OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray
This treatment applies to the following species: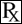 Company: Zoetis
Company: Zoetis
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug for oral use in dogs only.
OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray Caution
Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
|
WARNING Repeated use of meloxicam in cats has been associated with acute renal failure and death. Do not administer meloxicam transmucosal oral spray to cats. See Contraindications for detailed information. |
Description
Meloxicam belongs to the oxicam class of non-narcotic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). Each milliliter of OroCAM contains 5 mg meloxicam. Meloxicam is a yellow crystalline powder described chemically as 4 - Hydroxy - 2 - methyl - N - (5 - methyl - 2 - thiazolyl) - 2H - 1,2 - benzothiazine - 3 - carboxamide1,1 - dioxide with the following structural formula:
Indication:
OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray is indicated for the control of pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis in dogs.
Dosage and Administration
Always provide client information sheet with prescription.
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of OroCAM and other treatment options before deciding to use OroCAM.
Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual response. Due to the pump sizes, dogs weighing less than 5.5 pounds (2.5 kg) cannot be accurately dosed. OroCAM should be administered once daily at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg (0.045 mg/lb). See Bottle/Pump Assembly Instructions for Veterinarians and Administration Instructions for Owners.
Particular care should be given with regard to the accuracy of dosing and to selecting the correct bottle size based on the weight of the dog. See the Dosing Table below.
|
Weight range (kg) |
Weight range (lbs) |
Bottle Size (mL) / mg per spray |
No. of Sprays/treatment |
Dose amount (mg) |
|
2.5 - 3.7 |
5.5 - 8.3 |
6 / 0.25 |
1 |
0.25 |
|
3.8 - 6.2 |
8.4 - 13.8 |
6 / 0.25 |
2 |
0.50 |
|
6.3 - 8.3 |
13.9 - 18.4 |
6 / 0.25 |
3 |
0.75 |
|
8.4 - 12.5 |
18.5 - 27.6 |
11 / 0.50 |
2 |
1 |
|
12.6 - 18.8 |
27.7 - 41.5 |
11 / 0.50 |
3 |
1.50 |
|
18.9 - 27.1 |
41.6 - 59.7 |
33 / 1.075 |
2 |
2.15 |
|
27.2 - 40.5 |
59.8 - 89.1 |
33 / 1.075 |
3 |
3.23 |
|
40.6 - 54.0 |
89.2 - 118.8 |
33 / 1.075 |
4 |
4.3 |
|
54.1 - 57.2 |
118.9 - 125.8 |
33 / 1.075 |
5 |
5.38 |
Bottle/Pump Assembly Instructions for Veterinarians
Prior to dispensing, the pump should be screwed on to the bottle securely, the bottle gently shaken, and then the pump primed by actuating ten times (or until a fine spray appears) into an absorbent material. Once a bottle is assembled, the assembly date should be written on the bottle and the owner instructed to discard the bottle after 6 months. Wash hands after assembly.
Administration Instructions for Owners
OroCAM should be given according to your veterinarian’s instructions. Prior to each use, shake the bottle gently. If OroCAM is not used for two days or more, owners should reprime with one spray into an absorbent material, or until a fine spray appears. In case of pump failure, wipe nozzle and then re-prime the pump. If a partial dose has been administered to the pet due to pump failure, do not redose; wait until the next dosing time to administer OroCAM.
To administer OroCAM, grasp the corner of your dog’s mouth and gently pull it away from the gums, opening the cheek space. Place the tip of the applicator just inside the cheek space, directed towards the back of the cheek space. Holding the bottle and pump upright, fully depress the spray head taking special care to ensure no spray escapes from the mouth. If multiple sprays have been prescribed by your veterinarian, allow the pump to fully reflate before administering consecutive sprays. Immediately after administration of the spray, use a moist paper towel or tissue to clean the tip of the pump. Wash hands after administration of the product.
The end of the center tube should be covered by the fluid level. Once the fluid falls below the level of the center tube, sprays will not be adequate and the container should be replaced. There will be a residual volume of fluid at the bottom of the bottle which cannot be used.
