Fundoplication in Adults
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about fundoplication:
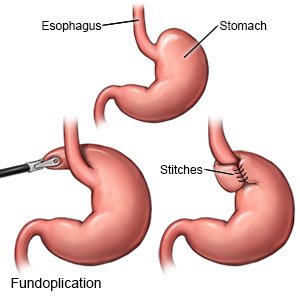
Fundoplication is surgery to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). During this surgery, the top part of your stomach is wrapped around the lower part of your esophagus. This prevents stomach acid from moving up into your esophagus.
How to prepare for surgery:
- You may need to have tests such as a scope or barium swallow in the weeks before surgery. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about these tests. Do not smoke for at least 4 weeks before surgery. Smoking can cause damage to your esophagus and prevent your body from healing properly. If you smoke and need help to quit, talk to your healthcare provider. You may need to stop taking blood thinning medicines for 1 week before surgery. He or she will tell you to use acetaminophen for pain instead of NSAIDs. NSAIDs can cause bleeding.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you not to eat or drink after midnight the night before your surgery. He or she will also tell you what medicines to take or not take the morning of your surgery.
What will happen during surgery:
- You will be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and pain free during your surgery. You will be given antibiotics to prevent an infection.
- Your surgery may be done as an open procedure. During an open procedure, a large incision will be made in your abdomen. Your healthcare provider will open your abdomen to do the surgery. Your surgery may instead, be done laparoscopically. Several small incisions will be made in your abdomen. Your healthcare provider will put a scope and tools through the incisions to do the surgery.
- The upper portion of your stomach will be wrapped around the esophagus. This will help the valve between the esophagus and stomach close better. Your healthcare provider may also repair the muscles of your esophagus if they are weak. The incisions are then closed with stitches or surgical tape and covered with bandages.
 |
What will happen after surgery:
Healthcare providers will help you walk to prevent blood clots. You may have a nasogastric (NG) tube in your nose. The NG tube goes through your nose into your stomach. It will be attached to suction. This will prevent fluid from backing up into your stomach. It also allows your surgery area to start healing. You may have a catheter in your bladder. You can leave the hospital when you are eating and drinking and your pain is controlled.
Risks of surgery:
You may bleed more than expected or get an infection. If your wrap slips or moves your GERD may come back or you may experience bloating or trouble swallowing. You may have a reaction to the anesthesia. Your esophagus, stomach, or other organs may be damaged during surgery.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have trouble breathing, chest pain, or a fast heart beat.
Related medications
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a fever or chills, stomach pain, nausea, or vomiting.
- You are bleeding.
- You have blood in your stools (may be bright red or black.)
Call your doctor if:
- You have pus or redness around your incision.
- You are unable to eat or drink.
- Your stomach is bloated.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent an infection caused by bacteria.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Slowly start to eat soft foods as directed. Ask your healthcare provider when you can resume your usual diet.
- Return to daily activities and exercise as directed. Slowly start to do more each day.
Wound care:
Keep your wounds clean and dry. When you are allowed to bathe or shower carefully wash your incisions with soap and water. Dry the area gently. Put on a new, clean bandage if directed.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
