Diverticulosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
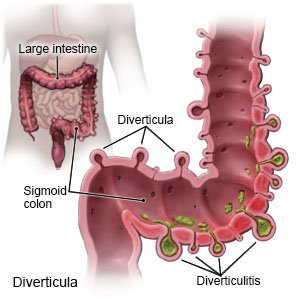
Diverticulosis is a condition that causes small pockets called diverticula to form in your intestine. These pockets make it difficult for bowel movements to pass through your digestive system.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have severe pain on the left side of your lower abdomen.
- Your bowel movements are bright or dark red.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever and chills.
- You feel dizzy or lightheaded.
- You have nausea, or you are vomiting.
- You have a change in your bowel movements.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
- Medicines to soften your bowel movements may be given. You may also need medicines to treat symptoms such as bloating and pain.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
The goal of treatment is to manage any symptoms you have and prevent other problems such as diverticulitis. Diverticulitis is swelling or infection of the diverticula. Your healthcare provider may recommend any of the following:
- Eat a variety of high-fiber foods. High-fiber foods help you have regular bowel movements. High-fiber foods include cooked beans, fruits, vegetables, and some cereals. Most adults need 25 to 35 grams of fiber each day. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you have more. Ask your healthcare provider how much fiber you need. Increase fiber slowly. You may have abdominal discomfort, bloating, and gas if you add fiber to your diet too quickly. You may need to take a fiber supplement if you are not getting enough fiber from food.

- Drink liquids as directed. You may need to drink 2 to 3 liters (8 to 12 cups) of liquids every day. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Apply heat on your abdomen for 20 to 30 minutes every 2 hours for as many days as directed. Heat helps decrease pain and muscle spasms.
Help prevent diverticulitis or other symptoms:
The following may help decrease your risk for diverticulitis or symptoms, such as bleeding. Talk to your provider about these or other things you can do to prevent problems that may occur with diverticulosis.
- Exercise regularly. Ask your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you. Exercise can help you have regular bowel movements. Get 30 minutes of exercise on most days of the week.

- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask him or her to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes increase your risk for diverticulitis. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Ask your healthcare provider if it is safe to take NSAIDs. NSAIDs may increase your risk of diverticulitis.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Diverticulosis
Treatment options
- Medications for Diverticulitis
- Medications for Diverticulitis with Hemorrhage
- Medications for Gastrointestinal Diverticula
- Medications for Gastrointestinal Diverticula with Hemorrhage
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
