Excede 200 Sterile Suspension (Canada)
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Zoetis
Company: Zoetis
ceftiofur crystalline free acid sterile injectable suspension
DIN 02360586
Veterinary Use Only
For subcutaneous injection at the base of the ear only in cattle and for intramuscular injection in horses
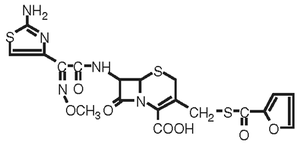
DESCRIPTION: EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is a ready-to-use formulation that contains ceftiofur crystalline free acid, the designation for 7 - [[2 - (2 - Amino - 4 - thiazolyl) - 2 - (methoxyimino)acetyl]amino] - 3 - [[(2 - furanylcarbonyl)thio]methyl] - 8 - oxo - 5 - thia - 1 - azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct - 2 - ene 2-carboxylic acid.
Ceftiofur crystalline free acid is a broad spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic active against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria including β-lactamase-producing strains. Like other cephalosporins, ceftiofur is bactericidal, in vitro, resulting from inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
Each mL contains 200 mg ceftiofur equivalents (as ceftiofur crystalline free acid).
Figure 1. The chemical structure of ceftiofur crystalline free acid.
Excede 200 Sterile Suspension Indications
Cattle (including lactating dairy cattle): EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is indicated for the treatment of Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida and Histophilus somni (Haemophilus somnus).
EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is also indicated for the treatment of bovine foot rot (interdigital necrobacillosis) associated with Fusobacterium necrophorum and Porphyromonas levii.
Horses: EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is indicated for the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections in horses caused by susceptible strains of Streptococcus equi ssp. zooepidemicus.
Dosage and Administration
Shake well before using. Shake bottle vigorously for at least 30 seconds before using. If the bottle is left sitting for more than 5 minutes, shake again to re-suspend the formulation.
Cattle:
Dosage: Administer a single dose of 6.6 mg ceftiofur equivalents (CE) per kg body weight (1.5 mL per 45 kg body weight) by subcutaneous (SC) injection in the base of the ear only. Follow carefully the injection procedure as described in the Administration section of the package insert.
Most animals will respond to treatment within three to five days. If no improvement is observed, the diagnosis should be reevaluated.
Table 1. Dose for EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension for cattle and horses.
|
Weight (kg) |
Weight (lb) |
Dose Volume (mL) at 6.6 mg/kg |
|
45 |
100 |
1.5 |
|
90 |
200 |
3.0 |
|
135 |
300 |
4.5 |
|
180 |
400 |
6.0 |
|
225 |
500 |
7.5 |
|
270 |
600 |
9.0 |
|
320 |
700 |
10.5 |
|
360 |
800 |
12.0 |
|
410 |
900 |
13.5 |
|
450 |
1000 |
15.0 |
Administration: EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is to be administered in cattle as a single SC injection in the base of the ear only, in the loose subcutaneous tissue at the posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head. EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is not to be administered in any other injection site in cattle (See Warnings).
Proper injection technique in cattle should be used when administering EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension.
Proper Injection Technique in cattle
● Complete immobilization with a halter is recommended during the period of familiarization with the injection technique.
● Avoid using in highly excited animals.
● The injection site should be clean (i.e., free from crusty debris, dirt or manure).
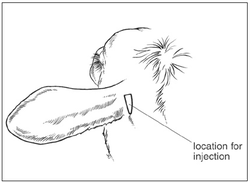
● The injection site is characterized by a natural depression behind the ear that is bounded by the ring-shaped auricular cartilage (forward), neck muscle (posterior) and the ear muscles (dorsal). See Figure 3.
● Hold the syringe and needle behind the ear to be dosed so the needle and syringe point in the direction of an imaginary line that would pass through the head toward the animal’s opposite eye. See Figures 2 and 3.
● Insert the needle through the loose skin in the dorsal posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head (base of the ear) while maintaining this angle. See Figure 2.
