Xipere Injection: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: triamcinolone acetonide
Dosage form: injection, suspension
Drug class: Ophthalmic steroids
J Code (medical billing code): J3299 (1 mg, injection)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
XIPERE ®(triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension), for suprachoroidal use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1957
Indications and Usage for Xipere Injection
XIPERE ®is a corticosteroid indicated for the treatment of macular edema associated with uveitis. ( 1)
Xipere Injection Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage is 4 mg (0.1 mL) administered as a suprachoroidal injection. ( 2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injectable suspension: triamcinolone acetonide 40 mg/mL in a single-dose vial. ( 3)
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
Potential Corticosteroid-Related Effects: Use of corticosteroids may produce cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, and glaucoma. ( 5.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
In controlled studies, the most common adverse reactions reported by ≥ 10% of patients and at a rate greater than control included elevated intraocular pressure and eye pain. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contactBausch & Lomb Incorporated at 1-800-553-5340or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Xipere Injection
XIPERE ®(triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension) 40 mg/mL is indicated for the treatment of macular edema associated with uveitis.
2. Xipere Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosing Information
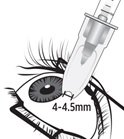
For suprachoroidal injection using the SCS Microinjector ®. The recommended dose of XIPERE ®is 4 mg (0.1 mL of the 40 mg/mL injectable suspension).
2.2 Preparation for Administration
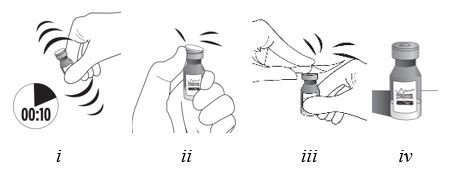
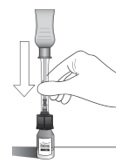
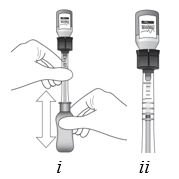
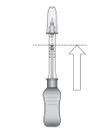
Step 9
Figure I
Invert the entire assembly so that the vial is directly above the syringe. Slide the white plunger handle all the way back and forth multiple times to fill the entire syringe with drug and remove any remaining air (see Figure I, iand ii).
NOTE: The syringe should be handled by the clear barrel during filling, connecting and disconnecting procedures. The white plunger handle has a stop to prevent complete removal of the plunger from the syringe.
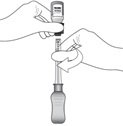
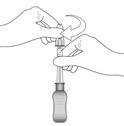
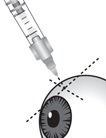
2.3 Administration
The suprachoroidal injection procedure should be carried out under controlled aseptic conditions, which include the use of sterile gloves, a sterile drape, a sterile eyelid speculum (or equivalent), and a sterile cotton swab. Adequate anesthesia and a broad-spectrum microbicide applied to the periocular skin, eyelid, and ocular surface are recommended to be given prior to the suprachoroidal injection.
If continued resistance is experienced during injection attempts:
- Remove the needle from the eye and examine the eye for any issues. If patient safety is not at risk, the physician may use medical judgment to restart the injection procedure at a new site adjacent to the original injection site.
- If resistance continues and patient safety is not at risk, the physician may use appropriate medical judgment to change to the additional included needle in the sterile tray. Twist to remove the needle and reconnect the syringe to the vial by twisting the syringe onto the vial adapter. Repeat the preparation and injection process as stated in Steps 9 – 18 with the additional needle (allowing for any partial dose given with the first needle when completing preparation Step 12).
Immediately following suprachoroidal injection, patients should be monitored for elevation of intraocular pressure. Appropriate monitoring may consist of a check for perfusion of the optic nerve head or tonometry.
Following suprachoroidal injection, patients should be instructed to report any symptoms suggestive of endophthalmitis or retinal detachment (e.g., eye pain, redness of eye, photophobia, blurring of vision) without delay [see Patient Counseling Information ( 17)] .
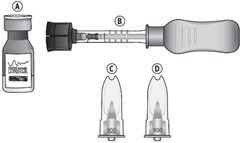
Each XIPERE ®package (microinjector syringe with vial adapter, 900-µm needle, 1100-µm needle, and vial of triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension 40 mg/mL) is single-dose and should only be used for the treatment of one eye.
After suprachoroidal injection, all drug product and components (used or unused) must be discarded appropriately.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injectable suspension: triamcinolone acetonide 40 mg/mL suspension in a single-dose glass vial for use with the supplied SCS Microinjector ®.
4. Contraindications
4.1 Ocular or Periocular Infections
XIPERE ®is contraindicated in patients with active or suspected ocular or periocular infections including most viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva, including active epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, varicella, mycobacterial infections, and fungal diseases.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Potential Corticosteroid-Related Effects
Use of corticosteroids may produce cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, and glaucoma. Use of corticosteroids may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
Corticosteroids should be used cautiously in patients with a history of ocular herpes simplex. Corticosteroids should not be used in patients with active ocular herpes simplex.
