blood sugar level range. The goal is to keep your blood sugar within the range so it does not go too high or too low. Your provider may recommend nutrition, physical activity, or medicine changes if your levels were often above or below range.
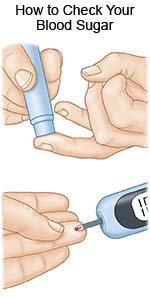
- Follow your meal plan. Your blood sugar can go up if you eat a large meal or you eat more carbohydrates than recommended. Work with a dietitian to develop a meal plan that is right for you.
- Exercise as directed. Physical activity, such as exercise, can help lower your blood sugar when it is high. It can also keep your blood sugar levels steady over time. Be active for at least 30 minutes, 5 days a week. Include muscle strengthening activities 2 days each week. Do not sit for longer than 30 minutes at a time. Work with your provider to create an activity plan. Children should get at least 60 minutes of physical activity each day.

- Check your ketones before exercise if your blood sugar level is above 240 mg/dL. Do not exercise if you have ketones in your urine because your blood sugar level may rise even more. Ask your healthcare provider how to lower your blood sugar when you have ketones.
Follow up with your diabetes care team provider as directed:
Your provider may refer you to a dietitian. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Diabetic Hyperglycemia
- Diabetes Medications and Alcohol Interactions
- FDA-Approved Weight Loss Drugs: Can They Help You?
- OneTouch Blood Glucose Meters
- Side Effects of Weight Loss Drugs
- Top 10 Diabetes Treatments You May Have Missed
- Which Drugs Cause Weight Gain?
Treatment options
- Medications for Diabetes, Type 1
- Medications for Diabetic Coma
- Medications for Diabetic Coma, in DM Type I
- Medications for Diabetic Coma, in DM Type II
- Medications for Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
Care guides
- Diabetes and your Skin
- Diabetic Gastroparesis
- Diabetic Hyperglycemia
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- How to Draw Up Insulin
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State
- Hypoglycemia in a Person with Diabetes
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