● The full length of the needle (1 inch long; 16 gauge) should be inserted under the skin.
● Smaller cattle or those of less body condition may have differing subcutaneous space at the base of the ear. The choice of needle should be consistent with the size and condition of cattle.
● Take appropriate precautions to avoid intra-arterial or intravenous injection.
● Deliver the entire contents of the syringe in the loose subcutaneous tissue.
Figure 2. Subcutaneous administration of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at the dorsal posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head (base of the ear).
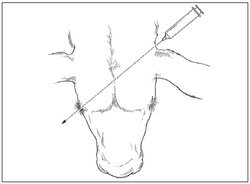
Figure 3. Injection location for the subcutaneous administration of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at the dorsal posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head (base of the ear).
● Inject slowly. In cold weather, keep at room temperature to improve syringeability and ease of administration.
For additional guidance on the proper injection technique in cattle please contact Zoetis Canada Inc., at toll-free 1-800-461-0917.
Horses:
Administer two intramuscular injections to horses, 4 days apart, at a dose of 6.6 mg ceftiofur equivalents (CE) per kg body weight (1.5 mL per 45 kg body weight) see Table 1. A maximum of 20 mL per injection site may be administered. Therapeutic drug concentrations are maintained for 6 days after the second injection (or a total of 10 days from the beginning of treatment) against Streptococcus equi ssp. zooepidemicus.
Contraindications
The use of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is contraindicated in animals previously found to be hypersensitive to the drug.
The use of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is contraindicated in animals with known allergy to ceftiofur or to β-lactam (penicillins and cephalosporins) group antimicrobials. Due to the extended exposure in horses, based on the drug’s pharmacokinetic properties, adverse reactions may require prolonged care.
|
CAUTIONS: Administration of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension into the arteries of the ear of cattle is likely to result in sudden death to the animal. |
Cattle: Do not administer EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at any site other than in the subcutaneous tissue at the base of the ear. As with other parenteral injections, localized post-injection bacterial infections may result in abscess formation. Attention to hygienic procedures can minimize their occurrence. Subcutaneous injection in cattle can cause a local tissue reaction that may result in trim loss of edible tissue at slaughter.
Horses: The administration of antimicrobials to horses under conditions of stress may be associated with acute diarrhea that can be fatal. If acute diarrhea is observed, additional doses of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension should not be administered and appropriate therapy should be initiated. Due to the extended exposure in horses, based on the drug’s pharmacokinetic properties, adverse reactions may require prolonged care. EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is slowly eliminated from the body, with approximately 17 days needed to eliminate 97% of the dose from the body. Animals experiencing adverse reactions may need to be monitored for this duration of time. The use of ceftiofur has not been evaluated in horses less than 4 months of age and in breeding, pregnant, or lactating horses. Persistent muscle stiffness and injection site swelling may occur (see Adverse Reactions). The long term effects on injection sites have not been evaluated.
Warnings
● Treated cattle must not be slaughtered for use in food for at least 13 days after the latest treatment with EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension.
● No milk withholding time is required when the drug is used according to the label directions.
● In cattle, administration by unapproved routes such as subcutaneous in the neck, intramuscular, or intramammary may lead to illegal residues.
● Do not use in horses intended for food.
● Do not use in veal calves. The withdrawal period has not been established in pre-ruminating calves.
● To limit the development of antimicrobial resistance:
• EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension should not be used as a mass medication.
• EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension should only be used for treating individual animals as per the indications. The choice of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension as the most appropriate treatment should be confirmed by clinical experience supported where possible, by pathogen culture and drug susceptibility testing.
• The extra-label use of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is not recommended.