5.2 Alterations in Endocrine Function
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, Cushing’s syndrome, and hyperglycemia can occur following administration of a corticosteroid. Monitor patients for these conditions with chronic use.
Corticosteroids can produce reversible HPA axis suppression with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency after withdrawal of treatment. Drug induced secondary adrenocortical insufficiency may be minimized by gradual reduction of dosage. This type of relative insufficiency may persist for months after discontinuation of therapy; therefore, in any situation of stress occurring during that period, hormone therapy should be reinstituted. Metabolic clearance of corticosteroids is decreased in hypothyroid patients and increased in hyperthyroid patients. Changes in thyroid status of the patient may necessitate adjustment in dosage.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
XIPERE ®was studied in a multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled, double-masked study in patients with macular edema associated with uveitis. Table 1 summarizes data available from the clinical trial for XIPERE ®treated patients and control patients.
The most common ocular (study eye) adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 2% of patients and non-ocular adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 5% of patients are shown in Table 1.
| aIncludes intraocular pressure increased and ocular hypertension | ||
| bDefined as not occurring on the day of the injection procedure, or occurring on the day of the injection procedure and not resolving the same day | ||
| cIncludes cataract, cataract cortical, and cataract subcapsular | ||
| dDefined as occurring on the day of the injection procedure and resolving the same day | ||
|
Adverse Reaction |
XIPERE
®
|
Control
|
|
Ocular |
||
|
Increased intraocular pressure, non-acute a, b |
13 (14%) |
9 (14%) |
|
Eye pain, non-acute b |
11 (12%) |
0 |
|
Cataract c |
7 (7%) |
4 (6%) |
|
Increased intraocular pressure, acute a, d |
6 (6%) |
0 |
|
Vitreous detachment |
5 (5%) |
1 (2%) |
|
Injection site pain |
4 (4%) |
2 (3%) |
|
Conjunctival haemorrhage |
4 (4%) |
2 (3%) |
|
Visual acuity reduced |
4 (4%) |
1 (2%) |
|
Dry eye |
3 (3%) |
1 (2%) |
|
Eye pain, acute d |
3 (3%) |
0 |
|
Photophobia |
3 (3%) |
0 |
|
Vitreous floaters |
3 (3%) |
0 |
|
Uveitis |
2 (2%) |
7 (11%) |
|
Conjunctival hyperaemia |
2 (2%) |
2 (3%) |
|
Punctate keratitis |
2 (2%) |
1 (2%) |
|
Conjunctival oedema |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Meibomianitis |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Anterior capsule contraction |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Chalazion |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Eye irritation |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Eye pruritus |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Eyelid ptosis |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Photopsia |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Vision blurred |
2 (2%) |
0 |
|
Non-ocular |
||
|
Headache |
5 (5%) |
2 (3%) |
Related/similar drugs
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with XIPERE ®in pregnant women to inform drug-associated risks. In animal reproductive studies from the published literature, topical ocular administration of corticosteroids has been shown to produce teratogenicity at clinically relevant doses. There is negligible systemic XIPERE ®exposure following suprachoroidal injection [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)] . Corticosteroids should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Animal Data
Animal reproduction studies using XIPERE ®have not been conducted. In animal reproductive studies from the published literature, topical ocular administration of corticosteroids to pregnant mice and rabbits during organogenesis has been shown to produce cleft palate, embryofetal death, herniated abdominal viscera, hypoplastic kidneys, and craniofacial malformations.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether ocular administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for XIPERE ®and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from XIPERE ®. There are no data on the effects of XIPERE ®on milk production.
11. Xipere Injection Description
XIPERE ®is a sterile, injectable suspension of triamcinolone acetonide, a synthetic corticosteroid for suprachoroidal use with the SCS Microinjector ®. Each mL of the aqueous suspension contains 40 mg of triamcinolone acetonide with 0.55% (weight/volume [w/v]) sodium chloride for tonicity, 0.5% (w/v) carboxymethylcellulose sodium, and 0.02% (w/v) polysorbate 80. It also contains potassium chloride, calcium chloride (dihydrate) and magnesium chloride (hexahydrate) as isotonicity agents, sodium acetate trihydrate(3.51 mg), sodium citrate dihydrate(1.53 mg), and water for injection. Hydrochloric acid may be used to adjust pH to a target value of 6.5. XIPERE ®does not contain an anti-microbial preservative.
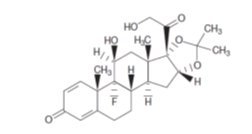
The chemical name for triamcinolone acetonide is 9-fluoro-11β,16ɑ,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with acetone. Its chemical structure is:
Molecular weight 434.50; molecular formula C 24H 31FO 6
Triamcinolone acetonide occurs as a white to cream-colored, crystalline powder having not more than a slight odor and is practically insoluble in water and very soluble in alcohol.
XIPERE ®is provided as an injectable suspension in a single-dose glass vial with a rubber stopper and an aluminum seal. The SCS Microinjector ®is a piston syringe and a needle approximately 1 mm in length (900-µm and 1100-µm needles are included) for conducting the suprachoroidal injection.
