Convenia Injectable Lyophile with Diluent (Canada)
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Zoetis
Company: Zoetis
cefovecin sodium sterile injectable lyophile
DIN 02295628
Veterinary Use Only
For Subcutaneous Use in Dogs and Cats Only
Description
Cefovecin is a semi-synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent from the cephalosporin class of chemotherapeutic agents. Cefovecin is the non-proprietary designation for (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)(methoxyimino) acetyl]amino] - 8 - oxo - 3 - [(2S) - tetrahydro - 2 - furanyl] - 5 - thia - 1 - azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct - 2 - ene - 2 - carboxylicacid, monosodium salt.
Figure 1: Chemical structure of cefovecin sodium.
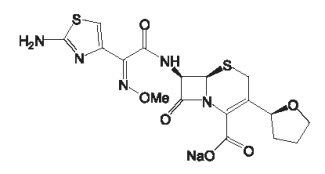
Each mL of CONVENIA® Injectable Lyophile reconstituted lyophile contains cefovecin sodium equivalent to 80.0 mg cefovecin, methylparaben 1.8 mg and propylparaben 0.2 mg as preservatives.
Convenia Injectable Lyophile with Diluent Indications
CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile is indicated for the treatment of bacterial infections in dogs and cats with the following conditions:
Dogs
SKIN: Skin infections including bacterial folliculitis, wounds, and abscesses caused by susceptible strains of Staphylococcus intermedius, Streptococcus canis (Group G, β hemolytic), and Escherichia coli.
URINARY TRACT: Urinary tract infections (cystitis) associated with susceptible strains of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis.
Cats
SKIN: Skin infections including abscesses and wounds caused by susceptible strains of Pasteurella multocida, Prevotella bivia, Bacteroides fragilis, and Staphylococcus intermedius.
EFFICACY CONFIRMATION: In controlled, double blind, 1:1 randomized field studies conducted in the United States, the efficacy of cefovecin was compared to cefadroxil. In these studies, the efficacy of a single injection of cefovecin was demonstrated to be non-inferior to twice daily oral administration of cefadroxil. The following rates reflect the population of animals in which clinical signs had been reduced to mild or absent 28 days after the completion of therapy:
|
Type of Infection |
Dogs |
Cats |
||
|
Cefovecin |
Cefadroxil |
Cefovecin |
Cefadroxil |
|
|
Skin |
109/117 (93.2%) |
107/113 (94.7%) |
106/108 (98.1%) |
99/106 (93.4%) |
|
Urinary Tract (cystitis) |
100/109 (91.7%) |
64/98 (65.3%) |
NA |
NA |
There were no serious adverse events reported during clinical field studies with either cefovecin or cefadroxil. Bacterial pathogens isolated in clinical field studies are provided in the MICROBIOLOGY section.
Dosage and Administration
To deliver the appropriate dose, reconstitute CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile with 10 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP. Shake and/or allow vial to sit until all material is visually dissolved.CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile is to be administered as a single subcutaneous injection at a dosage of 8 mg/kg or 0.1 mL/kg. A single injection provides a full 14 day course of therapy. When indicated, a second subcutaneous injection of 8 mg/kg can be administered 14 days after the first dose to provide therapeutic levels for a total of 28 days. Factors to be considered in the determination of an additional dose are the nature and severity of the infection, the susceptibility of the pathogen, and the immune status of the animal. Susceptibility of bacterial pathogens should be determined prior to treatment. Therapy with CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile may be initiated before the results of these tests are known. If acceptable response to treatment is not observed, then the diagnosis should be re-evaluated and appropriate alternative therapy considered.
Clinical Pharmacology
Cefovecin is rapidly and completely absorbed following subcutaneous administration. Non-linear kinetics are exhibited (plasma concentrations do not increase proportionally with dose). Cefovecin does not undergo hepatic metabolism and the majority of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Excretion of unchanged drug in the bile is a minor route of elimination. In vitro protein binding is greater than 98% in dog and cat plasma.Pharmacokinetic parameters following subcutaneous dosing at 8 mg/kg in the dog and cat are summarized in Figures 2a, and 2b, and in Table 1.
Figure 2a: Mean Plasma and Urine Concentrations following a Single 8 mg/kg Subcutaneous Dosage of CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile in Dogs.
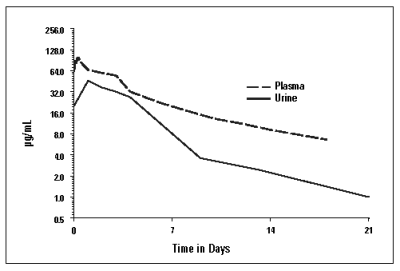
Figure 2b: Mean Plasma and Urine Concentrations following a Single 8 mg/kg Subcutaneous Dosage of CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile in Cats.