● Penicillins and cephalosporins can cause allergic reactions in sensitized individuals. Topical exposures to such antimicrobials, including ceftiofur, may elicit mild to severe allergic reactions in some individuals. Repeated or prolonged exposure may lead to sensitization. Avoid direct contact of the product with the skin, eyes, mouth and clothing. Sensitization of the skin may be avoided by wearing latex gloves. Persons with a known hypersensitivity to penicillins or cephalosporins should avoid exposure to this product. In case of accidental eye exposure, flush with water for 15 minutes. In case of accidental skin exposure, wash with soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing. If allergic reaction occurs (e.g. skin rash, hives, difficult breathing) seek medical attention.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Adverse Reactions
Cattle: Visible swellings have been noted at the injection site in about two thirds of treated animals, two days after injection in field conditions. These reactions will resolve within a maximum of 23 days. Injection site swellings may result in mild to moderate pain in some animals in the initial days following injection.
In very rare cases (i.e. in less than 1 out of 10000 animals), sudden death has been reported following administration of the product. In such cases, death has been attributed to intra-vascular administration of the product or anaphylaxis.
|
REPORTING SUDDEN DEATH CASES: Veterinarians should report any suspected adverse drug reaction including deaths occurring within 60 minutes of product administration and deaths preceded by recumbency and neurological signs, to Zoetis Canada Inc., at toll free 1-800-461-0917. Non-veterinarians should report any suspected adverse drug reaction, including cases of sudden death, to their veterinarian. |
Horses: The injection of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension in the horse may cause firmness, swelling/edema, pain, at the injection site and/or pyrexia (see ANIMAL SAFETY).
A total of 373 horses of various breeds, ranging in age from 4 months to 20 years, were included in the field study safety analysis. Adverse reactions reported in horses treated with EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension and the placebo control are summarized in Table 2.
Injection site swelling (edema) was reported in 10 of 278 (3.6%) EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension-treated horses and 1 of 95 (1%) of the placebo-treated horses. Of the 10 EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension-treated horses with injection site swelling, 8 horses had swellings of 4 cm or less in diameter, one horse had a 10 cm diameter swelling and one horse had injection site reactions to both injections measuring 25 x 12 cm each. The injection site reactions in EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension-treated horses resolved over 1 to 20 days.
At least one episode of diarrhea, loose, soft, or cowpie stools were observed in 25 of 278 (9%) of the Excede-treated horses and 7 of 95 (7%) of the placebo-treated horses. The duration of episodes in Excede-treated horses ranged from a single observation of loose stool to observations lasting 6 days. All cases were self-limiting and resolved with minimal (a single dose of loperamide) or no treatment.
Table 2. Number of horses with adverse reactions during the field study with EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension.
|
Adverse Reaction |
EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension (n=278) |
Placebo (n = 95) |
|
Diarrhea/Soft Stool |
25 (9%) |
7 (7%) |
|
Injection Site Swelling |
10 (4%) |
1 (1%) |
Clinical Pharmacology
Ceftiofur administered as either ceftiofur sodium (EXCENEL® brand of ceftiofur sodium sterile powder), ceftiofur hydrochloride (EXCENEL® RTU brand of ceftiofur hydrochloride sterile suspension) or ceftiofur crystalline free acid (EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension) is metabolized rapidly to desfuroylceftiofur, the primary metabolite.
Cattle: Administration of ceftiofur to cattle as ceftiofur crystalline free acid provides effective concentrations of ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur-related metabolites in plasma above the MIC90 for BRD label pathogens Pasteurella multocida, Mannheimia haemolytica and Histophilus somni for generally not less than 150 hours (6 1/4 days) after a single administration (see Figure 4).
Figure 4. Average plasma concentration of ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur-related metabolites after administration of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at 6.6 mg CE/kg SC via subcutaneous injection into the base of the ear (BOE Cattle) in beef cattle as well into the base of the ear (BOE Lactating) in lactating dairy cattle.
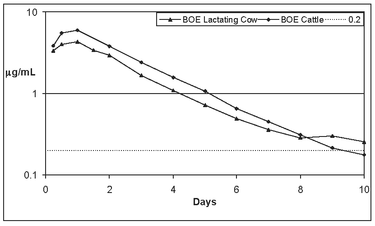
Beef cattle excrete ceftiofur and related residues by both urine and fecal routes whereas lactating dairy cows also excrete ceftiofur related residues through milk, resulting in lower average plasma concentrations. Mean concentrations above 0.2 µg/mL were greater than 168 hours (7 days) for both beef and dairy cattle.
