Vitrakvi: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: larotrectinib
Dosage form: capsules, oral solution
Drug class: Multikinase inhibitors
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 9, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VITRAKVI® (larotrectinib) capsules, for oral use
VITRAKVI® (larotrectinib) oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage for Vitrakvi
VITRAKVI is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with solid tumors that:
- have a neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase (NTRK) gene fusion without a known acquired resistance mutation,
- are metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and
- have no satisfactory alternative treatments or that have progressed following treatment.
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved test. (1, 2.1)
Vitrakvi Dosage and Administration
- Select patients for treatment with VITRAKVI based on the presence of a NTRK gene fusion (2.1, 14).
- Recommended Dosage in Adult and Pediatric Patients with Body Surface Area of 1 Meter-Squared or greater: 100 mg orally twice daily (2.2)
- Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients with Body Surface Area of Less Than 1 Meter-Squared: 100 mg/m2 orally twice daily (2.2)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Effects: Advise patients and caretakers of the risk of CNS adverse reactions including dizziness, cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and sleep disturbances. Advise patients not to drive or operate hazardous machinery if experiencing neurotoxicity. Withhold and modify dosage, or permanently discontinue VITRAKVI based on severity. (2.3, 5.1)
- Skeletal Fractures: Promptly evaluate patients with signs or symptoms of fractures. (5.2)
- Hepatotoxicity: Obtain liver function tests (ALT, AST, ALP and bilirubin) before initiation of VITRAKVI and every 2 weeks during the first 2 months of treatment, then monthly thereafter or as clinically indicated. Temporarily withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue VITRAKVI based on severity. (2.4, 5.3)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females with reproductive potential of potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.4, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, with VITRAKVI were increased AST, increased ALT, anemia, hypoalbuminemia, musculoskeletal pain, increased alkaline phosphatase, leukopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, hypocalcemia, fatigue, vomiting, cough, constipation, pyrexia, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness, and rash (6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-888-842-2937 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Avoid coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with VITRAKVI. If coadministration cannot be avoided, reduce the VITRAKVI dose. (2.5, 7.1)
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Monitor for adverse reactions more frequently in patients coadministered a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor with VITRAKVI and reduce the VITRAKVI dosage based on severity of adverse reactions. (7.1)
- Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inducers with VITRAKVI. If coadministration cannot be avoided, increase the VITRAKVI dose. (2.6, 7.1)
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers: Increase the VITRAKVI dose. (2.6, 7.1)
- Sensitive CYP3A4 Substrates: Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with VITRAKVI. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Vitrakvi
VITRAKVI is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with solid tumors that:
- have a neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase (NTRK) gene fusion without a known acquired resistance mutation,
- are metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and
- have no satisfactory alternative treatments or that have progressed following treatment.
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
2. Vitrakvi Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment with VITRAKVI based on the presence of a NTRK gene fusion in tumor specimens [see Clinical Studies (14)].
In patients with secretory breast cancer, mammary analogue secretory cancer (MASC), congenital mesoblastic nephroma (CMN), or infantile fibrosarcoma, consider treatment without confirmation of NTRK rearrangements in tumor specimens.
Information on FDA-approved tests is available at http://www.fda.gov/companiondiagnostics.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
For Grade 2 and higher liver function test abnormalities, refer to Section 2.4, Table 2, Dosage Modifications for Hepatotoxicity.
For all other Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions:
- Withhold VITRAKVI until adverse reaction resolves or improves to baseline or Grade 1. Resume at the next dosage modification if resolution occurs within 4 weeks.
- Permanently discontinue VITRAKVI if an adverse reaction does not resolve within 4 weeks.
The recommended dosage reductions for VITRAKVI for adverse reactions are provided in Table 1.
| Dosage Reduction | Adult and Pediatric Patients with Body Surface Area of 1 m2 or Greater | Pediatric Patients with Body Surface Area Less Than 1 m2 |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| First | 75 mg orally twice daily | 75 mg/m2 orally twice daily |
| Second | 50 mg orally twice daily | 50 mg/m2 orally twice daily |
| Third | 100 mg orally once daily | 25 mg/m2 orally twice daily* |
Permanently discontinue VITRAKVI in patients who are unable to tolerate VITRAKVI after three dose modifications.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Hepatotoxicity
The recommended dosage modifications for VITRAKVI liver function test abnormalities are provided in Table 2.
