Decision Aid for Herniated Disc in the Lower Back
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about making treatment decisions for your herniated (bulging) disc:
You can work with your healthcare provider to choose a treatment plan that works best for you. Your treatment choices include nonsurgical options and surgery. Your provider may recommend nonsurgical treatments first. Learn about the benefits and risks of nonsurgical treatment and surgery so you can make an informed choice.
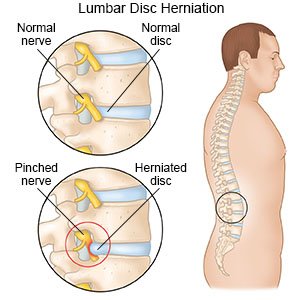
What you need to know about a herniated disc:
Discs are spongy cushions between the vertebrae (bones) in your spine. The bulging disc may press on your nerves or spinal cord. This pressure causes pain in your lower back, buttocks, groin, or legs. It can also cause numbness or weakness in one leg.
 |
Related medications
Benefits of treatment for a herniated disc:
- Nonsurgical treatment may help you feel better within 6 weeks. Over a period of a year, it may work as well as surgery in improving symptoms. The following are common nonsurgical treatments for a herniated disc:
- Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen your lower back and abdominal muscles.
- Medicines , such as NSAIDs, help decrease swelling and pain. An example of an NSAID is ibuprofen. Muscle relaxers decrease pain and muscle spasms.
- Epidural steroid injections help reduce swelling and pain for about 2 to 4 weeks. They may be recommended if you have no pain relief after 6 weeks of physical therapy and NSAIDs.
- Surgery can be done to fix your herniated disc if other treatments do not work. Surgery can be done to remove the herniated disc that is putting pressure on your spinal nerve. Surgery usually provides faster pain relief than nonsurgical treatment.
Risks of treatment:
Even with treatment, your symptoms may return, or you may develop another herniated disc. The following are risks of surgical and nonsurgical treatment:
- Nonsurgical treatment takes more time to provide pain relief than surgery. Medicines must be taken in limited doses. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems. Steroid injections are usually limited to about 4 each year because steroids can weaken bones and muscles. Steroids can also increase your risk for other infections, cause mood changes, and increase blood sugar levels.
- Surgery increases your risk for infection at the incision site and deep in the disc space. The protective layer of your spinal cord may tear or leak. This causes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to leak. You may have to lie flat for up to 7 days while the tear or leak heals. You may need disc surgery again. You may need surgery to remove your discs and fuse your vertebrae together. This surgery would limit movement in your back.
Questions to ask your healthcare provider to help you make decisions about treatment:
- Am I a good candidate for steroid injections?
- How will I know if signs and symptoms are becoming severe enough to need surgery?
- Am I a good candidate for surgery?
- How long is recovery from surgery?
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