Table 3. Pharmacokinetic parameters measured after a single SC administration of 6.6 mg CE/kg body weight (BW) of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension in the base of the ear.
|
Pharmacokinetic Parameter |
Beef Mean Value ± Standard Deviation |
Lactating Dairy Cattle Mean Value ± Standard Deviation |
|
Cmax (µg/mL) |
6.39 ± 1.79 |
4.44 ± 1.65 |
|
tmax (h) |
19.8 ± 5.81 |
19.00 ± 8.02 |
|
AUC0-LOQ (µg•h/mL) |
412 ± 67.3 |
313 ± 85.5 |
|
t>0.2, model (h) |
NE |
NE |
|
t>0.2, nca (h) |
218 ± 45.5 |
205 ± 35.7 |
|
t1/2 (h) |
40.7 ± 11.2 |
43.92 ± 9.84 |
Cmax = maximum plasma concentration (in µg CE/mL).
tmax = the time after injection when Cmax occurs (in hours).
AUC 0-LOQ = the area under the plasma concentration vs. time curve from time of injection to the limit of quantitation of the assay (0.15 µg CE/mL).
t>0.2, model = the time plasma concentrations remain above 0.2 µg CE/mL (in hours), estimated using compartmental pharmacokinetic techniques.
t>0.2, nca = the time plasma concentrations remain above 0.2 µg CE/mL (in hours), estimated using non-compartmental pharmacokinetic techniques.
t1/2 = terminal phase biological half life (in hours).
NE = Not estimated.
Horses: Two intramuscular injections of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at a dose of 6.6 mg/kg body weight in the horse provide concentrations of ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur related metabolites in plasma above the therapeutic target of 0.2 µg/mL for the entire 96 hour (4 day) dosing interval and for 6 days after the second injection (or a total of 10 days from the beginning of treatment) (see Figure 5 and Table 4).
Figure 5. Average plasma concentration of ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur related metabolites in horses following the intramuscular administration of either EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at a dose of 6.6 mg/kg administered twice at a 96 hour interval or ceftiofur sodium at a dose of 2.2 mg/kg BW once daily for 10 consecutive days.
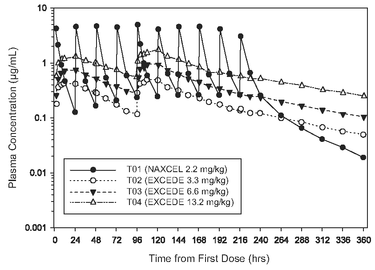
Table 4. Pharmacokinetic parameters measured after either two intramuscular injections of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at a dose of 6.6 mg/kg BW at a 96 hour interval or ceftiofur sodium at a dose of 2.2 mg/kg BW once daily for 10 consecutive days are summarized in the following table.
|
PK Parameter |
EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at 6.6 mg/kg BW administered twice 96 h apart |
ceftiofur sodium at 2.2 mg/kg BW once daily for 10 days |
||
|
AUC0-∞ (µg•h/mL) |
157 (19.1) |
353 (44.9) |
||
|
t>0.2 (h) |
262 (29.0) |
ND |
||
|
|
Dose 1 |
Dose 2 |
Dose 1 |
Dose 10 |
|
tmax (h) |
21.6 (5.8) |
15.6 (6.3) |
1.0 |
2.0 (3.3) |
|
Cmax (µg/mL) |
0.78 (0.19) |
1.0 (0.24) |
4.31 ± 0.78 |
3.99 (1.23) |
MICROBIOLOGY:
Cattle: Ceftiofur has demonstrated in vitro and in vivo activity against Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida and Histophilus somni, the three major pathogenic bacteria associated with BRD; and against Fusobacterium necrophorum and Porphyromonas levii associated with Foot Rot.