For CTCAE Grade 2 ALT and/or AST elevation, monitor liver function frequently as clinically indicated, to establish whether a dose interruption or reduction is required [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
| Severity* | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; ULN = upper limit of normal | |
|
|
| AST or ALT ≥ 5 × ULN with bilirubin ≤ 2 × ULN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] |
|
| AST or ALT > 3 × ULN with total bilirubin > 2 × ULN in the absence of alternative causes |
|
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Coadministration with Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Avoid coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with VITRAKVI. If coadministration of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the VITRAKVI dose by 50%. After the inhibitor has been discontinued for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume the VITRAKVI dose that was used prior to initiating the CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.6 Dosage Modifications for Coadministration with Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers
Avoid coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inducers with VITRAKVI. If coadministration of a strong CYP3A4 inducer cannot be avoided, double the VITRAKVI dose. Additionally, for coadministration with a moderate CYP3A4 inducer, double the VITRAKVI dose. After the inducer has been discontinued for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume the VITRAKVI dose that was used prior to initiating the CYP3A4 inducer [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.7 Dosage Modifications for Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Reduce the starting dose of VITRAKVI by 50% in patients with moderate (Child-Pugh B) to severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.8 Administration
VITRAKVI capsule or oral solution may be used interchangeably.
Do not make up a missed dose within 6 hours of the next scheduled dose.
If vomiting occurs after taking a dose of VITRAKVI, take the next dose at the scheduled time.
Oral Solution packaged in one bottle containing 100 mL
- Store the glass bottle of VITRAKVI oral solution in the refrigerator. Discard any unused VITRAKVI oral solution remaining after 90 days of first opening the bottle.
- Prior to preparing an oral dose for administration, refer to the Instructions for Use.
Oral Solution packaged in two bottles each containing 50 mL
- Store the glass bottles of VITRAKVI oral solution in the refrigerator. Discard any unused VITRAKVI oral solution remaining after 31 days of first opening the bottle.
- Prior to preparing an oral dose for administration, refer to the Instructions for Use.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules
- 25 mg: white opaque hard gelatin capsule, size 2, with blue printing of "BAYER" cross and "25 mg" on body of capsules. 25 mg larotrectinib is equivalent to 30.7 mg larotrectinib sulfate.
- 100 mg: white opaque hard gelatin capsule, size 0, with blue printing of "BAYER" cross and "100 mg" on body of capsule. 100 mg larotrectinib is equivalent to 123 mg larotrectinib sulfate.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Central Nervous System Effects
Central nervous system (CNS) adverse reactions occurred in patients receiving VITRAKVI, including dizziness, cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and sleep disturbances.
In patients who received VITRAKVI (n=444), all grades CNS effects including cognitive impairment, mood disorders, dizziness and sleep disorders were observed in 40.3% with Grades 3-4 in 3.8% of patients.
Cognitive impairment occurred in 11% of patients. The median time to onset of cognitive impairment was 6 months (range: 2 days to 56 months). Cognitive impairment occurring in ≥ 1% of patients included memory impairment (4.1%), disturbance in attention (3.6%), confusional state (2.3%), cognitive disorder (1.6%), delirium (1.4%), and hallucination (1.1%). Grade 3 cognitive adverse reactions occurred in 1.8% of patients and Grade 4 cognitive adverse reactions in 0.2% of patients. Among the 49 patients with cognitive impairment, 6% required a dose modification, and 18% required dose interruption.
Mood disorders occurred in 14% of patients. The median time to onset of mood disorders was 3.3 months (range: 1 day to 65 months). Mood disorders occurring in ≥ 1% of patients included anxiety (5%), agitation (3.2%), depression (3.2%), irritability (2.3%), and restlessness (1.1%). Grade 3 mood disorders occurred in 0.9% of patients. Among the 63 patients who experienced mood disorders, no patient required a dose modification, and 1.6% required dose interruption.
Dizziness occurred in 22% of patients, and Grade 3 dizziness occurred in 0.9% of patients. Among the 96 patients who experienced dizziness, 6% of patients required a dose modification, and 5% required dose interruption.
Sleep disturbances occurred in 12% of patients. Sleep disturbances included insomnia (9%), somnolence (3.4%), and sleep disorder (0.5%). Grade 3 sleep disturbances occurred in 0.2% of patients. Among the 54 patients who experienced sleep disturbances, no patient required a dose modification, and 3.7% required dose interruption.
