Migraine Headache
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
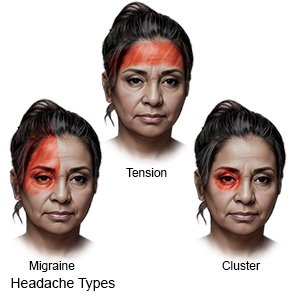
A migraine is a severe headache. The pain can be so severe that it interferes with your daily activities. A migraine can last a few hours up to several days. The exact cause of migraines is not known.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone call if:
- You feel like you are going to faint, you become confused, or you have a seizure.
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have a headache that seems different or much worse than your usual migraine headache.
- You have a severe headache with a fever or a stiff neck.
- You have new problems with speech, vision, balance, or movement.
Call your doctor or neurologist if:
- Your migraines interfere with your daily activities.
- Your medicines or treatments stop working.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
Some medicines may only be given while you are in the emergency department. You may also need medicines later to manage migraines or other health problems they can cause. Take medicine as soon as you feel a migraine begin, or as directed.
- Migraine medicines are used to help prevent or stop a migraine.
- NSAIDs help decrease swelling and pain or fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- Antinausea medicine may be given to calm your stomach and to help prevent vomiting. This medicine can also help relieve pain.
- Steroids may be given to prevent a migraine from coming back right away.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage your symptoms:
- Rest in a dark, quiet room. This will help decrease your pain. Sleep may also help relieve the pain.
- Apply ice to decrease pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the ice pack with a towel and place it on your head. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour.
- Apply heat to decrease pain and muscle spasms. Use a small towel dampened with warm water or a heating pad, or sit in a warm bath. Apply heat on the area for 20 to 30 minutes every 2 hours. You may alternate heat and ice.
- Keep a migraine record. Write down when your migraines start and stop. Include your symptoms and what you were doing when a migraine began. Record what you ate or drank for 24 hours before the migraine started. Keep track of what you did to treat your migraine and if it worked. Bring the migraine record with you to visits with your healthcare provider.
Common triggers for a migraine include the following:
- Stress, eye strain, oversleeping, or not getting enough sleep
- Hormone changes in women from birth control pills, pregnancy, menopause, or during a monthly period
- Skipping meals, going too long without eating, or not drinking enough liquids
- Certain foods or drinks such as chocolate, hard cheese, alcohol, or drinks that contain caffeine
- Foods that contain gluten, nitrates, MSG, or artificial sweeteners
- Sunlight, bright or flashing lights, loud noises, smoke, or strong smells
- Heat, humidity, or changes in the weather
Prevent another migraine:
- Prevent a medicine overuse headache. Take pain medicines only as long as directed. A medicine may be limited to a certain amount each month. Your healthcare provider can help you create a plan so you get a safe amount each month. Blood pressure medicine, antidepressants, or antiseizure medicine may be used to prevent migraines. This can help lower the amount of migraine medicine you need.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can trigger a migraine or make it worse. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Do not drink alcohol. Alcohol can trigger a migraine. It can also keep medicines used to treat your migraines from working.
- Be physically active. Physical activity, such as exercise, may help prevent migraines. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best activity plan for you. Try to get at least 30 minutes of physical activity on most days.

- Manage stress. Stress may trigger a migraine. Learn new ways to relax, such as deep breathing.
- Create a sleep schedule. Go to bed and get up at the same times each day. Do not watch television before bed.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Include healthy foods such as fruit, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meat, and fish. Do not have food or drinks that trigger your migraines.

- Drink more liquids to prevent dehydration. Your healthcare provider can tell you how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
Follow up with your doctor or neurologist as directed:
Bring your migraine record with you. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Migraine Headache
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