A summary of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) for various cattle pathogens is presented in Table 5. BRD isolates from 1988-1992 were obtained in the United States and Canada while BRD isolates from 1997-1998 and 1998-2002 were obtained in the U.S. Foot Rot isolates from 2006-2007 were obtained in the U.S. and Canada. Testing followed Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) Guidelines.1
Table 5.
|
*Species |
N |
MIC Range |
MIC90** |
Date tested |
|
Mannheimia haemolytica |
461 |
≤0.03-0.13 |
≤0.06 |
1988-1992 |
|
Pasteurella multocida |
318 |
≤0.03-0.25 |
≤0.06 |
1988-1992 |
|
Histophilus somni |
109 |
≤0.03-0.13 |
≤0.06 |
1988-1992 |
|
Mannheimia haemolytica |
110 |
≤0.03-0.25 |
≤0.06 |
1997-1998 |
|
Pasteurella multocida |
107 |
≤0.03-0.25 |
≤0.03 |
1997-1998 |
|
Histophilus somni |
48 |
≤0.03-0.25 |
≤0.03 |
1997-1998 |
|
Mannheimia haemolytica |
638 |
≤0.03-0.5 |
≤0.03 |
1998-2002 |
|
Pasteurella multocida |
733 |
≤0.03-0.5 |
≤0.03 |
1998-2002 |
|
Histophilus somni |
349 |
≤0.03-0.13 |
≤0.03 |
1998-2002 |
|
Fusobacterium necrophorum |
148 |
≤0.25 to >128 |
≤0.25 |
2006-2007 |
|
Porphyromonas levii |
141 |
≤0.25 to 16 |
≤0.25 |
2006-2007 |
* Clinical isolates supported by clinical data and indications for use.
** The minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of the strains.
The bacterial name Porphyromonas levii comes from the taxonomic reclassification of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies levii.
Ceftiofur breakpoints have been established for bacterial BRD pathogens for ceftiofur based on pharmacokinetic studies conducted with ceftiofur sodium and hydrochloride in cattle after a single intramuscular injection of 2.2 mg CE/kg BW in cattle, and the MIC and disk (30 µg) diffusion data. The following breakpoints are recommended by CLSI.
|
Zone Diameter (mm) |
MIC (µg/mL) |
Interpretation |
|
≥21 |
≤2.0 |
(S) Susceptible |
|
18-20 |
4.0 |
(I) Intermediate |
|
≤17 |
>8.0 |
(R) Resistant |
“Susceptible” or “S” indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited by generally achievable blood concentrations after treatment with ceftiofur sodium, ceftiofur hydrochloride or ceftiofur crystalline free acid. “Intermediate” or “I” is a technical buffer zone and isolates falling into this category should be retested. Alternatively the organism may be successfully treated if the infection is in a body site where drug is physiologically concentrated. “Resistant” or “R” indicates that the achievable drug concentrations are unlikely to be inhibitory and other therapy should be selected.
Standardized procedures1 require the use of laboratory control organisms for both standardized diffusion techniques and standardized dilution techniques. The 30 µg ceftiofur sodium disk should give the following zone diameters and the ceftiofur sodium standard reference powder (or disk) should provide the following MIC values for the reference strains. Ceftiofur sodium disks or powder reference standard are appropriate for both ceftiofur salts and ceftiofur crystalline free acid.
|
Organism Name (ATCC No.) |
MIC (µg/mL) |
Zone Diameter, mm Disk Content 30 µg |
|
E. coli ATCC 25922 |
0.25-1 |
26-31 |
|
S. aureus ATCC 29213 |
0.25-1.0 |
- |
|
S. aureus ATCC 25923 |
- |
27-31 |
|
P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 |
16.0-64.0 |
14-18 |
Horses: The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for ceftiofur against label-claim pathogens isolated from lower respiration tract infections in horses enrolled in a 2007-2008 field effectiveness study are presented in Table 6. All MICs were determined in accordance with the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) standards.