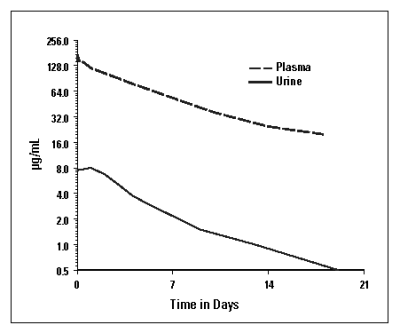
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of a Single 8 mg/kg Subcutaneous Dosage of CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile in Dogs and Cats
|
Parameter |
Estimate (± Standard Deviation) |
|
|
Dogs |
Cats |
|
|
Terminal plasma elimination half-life, T1/2 (h) |
133.1 (15.9) |
170.7 (20.8) |
|
AUC0-inf (µg•h/mL) |
12130 (2492) |
29023 (8267) |
|
Time of maximum concentration, Tmax (h) |
6.2 (3.0) |
1.5 (1.5) |
|
Maximum concentration, Cmax (µg/mL) |
121.1 (50.75) |
178.6 (42.7) |
MICROBIOLOGY: CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin with activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria including β-lactamase producing strains. Like other cephalosporins, cefovecin is bactericidal resulting from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. All MICs were determined in accordance with the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS).
Table 2: MIC Values of CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile Against Bacterial Pathogens Isolated From Skin and Urinary Tract Infections in Dogs Enrolled in Clinical Studies Conducted in the U.S. From 2001 to 2003.
|
Organism |
Number of Isolates |
µg/mL |
||
|
Range |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
||
|
Skin Infections |
||||
|
Staphylococcus intermedius |
47 |
≤ 0.06 to > 32 |
0.125 |
0.5 |
|
Streptococcus canis (Group G, β-hemolytic). |
31 |
≤ 0.06 to 0.5 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
|
Escherichia coli |
20 |
0.25 to 1 |
0.5 |
1 |
|
Urinary Tract Infections |
||||
|
Escherichia coli |
52 |
≤ 0.06 to > 32 |
0.5 |
2 |
|
Proteus mirabilis |
39 |
0.125 to 16 |
0.125 |
0.5 |
Table 3: MIC Values of CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile Against Bacterial Pathogens Isolated From Dogs (2000 to 2001).*
|
Organism |
Number of Isolates |
µg/mL |
||
|
Range |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
||
|
Staphylococcus intermedius |
51 |
≤ 0.06 to 2 |
0.12 |
0.25 |
|
Fusobacterium spp. |
35 |
≤ 0.06 to 1 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
|
Escherichia coli |
21 |
0.5 to 1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Streptococcus canis (Group G, β-hemolytic). |
18 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
|
Porphyromonas spp. |
16 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
*Correlation between in vitro susceptibility data and clinical response has not been determined.
Table 4: MIC Values of CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile Against Bacterial Pathogens Isolated From Skin Infections in Cats Enrolled in Clinical Studies Conducted in the U.S. From 2001 to 2003.
|
Organism |
Number of Isolates |
µg/mL |
||
|
Range |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
||
|
Pasteurella multocida |
66 |
≤ 0.06 to > 32 |
≤ 0.06 |
0.25 |
|
Prevotella bivia |
28 |
0.125 to 32 |
0.5 |
2 |
|
Bacteroides fragilis |
16 |
0.125 to 16 |
1 |
16 |
|
Staphylococcus intermedius |
11 |
≤ 0.06 to 1 |
0.5 |
1 |
Table 5: MIC Values of CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile Against Bacterial Pathogens Isolated From Cats (2000 to 2001).*
|
Organism |
Number of Isolates |
µg/mL |
||
|
Range |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
||
|
Pasteurella multocida |
45 |
≤ 0.06 to 0.12 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
|
Fusobacterium spp. |
30 |
≤ 0.06 to 0.12 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
|
Escherichia coli |
13 |
0.25 to 1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Porphyromonas spp. |
13 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
≤ 0.06 |
*Correlation between in vitro susceptibility data and clinical response has not been determined.
Susceptibility Testing
The interpretive criteria proposed in this section were determined in accordance with the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS).
Dilution Techniques: Quantitative methods are used to determine
antimicrobial minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized procedure. Standardized procedures are based on a dilution method (broth or agar) with standardized inoculum concentrations and standardized concentrations of cefovecin powder.
Diffusion Techniques: Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 30 µg cefovecin to test the susceptibility of microorganisms.