Contraindications
OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray should not be used in dogs that have a hypersensitivity to meloxicam or known intolerance to NSAIDs. Do not use OroCAM in cats. Acute renal failure and death have been associated with the use of meloxicam in cats.
Warnings
Animal Warnings
For oral use in dogs only.
Due to the pump sizes, dogs weighing less than 5.5 pounds (2.5 kg) cannot be accurately dosed. All dogs should undergo a thorough history and physical examination before the initiation of NSAID therapy. Appropriate laboratory testing to establish hematological and serum biochemical baseline data is recommended prior to and periodically during administration of any NSAID. Owners should be advised to observe for signs of potential drug toxicity (see Adverse Reactions and Animal Safety) and be given a Client Information Sheet about OroCAM Transmucosal Oral Spray.
Human Warnings
Not for use in humans. Keep this and all medications out of reach of children. Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans or contact with mucous membranes. Direct contact with skin, eyes, and mucous membranes should be avoided. If contact occurs with skin, the area should be washed immediately with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. In case of contact with eyes, flush immediately with water. Women in late pregnancy should avoid contact with this product.
Precautions
The use of OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray has not been evaluated in dogs younger than 6 months of age, dogs weighing less than 5.5 lbs (2.5 kg), dogs used for breeding, or in pregnant or lactating dogs. Meloxicam is not recommended for use in dogs with bleeding disorders, as safety has not been established in dogs with these disorders. As a class, cyclo-oxygenase inhibitory NSAIDs may be associated with gastrointestinal, renal and hepatic toxicity. Sensitivity to drug-associated adverse events varies with the individual patient. Dogs that have experienced adverse reactions from one NSAID may experience adverse reactions from another NSAID. Patients at greatest risk for renal toxicity are those that are dehydrated, on concomitant diuretic therapy, or those with existing renal, cardiovascular, and/or hepatic dysfunction. Concurrent administration of potentially nephrotoxic drugs should be carefully approached. NSAIDs may inhibit the prostaglandins that maintain normal homeostatic function. Such anti-prostaglandin effects may result in clinically significant disease in patients with underlying or pre-existing disease that has not been previously diagnosed. Because NSAIDs possess the potential to induce gastrointestinal ulcerations and/or perforations, concomitant use with other anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids, should be avoided.
If additional pain medication is needed after administration of the total daily dose of OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray, a non-NSAID, or non-corticosteroid class of analgesia, should be considered. The use of another NSAID is not recommended. Consider appropriate washout times when switching from corticosteroid use or from one NSAID to another.
The use of concomitantly protein-bound drugs with OroCAM™ (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray has not been studied in dogs. Commonly used protein-bound drugs include cardiac, anticonvulsant and behavioral medications. The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit metabolism of OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy.
Adverse Reactions
Field safety was evaluated in 280 dogs. There were a total of 79 adverse reactions observed in the meloxicam group (N=187) and 37 adverse reactions observed in the placebo group (N=93); some dogs may have experienced more than one type or occurrence of an adverse reaction. The most common adverse reactions involved the gastrointestinal system (see the following Table). Non-gastrointestinal adverse reactions were rare and included increased liver enzymes, hematuria, lethargy, polydipsia, and dehydration.
The incidence of adverse reactions observed in the study is tabulated below. The pattern suggests some gastrointestinal effects (vomiting, diarrhea) associated with OroCAM. The clinical signs were generally mild, transient (lasted 1-4 days during the 28-day study period), and resulted in complete recovery. There were no clinical signs related to the increased liver enzymes.
Table of Adverse Reactions Reported in the Field Study
|
Adverse Reaction* |
Meloxicam Transmucosal Oral Spray N = 187 |
Placebo (vehicle) N = 93 |
|
Vomiting |
22 |
6 |
|
Increased Liver Enzymes (ALT and/or Alk Phos) |
11 |
6 |
|
Diarrhea |
8 |
2 |
|
Lethargy |
6 |
2 |
|
Inappetence |
4 |
2 |
|
Hematuria |
1 |
0 |
|
Polydipsia |
1 |
1 |
|
Dehydration |
1 |
0 |
* Dogs may have experienced more than one type or occurrence of an event during the study.