Table 6. Activity of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension against pathogens isolated from horses treated with EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension in field studies in the U.S. during 2007-2008
|
Disease |
Pathogen |
Treatment Outcome |
N |
Time of Sample Collection |
MIC50 (µg/mL) |
MIC90 (µg/mL) |
MIC Range (µg/mL) |
|
Lower Respiratory Tract Infection |
Streptococcus equi esp. zooepidemicus |
Success |
93* |
Pre-Treatment |
0.06 |
0.12 |
0.03-0.5 |
|
Failure |
42 |
Pre-Treatment |
0.06 |
0.25 |
0.03-0.5 |
* One horse cultured Staphylococcus aureus (successfully treated) and is not represented in the table.
ANIMAL SAFETY:
Cattle: After parenteral administration, EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension, ceftiofur sodium and ceftiofur hydrochloride accede to the same principal metabolite, desfuroylceftiofur. Therefore, studies conducted with ceftiofur sodium are adequate to evaluate the systemic safety of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension. Results from a five-day tolerance study conducted with ceftiofur sodium in normal feeder calves indicated that ceftiofur was well tolerated at 55 mg CE/kg/day for five consecutive days, approximately 8 times the label recommended dose of ceftiofur crystalline free acid (6.6 mg CE/kg). Ceftiofur administered parenterally had no adverse systemic effects.
In a 15-day safety/toxicity study, five steer and five heifer calves per group were administered ceftiofur sodium intramuscularly at 0 (vehicle control), 2.2, 6.6, 11 or 22 mg CE/kg/day. This represents up to 3.3 times the label recommended dose of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension of 6.6 mg CE/kg. There were no adverse systemic effects, indicating that ceftiofur has an adequate margin of safety when injected intramuscularly into feeder calves.
Three residue studies were conducted in which injection sites were observed daily and descriptive evaluation of the injected ears was recorded at necropsy.
Base of the ear in beef cattle: In the first study, the animals were necropsied from 5 to 14 days post-injection and none of the 60 animals had drooping ears. Ten (10) of the animals showed swelling at the injection site and of those 8 resolved prior to necropsy.
In the second study, 72 animals were injected at the dorsal posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head (base of the ear) at a dose rate of 6.6 mg/kg of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension (range of volume injected: 5.8 to 10.2 mL). Animals were necropsied between 4 and 13 days post-injection. None of the animals showed signs of drooping ears but all showed signs of swelling at some time after administration with 23 resolving prior to necropsy. At necropsy, signs of inflammation (hemorrhage, congestion, and firmness of tissue) and presence of drug material were seen in the area around the injection site and on the carcass. At 13 days post-injection, gross lesions were found in the inedible portions of the base of the ear in all 18 animals, and in the exposed carcass tissue in 11 of 18 animals.
Base of the ear in adult dairy cows: In the third study, 6 dairy cows were injected at the dorsal posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head (base of the ear) at a dose rate of 6.6 mg/kg of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension (range of volume injected: 19.4 to 29.3 mL). No animals exhibited drooping ears at any time after treatment but all animals had signs of swelling at the injection site at all observation times after treatment. Cows were slaughtered at 10 days after injection. At necropsy, all 6 cows showed evidence of injection site inflammation (discoloration of fat tissue/fascia) and 4 of 6 cows had discoloration of tissue dorsal and posterior to the ear canal on the carcass. In addition to discoloration, tan nodules and a milky white fluid exudate were also present at the sectioned surface.
The local tolerance of the ear to a single SC injection at the dorsal posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head (base of the ear) of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension was evaluated in a large multilocation field study in beef cattle. None of the 2926 animals treated with EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at the base of the ear were removed from the study due to ear irritation even though a few were observed with swelling of the injection site. No leak back or excessive bleeding was observed for 99.8% of animals receiving EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension. On Days 28 and 56 following injection of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension, 97.8% and 98.9% of ears were observed as normal with no injection site swelling and had >99% normal ear carriage on both days. It was concluded that administration of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at the base of the ear was acceptable in beef animals under feedlot conditions.