Cefovecin MIC values and zone diameters should be interpreted according to the following proposed breakpoint criteria:
|
MIC (µg/mL) |
Zone diameter (mm) |
Interpretation |
|
≤ 2 |
≥ 23 |
Susceptible (S) |
|
4 |
20 to 22 |
Intermediate (I) |
|
≥ 8 |
≤ 19 |
Resistant (R) |
A report of “Susceptible” indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited by generally achievable drug concentrations. A report of “Intermediate” is a technical buffer and isolates falling into this category should be retested. Alternatively, the organism may be successfully treated if the infection is in a body site where the drug is physiologically concentrated. A report of “Resistant” indicates that achievable drug concentrations are unlikely to be inhibitory and other therapy should be selected.
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory control organisms to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. Cefovecin powder should produce the following MIC values in these quality control strains:
|
Control Strain |
MIC (µg/mL) |
|
|
Aerobes |
Broth Microdilution |
Agar Dilution |
|
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 |
0.5 to 2 |
NA |
|
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 |
0.5 to 2 |
NA |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619 |
0.12 to 0.5 |
NA |
|
Hemophilus somnus ATCC 700025 |
0.001 to 0.008 |
NA |
|
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae ATCC 27090 |
0.008 to 0.03 |
NA |
|
Anaerobes |
||
|
Bacteroides fragilis ATCC 25285 |
8 to 32 |
8 to 32 |
|
Brucella thetaiotaomicron ATCC 29741 |
16 to 28 |
16 to 64 |
As with standardized dilution techniques, diffusion methods require the use of laboratory control microorganisms that are used to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. For the diffusion technique, the 30 µg cefovecin disk should produce the following zone diameters in these quality control strains:
|
Control Strain |
Zone diameter (mm) |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619 |
25 to 31 |
|
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 |
26 to 35 |
|
Hemophilus somnus ATCC 700025 |
38 to 51 |
|
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae ATCC 27090 |
34 to 43 |
|
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 |
25 to 30 |
CONTRAINDICATIONS: CONVENIA should not be administered to dogs or cats with a known allergy to cephalosporins. In penicillin-allergic animals, CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile should be used with caution. If an allergic reaction or anaphylaxis occurs, CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile should not be administered again and appropriate therapy should be instituted. Anaphylaxis may require treatment with epinephrine and other emergency measures, including oxygen, intravenous fluids, intravenous antihistamine, corticosteroids, and airway management, as clinically indicated.
CAUTIONS: The safe use of CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile in animals less than 4 months of age, pregnant dogs, dogs used for breeding purposes or in lactating dogs has not been established. Safety has not been established for IM or IV administration or long-term use. The safe use of this product administered concomitantly with other protein-bound drugs has not been studied. Such drugs commonly used include NSAIDs, cardiac, anticonvulsant, and behavioral medications. When tested in an in vitro equilibrium dialysis system using canine and feline plasma, cefovecin has been shown to result in an increase in the free concentration of carprofen, furosemide, doxycycline and ketoconazole in dog plasma, and in the free concentration of furosemide and ketoconazole in cat plasma. The clinical relevance of these observations is unknown.
Positive direct Coombs’ test results and false positive reactions for glucose in the urine have been reported during treatment with some cephalosporin antibacterials. Transient leukopenias have been reported in humans receiving cephalosporins. Some antibacterials, including cephalosporins, can cause lowered albumin values due to interference with certain testing methods.
Occasionally, cephalosporins and NSAIDs have been associated with myelotoxicity, thereby creating a toxic neutropenia. Other hematological reactions seen with cephalosporins include neutropenia, anemia, hypoprothrombinemia, thrombocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time (PT) and partial thromboplastin time (PTT), platelet dysfunction and transient increases in serum aminotransferases.
Warnings
Keep out of reach of children. Not for use in humans. Consult a physician in case of accidental human exposure. For use in dogs and cats only. Antimicrobial drugs, including penicillins and cephalosporins, can cause allergic reactions in sensitized individuals. To limit the development of antimicrobial resistance:- cefovecin should not be used in food-producing animals.
- the extra-label drug use of cefovecin is not recommended.
SAFETY: Laboratory and clinical field studies have demonstrated that CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile is well tolerated in dogs and cats after subcutaneous administration.
DOGS:
Sixty-three different pure breeds and 25 different mixed breeds were represented in the 393 dogs enrolled in clinical field studies and receiving CONVENIA. Injectable Lyophile 226 dogs completed the studies and were included in the efficacy analysis with no serious adverse events reported. CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile was used in dogs receiving other commonly used veterinary products such as heartworm preventatives, flea control products, sedatives/tranquilizers, anesthetic agents, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, and vaccines with no serious adverse events reported.
In a margin of safety study, CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile was administered subcutaneously to healthy 4-month old beagle dogs at 1.5, 4.5, and 7.5 times the label dosage (12, 36, or 60 mg/kg) at one-half the recommended treatment interval (once weekly) for 4 consecutive weeks with no significant adverse reactions. Transient swelling was observed at the injection site. There were no clinically significant changes in clinical pathology variables and no treatment related gross or histopathological changes.