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the MSDS, contact Abbott Animal Health at (888) 299-7416.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact the FDA at 1-888-FDAVETS or online at http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth
Information for Dog Owners
OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray, like other drugs of its class, is not free from adverse reactions. Owners should be advised of the potential for adverse reactions and be informed of the clinical signs associated with drug intolerance. Adverse reactions may include vomiting; diarrhea; decreased appetite; dark or tarry stools; increased water consumption; increased urination; anemia; yellowing of gums, skin, or white of the eye due to jaundice; lethargy; incoordination; seizure; or behavioral changes. Serious adverse reactions associated with this drug class can occur without warning, and in rare situations, result in death (see Warnings and Adverse Reactions). Owners should be advised to discontinue OroCAM (meloxicam) Transmucosal Oral Spray and contact their veterinarian immediately if signs of intolerance are observed. The vast majority of patients with drug related adverse reactions have recovered when the signs are recognized, the drug is withdrawn, and veterinary care, if appropriate, is initiated. Owners should be advised of the importance of periodic follow-up for all dogs during administration of any NSAID.
Clinical Pharmacology
Absorption
Meloxicam is rapidly absorbed following oral transmucosal administration of OroCAM. Following administration of 0.2 mg/kg of OroCAM to 20 female adult Beagle dogs, the mean (± 1SD) peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was 0.62 ± 0.06µg/mL and the mean time to peak concentration (Tmax) was 4.5 [Range: 0.5 to 8] hours.
Distribution
There is a linear relationship between the dose of OroCAM administered and plasma meloxicam concentrations observed in the therapeutic dose range (0.1-0.2 mg/kg). Approximately 97% of meloxicam is bound to plasma proteins. The mean apparent volume of distribution (V/F) is 0.30 ± 0.02 L/kg.
Metabolism
Meloxicam is predominantly found in plasma and is also a major biliary excretion product. Urine contains only traces of the parent compound. Meloxicam is metabolized to an alcohol, an acid derivative, and to several polar metabolites. All major metabolites have been shown to be pharmacologically inactive.
Elimination
Approximately 75% of the administered dose is eliminated via feces and the remainder is eliminated via urine. Following oral transmucosal administration of OroCAM, meloxicam is eliminated from plasma with a mean apparent clearance (CL/F) of 0.007 ± 0.001 L/hr/kg and a mean half-life of 30 ± 4 hours.
Effectiveness
Effectiveness was demonstrated using OroCAM in a masked, placebo-controlled, multi-site field study involving client-owned dogs. In this study, 280 dogs diagnosed with osteoarthritis were randomly administered OroCAM, or a placebo. Dogs received a daily meloxicam dose, equivalent to 0.1 mg/kg, or placebo for 28 days. Effectiveness was evaluated in 258 dogs (n=170 in the OroCAM group, n=88 in the placebo group) and field safety was evaluated in 280 dogs. Treatment success for each dog was based on a client-specific outcomes measure (CSOM), a parameter evaluated by dog owners. There was a statistically significant difference (p< 0.05) and numerically more successfully-treated dogs in the OroCAM group than the placebo group. The percent of treatment successes on Day 28 was 73% in the OroCAM group and 47% in the placebo group.
Dose Acceptance
The same pump apparatus was used in both treatment groups.
There was no apparent change in the level of acceptance over the course of the 28-day treatment period. At the end of the treatment period, owners were asked to indicate whether or not the dose procedure was acceptable. Of the 205 owners that provided a response, 85.1% indicated that the dosing procedure was acceptable and 14.9% indicated that the dosing procedure was not acceptable.
Owner observations of dog’s reactions to dosing included [reaction (number of dogs exhibiting reaction)]: coughing/gagging (3), sneezing (2), drooling (1), spitting (1), wheezing (1), smacking lips (1), rubbing face on bedding (1).