The local tolerance of the ear to a single SC injection at the dorsal posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head (base of the ear) of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension was evaluated in a multilocation field study in adult dairy cattle. None of the 114 animals treated with EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at the base of the ear were removed from the study due to ear irritation even though a few were observed with swelling of the injection site. No leak back or excessive bleeding was observed for 99.1% of animals receiving EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension. The volumes administered ranged from 15 to 30 mL. On Days 28 and 56 following injection of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension, 94.7% and 100% of ears were observed as normal with no injection site swelling on both days. It was concluded that administration of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at the base of the ear was acceptable in adult dairy cattle.
The consequences of purposeful intra-arterial injection of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension were investigated in feeder cattle. Two heifers (BW approximately 225 kg) were given a single 6.6 mg CE/kg bolus dose of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension in the middle auricular artery. Both heifers collapsed immediately and died within approximately eight minutes of injection. Intra-arterial injection of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension in the ear will result in death and must be avoided.
As a subcutaneous injection in the ear may potentially result in inadvertent intravenous administration of an injectable product, the consequences of purposeful intravenous injection of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension were investigated in feeder cattle. Three heifers and three steers (BW range 197-223 kg) were given a single 6.6 mg CE/kg bolus dose of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension in the jugular vein and were monitored for adverse effects following injection. One steer and one heifer had transient (2 - 5 minutes) increases in heart rate without any other untoward signs in these or the other cattle. Intravenous injection of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is an unacceptable route of administration.
Horses: Two studies, a target animal safety (TAS) study and a pharmacokinetic (PK) study (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY section), were conducted to assess the safety of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension in the horse.
In the TAS study, healthy adult horses received 6 intramuscular (lateral neck) injections of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at doses of either 6.6 (1X), 13.2 (2X) or 19.8 (3X) mg CE/kg with a 4 day interval between each injection. In the TAS study, there were no treatment related gastrointestinal findings for the three EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension treatment groups. In the PK study, one horse treated with 13.2 mg CE/kg (2X) EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension experienced a mild episode of colic the day after the second injection of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension. The horse recovered without treatment.
Injection sites were observed in both studies. In both studies, the largest injection volume administered was 20 mL per injection site. There were no observations of erythema, necrosis or drainage at the injection sites in these studies. Firmness, swelling, and/or pain were observed in at least one injection site in all horses treated at the label dose. In the TAS study, injection site reaction measurements ranged from no measurable reaction to 16 x 33 x 1.5 cm. In the PK study, the largest area of edema associated with the injection site ranged from no detectable reaction to 30 x 36 cm area of edema. Injection site reactions developed within 2 days of injection and resolved within 1-18 days. In the PK study, 2 horses had small areas of firmness that had not resolved at the end of the study (21 days after injection). In both studies, a greater incidence of injection site reactions occurred after the second injection, and in several horses, swelling at the injection site resolved then recurred 1-5 days later.
In the PK study, several horses developed clinical signs consistent with foot pain (stiff in the front limbs when turned in tight circles, and increased pulse and heat to the front feet). One horse in the ceftiofur sodium group and one horse in the 13.2 mg CE/kg (2X) EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension group were euthanized due to laminitis. Clinical signs of foot pain (stiff front limbs and increased heat and pulses in feet) affected more horses, for a longer period of time, in all EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension-treated groups as compared to the ceftiofur sodium.treated group. The study housing (multi-horse pens on concrete slabs) and diet (free choice alfalfa/grass mix and once a day pellets) may have contributed to the development of foot pain. The prevalence and severity of injection site reactions in EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension-treated horses may also have contributed to the development of a stiff gait. A causal relationship between ceftiofur and foot pain could not be definitively determined.
