Bronchospasm
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Bronchospasm
is a narrowing of your airway that usually comes and goes. It may make it hard for you to breathe. Severe bronchospasm may be life-threatening. Severe bronchospasm may become life-threatening.
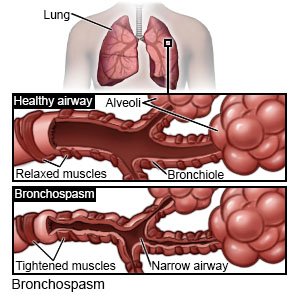 |
Bronchospasms may be triggered by one or more of the following:
- Family or personal history of asthma or allergies, such as to pollen, mold, dust, animal dander, latex, or food additives
- Upper respiratory infections such as a chest cold
- Exercise or increased activity
- Air irritants such as smoke, air pollution, strong odors, cold or dry air, or too much air from a ventilator
- Medicines such as antibiotics, blood pressure medicines, aspirin, or NSAIDs
Signs and symptoms of bronchospasm:
- Trouble breathing, often at night, in the morning, or during or after exercise
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing (whistling sound when you breathe)
- Chest tightness and pressure
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have chest pain.
- You have severe shortness of breath or trouble breathing.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Seek care immediately if:
- You cough or spit up blood.
- You are short of breath.
- You have blue fingernails or toenails.
- Your heartbeat is fast or not even.
Call your doctor or pulmonologist if:
- You have a fever.
- You have a cough that will not go away.
- Your wheezing worsens.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Bronchodilators help expand your airway for easier breathing. Some of these medicines may help prevent future spasms.
- Inhaled steroids help reduce swelling in your airway and soothe your breathing. These are used for long-term control.
- Anticholinergics help relax and open your airway.
Prevent bronchospasms:
- Avoid triggers. Your healthcare provider can help you identify your triggers. You may need to keep a diary of your symptoms. Include where you were and what you were doing when symptoms started. Also include how long symptoms lasted. Make a note of anything that helped or made your symptoms worse. Bring your diary to visits with your healthcare provider. He or she may also recommend skin prick tests or other tests to help find triggers.
- Warm up before you exercise. Ask your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you.
- Keep your immune system healthy. Try to avoid people who are sick. Ask about vaccines you may need. Vaccines help prevent certain infections that can cause breathing problems. Your provider can tell you if you should also get vaccines not listed below:
- Get an influenza (flu) vaccine as directed. The flu vaccine is recommended for everyone 6 months or older. Get the vaccine as soon as recommended each year, usually in September or October.
- Get a pneumonia vaccine as directed. The vaccine is recommended for all adults aged 50 or older. Adults aged 19 to 49 years who are at high risk for pneumonia should also receive the vaccine. You may need 1 dose or 2. The number depends on the vaccine used and your risk factors. Children routinely receive 4 doses of the pneumonia vaccine, starting at 2 months.
- Get a COVID-19 vaccine as directed. At least 1 dose of an updated vaccine is recommended for everyone 6 months or older. COVID-19 vaccines are given as a shot in 1 to 3 doses, depending on the age of the person who receives it. COVID-19 vaccines are updated throughout the year. Your healthcare provider can help you schedule all needed doses as updated vaccines become available.
- Breathe through your nose when you are in cold, dry air or weather. This may help reduce lung irritation by warming the air before it reaches your lungs.
Follow up with your doctor or pulmonologist as directed:
You may need more testing to find the cause of your condition. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Bronchospasm
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