Advise patients and caretakers of these risks with VITRAKVI. Advise patients not to drive or operate hazardous machinery if they are experiencing neurologic adverse reactions. Withhold or permanently discontinue VITRAKVI based on the severity. If withheld, modify the VITRAKVI dosage when resumed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Skeletal Fractures
Skeletal fractures can occur in patients taking VITRAKVI.
Among 444 patients who received VITRAKVI across clinical trials, fractures occurred in 7% of patients; 6% of 290 adult patients and 10% of 154 pediatric patients. Median time to first fracture was 13 months (range 27 days to 73 months) in patients followed per fracture. The most common fractures were of the rib (1.4%), fibula, foot, or wrist (0.7% each). Most fractures were associated with minimal or moderate trauma. Some fractures were associated with radiologic abnormalities suggestive of local tumor involvement. VITRAKVI treatment was interrupted due to fracture in 1.4% patients.
Promptly evaluate patients with signs or symptoms of potential fracture (e.g., pain, changes in mobility, deformity). There are no data on the effects of VITRAKVI on healing of known fractures or risk of future fractures.
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity including drug-induced liver injury (DILI) has occurred in patients taking VITRAKVI.
In patients who received VITRAKVI (n=444), increased AST of any grade occurred in 62% of patients and increased ALT of any grade occurred in 61%. Grade 3-4 increased AST or ALT occurred in 7% and 8% of patients, respectively [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The median time to onset of increased AST was 1.9 months (range: 4 days to 3.8 years). The median time to onset of increased ALT was 1.9 months (range: 1 day to 4.9 years). Increased AST and ALT leading to dose modifications occurred in 1.6% and 3.2% of patients, respectively. Increased AST or ALT led to permanent discontinuation in 4 (0.9%) patients.
There have been reports from clinical studies and postmarketing cases of Grade ≥ 2 increases in ALT and/or AST with increases in bilirubin ≥ 2 × ULN.
Obtain liver function tests (ALT, AST, ALP and bilirubin) before initiation of VITRAKVI and monitor every 2 weeks during the first 2 months of treatment, then monthly thereafter, or more frequently following the occurrence of Grade 2 or greater AST or ALT elevation. Temporarily withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue VITRAKVI based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on literature reports in human subjects with congenital mutations leading to changes in TRK signaling, findings from animal studies, and its mechanism of action, VITRAKVI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Larotrectinib resulted in malformations in rats and rabbits at maternal exposures that were approximately 11- and 0.7-times, respectively, those observed at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use an effective method of contraception during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of VITRAKVI [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Central Nervous System Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Skeletal Fractures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Unless noted, data in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and below reflects exposure to VITRAKVI in 444 patients, including 62% patients exposed for greater than 6 months, 44% patients exposed for greater than 1 year, and 30% patients exposed for greater than 2 years. VITRAKVI was studied in one adult dose-finding trial [LOXO-TRK-14001 (n = 75)], one pediatric dose-finding trial [SCOUT (n = 154)], and one single arm trial [NAVIGATE (n = 215)]. All patients had an unresectable or metastatic solid tumor and no satisfactory alternative treatment options or disease progression following treatment.
Across these 444 patients, the median age was 44 years (range: 18 days to 90 years); 35% were younger than 18 years; 53% were female; 59% were White, 24% were Asian and, 4% were Black; and 7% were Hispanic/Latino. Most adults (91%) received VITRAKVI 100 mg orally twice daily and 91% of pediatrics (< 18 years) received VITRAKVI 100 mg/m2 twice daily up to a maximum dose of 100 mg twice daily. The dose ranged from 50 mg daily to 200 mg twice daily in adults and 9.6 mg/m2 twice daily to 120 mg/m2 twice daily in pediatrics [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
The most common serious adverse reactions (≥ 2%) were pneumonia, pyrexia, and dyspnea. Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions occurred in 60% of patients; adverse reactions leading to dose interruption or modification occurred in 45% and 11% of patients, respectively, and 12% permanently discontinued VITRAKVI for adverse reactions.
