Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
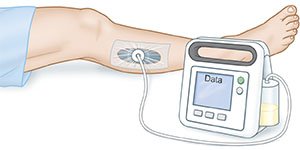
NPWT uses a device called a wound vacuum (wound vac) or vacuum pump to help with wound healing. Suction from the device removes excess drainage from your wound and pulls wound edges closer together. NPWT also helps closed incision sites heal. NPWT promotes healthy tissue growth by increasing blood flow to your wound or incision site. NPWT also reduces bacteria that cause infections. You and your healthcare providers will be taught about your specific NPWT device, alarms, and dressing changes. NPWT is also called vacuum-assisted closure (VAC).
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a sudden increase or large amount of blood from your wound or incision site.
- You have a fever of 102°F (38.8°C) or higher.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever or nausea, or you vomit.
- Your wound or skin around your wound is red, swollen, and feels warm.
- The skin around your wound or incision site is raw, irritated, or develops blisters.
- You see pus coming from your wound or incision site, or it smells bad.
- You are dizzy or confused.
- You have questions or concerns about the device, your condition, or care.
Related medications
How NPWT works:
Moist foam packing or gauze is placed in your wound or over your incision site. Suction tubing may already be implanted within the foam. If not, tubing will be placed in the middle of the foam or gauze. Then your wound or incision site and part of the tubing will be covered completely by a clear dressing. The tubing is attached to a collection canister on the device. Your healthcare provider may set the device for continuous or periodic suction. When the suction is turned on, the foam packing and wound will contract (tighten) and bring the wound edges together. The suction will also help keep your incision site closed.
What else you need to know about NPWT:
- NPWT is used 24 hours a day. Do not change the settings on the device unless directed. If the NPWT device is turned off for 2 hours or more, the dressing needs to be replaced. Ask your healthcare provider which type of dressing to use.
- The NPWT device may use electrical, mechanical, or battery power. Your provider will tell you which kind of device you have. Make sure you understand how the device works so it does not lose power.
- You can shower with the dressing in place. Do not remove your dressing unless directed. Do not take the device into the bathtub or shower with you. Do not get the device wet. You may need to clamp the tubing and disconnect it from the device before you shower. Ask your provider for more information about taking a shower.
Follow up with your doctor or wound specialist as directed:
Your healthcare provider will need to monitor your wound. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