In a separate 30-day drug tolerance study, healthy 7-month old beagle dogs were administered a single subcutaneous dose at 22.5 times the label dosage (180 mg/kg) with no significant adverse reactions. Transient edema was observed near the injection site. There were no treatment-related changes in clinical pathology, feed consumption, body weights or physical examination findings.
CATS:
Four different pure breeds and five different mixed breeds were represented in the 147 cats enrolled in clinical field studies and receiving CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile. One hundred and eight cats completed the studies and were included in the efficacy analysis with no serious adverse events reported. CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile was used in cats receiving other commonly used veterinary products such as heartworm preventatives, flea control products, sedatives/tranquilizers, anesthetic agents, and vaccines with no serious adverse events reported.
In a margin of safety study, CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile was administered subcutaneously to healthy 4-month old domestic shorthair cats at 1.5, 4.5, and 7.5 times the label dosage (12, 36, or 60 mg/kg) at one-half the recommended treatment interval (once weekly) for 4 consecutive weeks with no significant adverse reactions. Over the 4-week treatment period, single incidents of soft stools were observed in 1 of 8 cats treated with 1.5 times the label dosage (12 mg/kg), 2 of 8 cats treated with 4.5 times the label dosage (36 mg/kg), and 1 of 8 cats treated with 7.5 times the label dosage (60 mg/kg). Two incidents each of soft or runny stools were observed in 2 of 8 cats treated with 7.5 times the label dosage (60 mg/kg). Transient swelling was observed at the injection site. There were no clinically significant changes in clinical pathology variables and no treatment related gross or histopathological changes.
In a separate 30-day drug tolerance study, healthy 7-month old domestic shorthair cats were administered a single subcutaneous dose at 22.5 times the label dosage (180 mg/kg) with no significant adverse reactions. Transient edema was observed at or near the injection site. There were no treatment-related changes in clinical pathology, feed consumption, body weights or physical examination findings.
Adverse Reactions
Although all adverse reactions are not reported, the following information is based on voluntary post approval drug experience reporting. It is generally recognized that this results in significant under-reporting. The adverse events listed here reflect reporting and not necessarily causality. Adverse events are listed by body system, in decreasing order of frequency:CATS:
- Systemic disorders: anorexia, lethargy, death, lack of efficacy, weight loss, fever
- Digestive tract disorders: vomiting, diarrhea
- Neurological disorders: ataxia, seizure NOS
DOGS:
- Systemic disorders: lethargy, anorexia, lack of efficacy, death
- Digestive tract disorders: vomiting, diarrhea
There were no serious adverse events reported during clinical field studies with CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile. Abnormal health observations reported in cefovecin and cefadroxil-treated animals are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6: Number (Percentage) of Animals with Abnormal Health Observations Reported During Clinical Field Studies with CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile.
|
Abnormal Observation |
Dogs |
Cats |
||
|
Cefovectin (N=226) |
Cefadroxil (N=228) |
Cefovectin (N=108) |
Cefadroxil (N=106) |
|
|
Lethargy |
10 (4.4%) |
22 (9.6%) |
4 (3.7%) |
7 (6.6%) |
|
Inappetence / Decreased Appetite |
13 (5.8%) |
21 (9.2%) |
6 (5.6%) |
5 (4.7%) |
|
Vomiting |
11 (4.9%) |
36 (15.8%) |
9 (8.3%) |
13 (12.3%) |
|
Diarrhea / Soft Feces |
13 (5.8%) |
23 (10.1%) |
7 (6.5%) |
29 (27.4%) |
Storage
Store un-reconstituted product in the original carton refrigerated at 2° to 8°C.Store reconstituted product in the original carton refrigerated for up to 56 days. CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile should be protected from light. After each use it is important to return the unused portion back to the refrigerator in the original carton. As with other cephalosporins, the color of the solution may vary from clear to amber at reconstitution and may darken over time. Solution color does not adversely affect potency.
PRESENTATION: CONVENIA Injectable Lyophile package contains: vial 1, cefovecin sodium as a lyophilized cake; and vial 2, 10 mL of sterile diluent.
Zoetis® and Convenia are registered trademarks of Zoetis or its licensors.
Zoetis Canada Inc., Kirkland QC H9H 4M7
40019776
10017225-11-1
CPN: 1198557.1
16,740 TRANS-CANADA HIGHWAY, KIRKLAND, QC, H9H 4M7
| Order Desk: | 800-663-8888 | |
| Technical Services Canada: | 800-461-0917 | |
| Technical Services USA: | 800-366-5288 | |
| Website: | www.zoetis.ca |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2025 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2025-08-27
