Dilation and Curettage
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
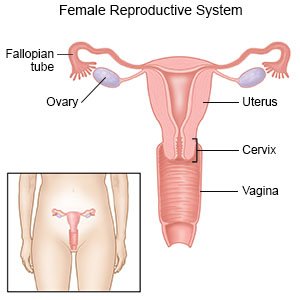
Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a procedure to remove tissue from the lining of your uterus.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have signs of an allergic reaction, such as hives, trouble breathing, or severe swelling.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have heavy vaginal bleeding that soaks 1 pad in 1 hour for 2 hours in a row.
- You have a fever higher than 100.4°F (38°C).
- You have abdominal cramps for more than 2 days.
- Your pain does not get better, even after treatment.
Related medications
Call your doctor or gynecologist if:
- You have foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
- You do not get your monthly period.
- You feel depressed or anxious.
- You feel very tired and weak.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Antibiotics help fight or prevent a bacterial infection.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Use sanitary pads if needed. You may have light bleeding for up to 2 weeks. Do not use tampons. Use sanitary pads instead. This will help prevent a vaginal infection.
- Rest as needed. Slowly start to do more each day. Return to your daily activities as directed.
- Do not have sex for at least 2 weeks after the procedure. This will help prevent an infection.
- Use birth control right after your procedure. Your monthly period should start again in 4 to 8 weeks. During this time, you could still ovulate (release an egg). Use birth control as directed to prevent pregnancy during this time.
Follow up with your doctor or gynecologist as directed:
Your uterus will be checked to make sure it is healing. You may also be given results of any tests done on removed tissue. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