Animal Safety:
Six Month Laboratory Safety Study
In a six month target animal safety study, meloxicam transmucosal oral spray was administered to the oral mucosa of healthy adult Beagle dogs (eight dogs per group) at 1x, 2x, 3x, and 5x the recommended dose. Gastrointestinal adverse effects were the main clinical signs observed during the study. There were a higher number of vomiting episodes in dogs exposed to meloxicam transmucosal oral spray than in dogs in the control group. The highest number of vomiting episodes occurred in the 5x treatment group. Episodes of blood in feces were seen in all treatment groups; however, the largest number of dogs exhibiting at least one episode occurred in the 5x group. There were a similar number of episodes of feces with abnormal consistency in all five groups.
Treatment-related decreases were seen in white blood cell (WBC) and absolute neutrophil counts in dogs in the 1x, 2x, and 3x treatment groups. Treatment-related decreases in albumin values were seen in dogs in the 1x, 3x, and 5x treatment groups. Elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) values, above the reference range, were seen in four study dogs; one control (0x) dog, one 1x dog, and two 3x dogs. All increases were less than two times the upper limit of the reference range. One 1x dog exhibited an alanine aminotransferase (ALT) value on week 4 that was between two and three times the upper limit of the reference range. This same dog had a mildly elevated ALT value at baseline.
Endoscopic lesions of the pyloric antrum were seen in multiple study dogs in the control and treatment groups. Pyloric lesions, consisting of erosions, hemorrhage, or striations, were recorded at baseline and frequently throughout the study period, making interpretation of clinical significance difficult. Erosions were seen on week 8 in the proximal duodenum of one 1x dog, one 2x dog, and one 3x dog. One dog in the 2x group exhibited erosions in the fundus on week 26. One dog in the 3x group exhibited erosions or hemorrhage in the cardia on week 26. One control (0x) dog had erosive lesions in the lesser curvature, cardia, and proximal duodenum on week 8, and the fundus on week 26. This dog was diagnosed on week 8 with acute necrotizing enteritis. None of the endoscopic lesions correlated with findings on gross pathology examination.
Quantifiable meloxicam concentrations were found in all control (0x) dogs throughout the study. Concentrations were well below the amounts found in dogs in the 1x to 5x treatment groups.
Gross pathology revealed an ulcer in the fundic mucosa of one 3x dog, and several shallow pink erosions in the duodenal mucosa of one 5x dog.
3 month Laboratory Safety Study - Local Tolerance
In a 3 month target animal safety study, meloxicam transmucosal oral spray was administered to the oral mucosa of 6 to 7 month old healthy Beagle dogs. There were two treatment groups.
Group 1 received water as a control. Group 2 received 2x the recommended daily dose of the final formulation of meloxicam transmucosal oral spray on the first day of the study, and 1x the recommended daily dose thereafter. No treatment-related lesions were seen at dosing sites. Clinical pathology variables did not exhibit clinically relevant treatment-related effects.
Gastrointestinal adverse clinical effects, mostly vomiting, were noted.
Storage Conditions: Store at controlled room temperature, between 20°-25°C (68°-77°F). Brief excursions between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F) are permitted. Shelf-life after first opening the container: 6 months. At the time of pump/bottle assembly, the assembly date should be written on the label and the owner should be instructed to discard the bottle after 6 months. Do not use after the expiry date stated on the carton and the bottle. Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
How Supplied
OroCAM is supplied in three vial sizes containing 6 mL, 11 mL and 33 mL of meloxicam. Each vial has a different metered dose pump delivering a dose of 0.25 mg, 0.50 mg, or 1.075 mg, per spray, respectively.NADA 141-346, Approved by FDA
Manufactured for Abbott Laboratories, North Chicago, IL 60064 USA
Rev 2012
Product of Spain
04943-04
A1-0065/R2
CPN: 3690507.0
333 PORTAGE STREET, KALAMAZOO, MI, 49007
| Telephone: | 269-359-4414 | |
| Customer Service: | 888-963-8471 | |
| Website: | www.zoetis.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". DVMetrics assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the DVMetrics service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2025 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2025-08-27
