Heart Attack
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
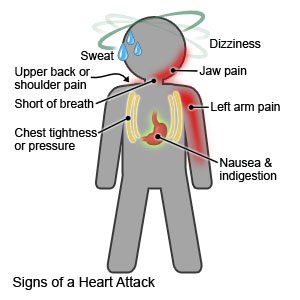
A heart attack happens when the blood vessels that supply blood to your heart are blocked. This can damage your heart or lead to an abnormal heart rhythm or heart failure. A heart attack is also called a myocardial infarction.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Activity:
Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Call a healthcare provider before you get out of bed. Do not try to get out of bed by yourself. Tell your healthcare provider if you feel weak, dizzy, or like you are going to faint.
You may need extra oxygen
if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils. Ask your healthcare provider before you take off the mask or oxygen tubing.
You may need to wear pressure stockings.
The stockings are tight and put pressure on your legs. This improves blood flow and helps prevent clots.
Heart medicines:
- Nitroglycerin opens the arteries to your heart so the heart gets more oxygen. Nitroglycerin can be given in an IV, by mouth, or as a patch or paste.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors help relax your blood vessels so your heart can get the blood it needs.
- Aldosterone antagonists help remove extra fluid from your body and protect your heart from more damage.
- Beta-blockers decrease your blood pressure and help you have a steady and regular heartbeat.
- Calcium channel blockers slow your heartbeat, open up small blood vessels, and decrease your blood pressure.
Related medications
Other medicines:
- Aspirin may be given to help thin your blood to keep clots from forming. This medicine makes it more likely for you to bleed or bruise.
- Clot busters help break apart blood clots to increase blood flow to your heart. It is given in your IV and may be given at the same time as other blood thinners. This medicine may decrease the amount of damage to your heart. You will bleed and bruise more easily while you are getting this medicine.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
- Cholesterol medicine decreases the amount of cholesterol and plaque in your blood.
Monitoring:
- Pulse oximetry measures the amount of oxygen in your blood.

- An EKG records your heart rhythm and how fast your heart beats. It is used to check for damage to your heart.
- An arterial line is a tube that is placed into an artery, usually in the wrist or groin. An arterial line may be used to measure your blood pressure or to take a blood sample.
- A CVP line , or central line, is a catheter placed into a large blood vessel to give you medicines or fluids. It may also be hooked to a monitor to take pressure readings.
- A pulmonary artery catheter is a balloon-tipped catheter (thin tube) inserted through a vein in your neck or groin. It measures the pressure in your heart and lungs to show healthcare providers how your heart responds to heart medicine.
Tests:
- Blood tests will check for heart damage, and test your kidney function. They may also show how much oxygen and carbon dioxide is in your blood.
- An echocardiogram is a type of ultrasound. Sound waves are used to show the structure and function of your heart.
- Angiography is a test used to look for blockage in your coronary arteries, such as plaque or blood clots. A thin tube called a catheter is placed into an artery, usually in your groin. Contrast liquid is put through the catheter, and x-ray pictures are taken of the blood flow. Tell healthcare providers if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- A stress test helps healthcare providers see the changes that take place in your heart while it is under stress. Healthcare providers may place stress on your heart with exercise or medicine. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about this test.
Treatment:
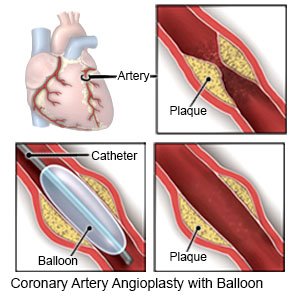
- Angioplasty is a procedure to open an artery blocked by plaque. A small tube with a balloon on the end is threaded into the blocked artery. After the tube is in the artery, the balloon is filled with liquid. As the balloon fills, it presses the plaque against the artery wall so blood can flow through the artery more easily.
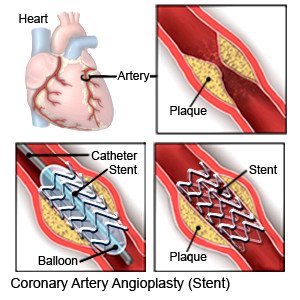
- Coronary intravascular stent placement is also called coronary artery stenting. The stent is a small mesh wire that is inserted into an artery to keep it open so blood can flow through it. When the stent is expanded, it attaches to the artery wall and keeps the artery open.
- Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) is a catheter that is inserted into a blood vessel in your groin. It has a balloon on the end that rests just outside of your heart. This balloon inflates and deflates in time with your heartbeat. An IABP can help increase blood flow through your body, while decreasing how hard your heart has to work. It may also help increase blood flow to your heart. You will need to stay in bed with your leg straight while you have an IABP.
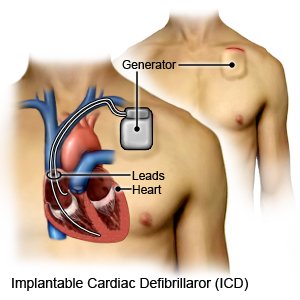
- An implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a small device that monitors your heart rate and rhythm. If your ICD senses that your heart is not beating correctly, it will give it a small electrical shock. This helps your heart start beating normally again.
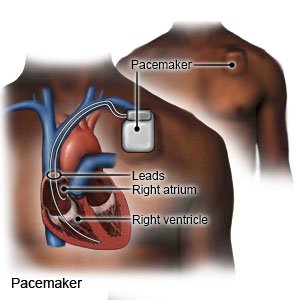
- A pacemaker is a machine that helps your heart beat at a normal speed and in a regular rhythm. The pacemaker can read your heart rhythm. If your heart does not beat as it should, the pacemaker sends small electric signals to your heart. You may have a temporary pacemaker, or it may be permanent.
- Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery is also known as heart bypass surgery or open-heart surgery. CABG can improve blood flow to your heart by sending blood around a blocked part of an artery. It may also decrease your risk for a heart attack in the future.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
Damage to your heart can lead to an abnormal heart rhythm. You may go into cardiogenic shock. This means your heart cannot get enough blood to your organs. You may develop heart failure. The damage from the heart attack may cause your heart to rupture. A heart attack can be life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Heart Attack
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
