Peritoneal Dialysis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Peritoneal dialysis
is done to remove wastes, chemicals, and extra fluid from your body. A liquid called dialysate is put into your abdomen through a catheter (thin tube). The liquid stays in your abdomen for several hours at a time. This is called dwell time. The dialysate pulls wastes, chemicals, and extra fluid from your blood through the peritoneum. The peritoneum is a thin lining on the inside of your abdomen. The peritoneum works as a filter as the wastes are pulled through it. The process of filling and emptying your abdomen with dialysate is called an exchange.
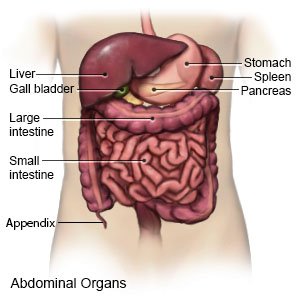 |
Call your doctor or dialysis specialist if:
- You have trouble breathing or a dull pain in your abdomen while you do a dialysis exchange.
- Dialysate is not flowing correctly into or out of your abdomen during an exchange.
- Your catheter has a crack or hole in it, or it has come part or all of the way out of your abdomen.
- You have constipation, stomach pain, and are vomiting.
- A new bump has grown in your abdomen since you started doing CAPD exchanges.
- Your catheter exit site is red, tender, painful, or draining fluid or pus.
- The dialysate that drains out of your abdomen looks cloudy.
- The exit site is bigger than it used to be.
- You have sudden weight gain, or your arms or legs are swollen.
- You have a fever or chills.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Types of peritoneal dialysis, and how they are done:
- Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) means you do the exchanges by hand. An exchange will take about 40 minutes. The solution will stay in your abdomen for at least 4 to 6 hours. You may need to change the solution 4 or more times during the day. You can sleep with the solution in your abdomen through the night without having to wake up for an exchange.
- Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) uses a machine called a cycler. It puts the dialysate in your abdomen and drains it out after the exchange is complete. You may do 1 exchange by hand that lets the dialysate dwell in your abdomen during the day. At night, you can connect your catheter to the cycler to drain it. Peritoneal dialysis exchanges will also be done while you sleep. If you sleep for 8 to 9 hours, the machine may do 3 to 5 exchanges during that time. Your dialysis team will teach you how to set up and use the cycler.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How to get ready to do a CAPD exchange:
Exchanges should be done in a well-lit room. There should be no pets, dander, strong breezes, or fans in the room. They can increase your risk for an infection.
- Gather your supplies.
- Dialysate bag and waste product bag
- IV stand (used to hang your dialysate bag)
- Y-shaped tubing and tubing clamps
- Medical gloves and a medical mask
- New plastic syringe without a needle (if needed)
- Wash your hands with soap and water. Scrub them for at least 15 seconds. Dry your hands well with a clean towel or new paper towel. Your healthcare provider may also recommend that you use an alcohol-based hand gel after you dry your hands. The gel will help kill any bacteria that remain after you wash your hands.

- Put on your mask, and then your gloves. Make sure the mask covers both your nose and your mouth. This will help prevent germs from your nose or mouth reaching the exit site. Put on your gloves. Do not touch anything other than the bandage and your supplies when your gloves are on.
How to do a CAPD exchange:
- Flush the tubing with dialysate. Connect the lower end of the Y tubing to your catheter. Connect the 2 other ends of the tubing to the dialysate bag and the waste bag. Clamp the tubing that goes to your abdomen. Allow 100 milliliters (mL) of fresh dialysate to flow out of the bag. Let it drain down the tubing into the waste bag. Then clamp the tubing that goes to the waste bag.
- Let the dialysate flow into your abdomen. Hang the bag at a higher level than your abdomen. Remove the clamp to let the rest of the dialysate flow into your abdomen. This should take no more than 10 minutes. You may lie, sit, or stand while the dialysate flows in. After all of the dialysate is in your abdomen, wash your hands and put on new gloves. Disconnect the catheter from the tubing. Clamp the catheter closed. Leave the dialysate in your abdomen for 3 to 5 hours of dwell time.
- Drain the dialysate out of your abdomen. Wash your hands again. Put on your mask and new gloves. Connect the Y tubing to the catheter. Clamp the tubing that goes to the dialysate bag. Hang the bag at a lower level than your abdomen. Remove the clamp from the tubing that goes to the waste bag. Let the dialysate drain from your abdomen into the waste bag. It should take less than 45 minutes to drain the dialysate out of your abdomen. The dialysate that drains out should be clear. Then close the waste bag and dispose of it as directed. Wash your hands.
What you need to know about weight gain:
Weight gain may happen from extra sugar you will get from the dialysate. You will get instructions for a dialysis diet to follow. The diet will help you get the right nutrients and calories. Weight gain may also happen if your body is retaining (holding in) fluid. Do the following to manage weight gain from extra fluid:
- Limit liquids as directed by your healthcare provider. Keep a record of the amount of liquid you drink and urine you pass each day. This is called intake and output.
- Weigh yourself each day. Sudden weight gain can be a sign of fluid retention. Use the same scale in the same place each time. Weigh yourself after you use the bathroom but before you eat. Keep a record of your weight each day.
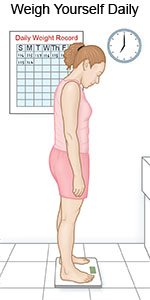
- Bring your intake and output and daily weight records to follow-up visits. Your healthcare provider will tell you if you have too much fluid in your body, and what to do to correct it.
Follow up with your doctor or dialysis specialist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