EFFICACY: The efficacy of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension was evaluated in several well-controlled clinical efficacy studies.
Cattle: Bovine respiratory disease (BRD), whether it occurs in beef cattle or in dairy cattle, has the same major bacterial pathogens (Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida and Histophilus somni) associated with it. Ceftiofur, a time-dependent killing antibiotic, requires concentrations of drug that are above the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for an adequate amount of time to be effective in treating the infection. For ceftiofur, the time above a plasma concentration of 0.2 µg/mL (t>0.2) of ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur related residues/mL is used as the therapeutic threshold (pivotal metric) for which comparisons of therapeutic durations are made for EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension. The concentration of 0.2 µg of ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur related residues/mL is approximately 3 to 6 times the MIC90s of Mannheimia haemolytica, P. multocida and H. somnus which range from ≤0.03 to ≤0.06 µg/mL.
In the pivotal pharmacokinetic study, for the lactating dairy cow BRD treatment indication, the t>0.2 for plasma concentrations of ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur related residues were established for lactating dairy cows. In that study, 12 adult lactating dairy cows were administered a single dose of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension at 6.6 mg ceftiofur equivalents (CE)/kg BW in the dorsal posterior aspect of the ear where it attaches to the head (base of the ear). The mean t>0.2, for ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur related residues, was 205 hours (8.5 days).
The effectiveness of EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension for the treatment of bovine foot rot was evaluated in a six-location field effectiveness study. Cattle diagnosed with bovine foot rot were enrolled and treated with EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension, administered by subcutaneous injection in the base of the ear as a single dose of 6.6 mg CE/kg body weight or an equivalent volume of a vehicle control. Cattle were clinically evaluated 7 days post-treatment for treatment success, which was based on defined decreases in lesion, swelling and lameness scores. A total of 169 beef and dairy cattle were included in the analysis. There was a statistically significant difference (p=0.0054) in treatment success for EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension-treated cattle (58.4%) compared to vehicle-treated control cattle (13.2%).
Horses: A double masked, randomized, negative control, field study evaluated the effectiveness of two intramuscular doses of 6.6 mg CE/kg body weight EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension administered 4 days apart for the treatment of lower respiratory infections caused by Streptococcus equi ssp. zooepidemicus in the horse. In this study, a total of 278 horses were treated with EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension, and 95 horses were treated with saline injections. One hundred ninety-three horses (136 EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension and 57 saline placebo) were included in the statistical analysis. Therapeutic success was characterized by no worsening of clinical signs at Day 4, clinical improvement at Day 9, resolution of the clinical signs by Day 15, and no recurrence of clinical signs by Day 25 after initial dosing. EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension was superior to the saline control. Table 7 summarizes the clinical success rates obtained 15 and 25 days after the first dose.
Table 7. Clinical success rates at Day 15 and 25.
|
Efficacy Parameter |
EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension |
Saline Control |
P-value |
|
Clinical success Day 15 |
73.53% |
38.60% |
N/A |
|
Clinical success Day 25 |
69.12% |
31.58% |
0.0215 |
Storage
Store between 15 and 25°C. Once broached, contents should be used within 12 weeks.PRESENTATION: EXCEDE 200 sterile suspension is available in a 100 mL vial.
1 Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Proposed Standard. CLSI Document M31-A (ISBN 1-56238-377-9). CLSI, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087-1832, 1999.
Zoetis is a trademark and Excede is a registered trademark of Zoetis or its licensors, used under license by Zoetis Canada Inc.
© Zoetis Canada Inc., 2014
Zoetis Canada Inc., Kirkland QC H9H 4M7
1530-11-3
30228300
CPN: 1198446.4
16,740 TRANS-CANADA HIGHWAY, KIRKLAND, QC, H9H 4M7
| Order Desk: | 800-663-8888 | |
| Technical Services Canada: | 800-461-0917 | |
| Technical Services USA: | 800-366-5288 | |
| Website: | www.zoetis.ca |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2025 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2025-08-27