12. Xipere Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Triamcinolone acetonide is a synthetic glucocorticoid (glucocorticoids are often referred to as corticosteroids) with immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activity. The primary mechanism of action for triamcinolone acetonide is as a corticosteroid hormone receptor agonist.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In animal studies, data demonstrated that suprachoroidal injections resulted in larger amounts in total of triamcinolone acetonide found in the sclera, choroid, retinal pigment epithelial and retina, than with intravitreal injections of triamcinolone acetonide. Lower amounts of triamcinolone acetonide were found in the anterior segment and lens as compared to intravitreal injections of triamcinolone acetonide.
Plasma triamcinolone acetonide concentrations were evaluated in 19 patients with dosing of 4 mg XIPERE ®at Day 0 and Week 12. Plasma triamcinolone acetonide concentrations in all 19 patients were below 100 pg/mL at Week 4, 12, and 24 (concentrations ranged from < 10 pg/mL [LLOQ (lower limit of quantitation) of the assay] to 88.9 pg/mL), with the exception of one patient with a value of 243.4 pg/mL prior to the second dose at Week 12.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No information is available on the carcinogenic potential of triamcinolone acetonide.
Mutagenesis
No information is available on the mutagenic potential of triamcinolone acetonide.
Fertility
No information is available on the effect of triamcinolone acetonide on fertility.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of XIPERE ®was assessed in a 6-month, randomized, multicenter, double-masked, sham-controlled study in patients with macular edema associated with anterior-, intermediate-, posterior-, or pan-uveitis. Patients were treated at baseline and Week 12.
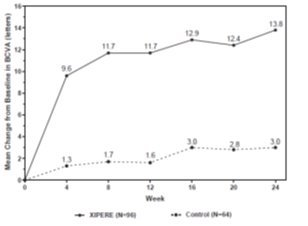
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients in whom best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) had improved by ≥ 15 letters from baseline after 24 weeks of follow-up (Table 2).
| *The p-value was based on a Cochran Mantel Haenszel test for general association between treatment and response with stratification by country. | ||
|
Patients Who Gained ≥ 15 Letters from Baseline at Week 24 |
XIPERE
®
|
Control
|
|
n (%) |
45 (47%) |
10 (16%) |
|
Estimated Difference (95% CI) |
31% (15%, 46%) |
|
|
CMH p-value* |
< 0.01 |
|
A statistically significantly greater proportion of patients treated with XIPERE ®achieved a ≥ 15-letter improvement in BCVA than control patients (p < 0.01) at Week 24.
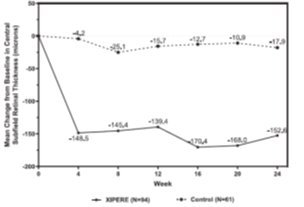
BCVA mean change from baseline at different visits is shown in Figure 1. Central subfield retinal thickness (CST) mean change from baseline at different visits is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1: Mean Change from Baseline in BCVA
Figure 2: Mean Change from Baseline in CST
16. How is Xipere Injection supplied
XIPERE ®is supplied with the following sterile components for administration, sealed in a Tyvek covered tray, and one single-dose glass vial, in a carton with a package insert (NDC 24208-040-40):
- One SCS Microinjector ®syringe with vial adapter attached
- One 30-G x 900-µm needle
- One 30-G x 1100-µm needle
- One single-dose vial of triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension 40 mg/mL (NDC 24208-040-41)
Storage:Store at 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F); do not freeze. The drug vial should be protected from light by storing in the carton. Discard unused portion.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Corticosteroid-Related Effects
Advise patients that they may develop elevated intraocular pressure following treatment, which may need to be managed with medication or surgery.
When to Seek Physician Advice
Advise patients that if the eye becomes red, sensitive to light, painful, or develops a change in vision, they should seek immediate care from an ophthalmologist.
Distributed by:
Bausch & Lomb Americas Inc.
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
Patented. See https://patents.bausch.com for US patent information.
XIPERE ®, SCS ®, and SCS Microinjector ®are trademarks of Clearside Biomedical, Inc. used under license.
© 2022 Bausch & Lomb Incorporated or its affiliates
9772102
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC24208-040-40
XIPERE ®
(triamcinolone acetonide
injectable suspension) 40 mg/mL
For suprachoroidal use
Carton contains:
• One single-dose glass vial of triamcinolone acetonide
injectable suspension 40 mg/mL
• One SCS Microinjector® syringe with
vial adapter attached
• One 30-G x 900-μm needle
• One 30-G x 1100-μm needle
• One package insert
Rx only
Store at 15°C to 25°C
(59°F to 77°F).
Do not freeze.
Protect from light.
BAUSCH + LOMB
97719XX
| XIPERE
triamcinolone acetonide injection, suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Bausch & Lomb Incorporated (196603781) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcami Carolinas Corporation | 832394733 | manufacture(24208-040) | |
More about Xipere (triamcinolone ophthalmic)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (1)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: ophthalmic steroids
- Breastfeeding
- En español