Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system contains lymph vessels, lymph nodes, and glands, such as the spleen and thymus. Lymph vessels carry lymph fluid throughout the body. Lymph fluid contains lymphocytes (white blood cells) that help fight infection and disease. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma causes lymphocytes to grow and divide without control and to form tumors. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can develop in any lymph tissue in the body. Common places are lymph nodes in the neck, underarm, and chest. Cancer cells can travel from lymph node to lymph node and spread through the body. Childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma usually affects older children. Some types are rare in children of any age.
What causes childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
The cause of non-Hodgkin lymphoma is not known. The following may increase your child's risk:
- Long-term exposure to chemicals, such as pesticides, or nitrates in drinking water
- A family history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Exposure to high amounts of radiation
- A weakened immune system
- Certain viral or bacterial infections
What are the signs and symptoms of childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
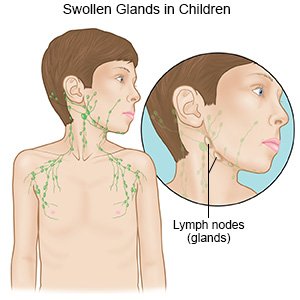
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, arm, or groin
- Trouble breathing, or a cough
- Feeling weaker or more tired than usual
- Fever, itchy skin or a rash, or night sweats
- Pain or swelling in the abdomen and pain in the lower back or in both legs
- Weight loss without trying
How is childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma diagnosed?
Your child's healthcare provider will ask about your child's symptoms and when they began. Tell the provider if your child has a family history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma or other risk factors. Your child's provider will check your child's organs to help find problems non-Hodgkin lymphoma can cause. For example, shortness of breath may mean lymph tissue in your child's lung or chest is affected. The following tests may be used to diagnose non-Hodgkin lymphoma or to find out if it is early stage or later stage:
- Blood tests may show abnormal white blood cells or signs of anemia (not enough red blood cells). The tests may also be used to measure the amount of inflammation in your child's blood. Blood tests can also be used to check liver and kidney function.
- A biopsy is a procedure to remove a tissue sample to be tested. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is diagnosed from a lymph node biopsy. Your child's provider may also test a bone marrow sample to see if the cancer has spread to your child's bones.
- X-ray, ultrasound, CT, MRI, or PET scan pictures may show where the cancer is located. Your child's healthcare provider may also use the x-rays to look for blockages, signs of infection, or other health problems. Your child may be given contrast liquid to help the cancer show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if your child has ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. An MRI machine uses a powerful magnet. Do not let your child enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet. Tell the healthcare provider if your child has any metal in or on his or her body.
Related medications
How is childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma treated?
Treatment will depend on your child's age and development. Treatment will also depend on the size and location of any tumors. The type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma your child has may also factor into the treatment decision.
- Chemotherapy is medicine used to treat cancer by killing tumor cells. Chemotherapy may also be used to shrink lymph nodes that contain cancer.
- Radiation therapy uses x-rays or gamma rays to treat cancer. Radiation kills cancer cells and may stop the cancer from spreading. It may be given alone or with chemotherapy to treat cancer.
- A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace your child's diseased bone marrow with healthy marrow. Your child may be given bone marrow from a donor. Your child's own marrow may be used if it is collected when the cancer is in remission (not active). The bone marrow transplant is given to your child in an IV while he or she is in the hospital.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to care for my child?
- Have your child rest as needed. Your child should return to activities slowly, and do more as he or she feels stronger.
- Offer your child a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include vegetables, fruit, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, fish, nuts, whole-grain breads and cereals. Healthy foods will help your child get the protein, carbohydrates, and other nutrients his or her body needs. You may need to change the foods your child eats depending on his or her treatments and side effects. Your child may also need to eat more calories than usual. Work with a dietitian to plan the best meals and snacks for your child. Ask if your child should take vitamins.

- Keep your child away from people who have a cold or the flu. Also try to keep your child away from large groups of people to decrease his or her risk.
- Talk to your older child about not smoking. Talk to your healthcare provider if your child needs help quitting. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Ask your child's healthcare provider for information before your child uses these products.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has chest pain.
- Your child has more trouble breathing than usual.
- Your child has a seizure.
- Your child cannot think clearly, or feels confused.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child is too dizzy to stand, or has trouble keeping his or her balance.
- Your child's legs swell.
- Your child feels weak or numb on one side of his or her body.
When should I call my child's oncologist?
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child has back pain and weakness in his or her legs.
- Your child has chills, a cough, red or swollen skin, or feels weak and achy.
- Your child is vomiting and cannot keep any food or liquids down.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
