MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) for Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
is a test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to take pictures inside your child's body. An MRI is used to see blood vessels, tissue, muscles, and bones. It can also show organs, such as your child's heart, lungs, or liver. An MRI can help your child's healthcare provider diagnose or treat a medical condition. It does not use radiation.
Help your child prepare for an MRI:
- Tell your child what to expect before, during, and after the MRI.
- Tell your child's healthcare provider about all your child's current medicines. The provider will tell you which medicines to give or not give on the day of the MRI. Your child may be given medicine to help him or her feel calm and relaxed during the MRI.
- Tell your child's provider if your child has any metal in his or her body, such as an implant or aneurism clip. Tell your child's provider if your child has a tattoo or wears a medicine patch.
- Have your child remove any metal items, such as jewelry, glasses, or hearing aids before your child enters the MRI room.
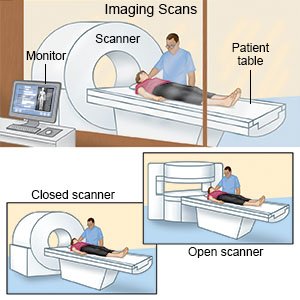
What will happen during an MRI:
Your child's healthcare provider will ask him or her to lie on a table. Contrast liquid may be used to help a body part show up more clearly. The contrast is given through an IV placed in a vein in your child's arm. The table will be moved into an open space in the middle of the machine. Your child will need to lie still during the MRI. It is normal to hear knocking, thumping, or clicking noises from the machine.
 |
Risks of an MRI:
An MRI may cause a metal object in your child's body to move out of place. This may cause serious injury, or stop the object from working properly.
Related medications
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has signs of an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Examples include trouble breathing, mouth or face swelling, and fainting.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child is dizzy or feels faint.
- Your child has a rash, itching, or swollen skin.
- Your child has nausea or is vomiting.
- Your child is suddenly urinating less than usual.
Call your child's doctor if:
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Have your child drink liquids as directed:
Liquids will help flush the contrast liquid out of your child's body. Ask how much liquid your child should drink, and which liquids are best for him or her.
Follow up with your child's doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