The most common adverse reactions (1% each) that resulted in permanent discontinuation of VITRAKVI were increased ALT and increased AST.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 3%) resulting in dose interruption were increased ALT (6%), increased AST (5%), neutrophil count decreased (4.7%), pyrexia (4.3%), and vomiting (3.2%). Most (64%) adverse reactions leading to dose interruption occurred during the first three months of exposure.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%), including laboratory abnormalities, in order of decreasing frequency were increased AST, increased ALT, anemia, hypoalbuminemia, musculoskeletal pain, increased alkaline phosphatase, leukopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, hypocalcemia, fatigue, vomiting, cough, constipation, pyrexia, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness, and rash.
Adverse reactions of VITRAKVI occurring in ≥ 10% of patients and laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline in ≥ 20% of patients are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively.
| Adverse Reaction* | VITRAKVI N = 444 |
|
|---|---|---|
| All Grades†
(%) | Grade 3-4‡
(%) |
|
|
||
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||
| Musculoskeletal Pain§ | 41 | 3.6 |
| General | ||
| Fatigue¶ | 31 | 2.5 |
| Pyrexia | 26 | 2.3 |
| Edema# | 17 | 0.7 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||
| CoughÞ | 29 | 0.5 |
| Dyspneaß | 17 | 2.7 |
| Nasal congestion | 10 | 0 |
| Nervous System | ||
| Dizzinessà | 22 | 0.9 |
| Headache | 17 | 0.9 |
| Cognitive Impairmentè | 11 | 2 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Vomiting | 30 | 1.1 |
| Constipation | 27 | 0.5 |
| Diarrhea | 26 | 2.9 |
| Nausea | 25 | 0.5 |
| Abdominal painð | 24 | 1.4 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
| Rashø | 21 | 0.2 |
| Psychiatric | ||
| Mood disordersý | 14 | 0.9 |
| Sleep Disturbance£ | 12 | 0.2 |
| Investigations | ||
| Increased weight | 17 | 4.1 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition | ||
| Decreased appetite | 14 | 1.1 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 18 | 0.7 |
| Urinary tract infection¥ | 14 | 1.8 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 11 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in ≤ 10% of patients include fractures (7%).
| Laboratory Abnormality | VITRAKVI* | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%)† | Grade 3-4 (%)† |
|
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased AST | 62 | 7 |
| Increased ALT | 61 | 8 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 44 | 2.7 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 40 | 3 |
| Hypocalcemia | 32 | 3.1 |
| Hematology | ||
| Anemia | 45 | 8 |
| Leukopenia | 37 | 3.8 |
| Lymphopenia | 35 | 11 |
| Neutropenia | 34 | 11 |
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on VITRAKVI
Strong and Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Coadministration of VITRAKVI with a strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor may increase larotrectinib plasma concentrations, which may result in a higher incidence of adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of VITRAKVI with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, including grapefruit or grapefruit juice. If coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided, modify VITRAKVI dose as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. In patients coadministered a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor with VITRAKVI, monitor for adverse reactions more frequently and reduce the VITRAKVI dosage based on the severity of emergent adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Strong and Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers
Coadministration of VITRAKVI with a strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducer may decrease larotrectinib plasma concentrations, which may decrease the efficacy of VITRAKVI [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of VITRAKVI with strong CYP3A4 inducers, including St. John's wort. If coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inducers cannot be avoided, modify VITRAKVI dose as recommended. For coadministration with moderate CYP3A4 inducers, modify VITRAKVI dose as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
7.2 Effects of VITRAKVI on Other Drugs
Sensitive CYP3A4 Substrates
Coadministration of VITRAKVI with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates may increase their plasma concentrations, which may increase the incidence or severity of adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of VITRAKVI with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. If coadministration of these sensitive CYP3A4 substrates cannot be avoided, monitor patients for increased adverse reactions of these drugs.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on literature reports in human subjects with congenital mutations leading to changes in TRK signaling, findings from animal studies, and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], VITRAKVI can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on VITRAKVI use in pregnant women. Administration of larotrectinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in malformations at maternal exposures that were approximately 11- and 0.7-times, respectively, those observed at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Published reports of individuals with congenital mutations in TRK pathway proteins suggest that decreases in TRK-mediated signaling are correlated with obesity, developmental delays, cognitive impairment, insensitivity to pain, and anhidrosis.
Animal Data
Larotrectinib crosses the placenta in animals. Larotrectinib did not result in embryolethality at maternally toxic doses [up to 40 times the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily] in embryo-fetal development studies in pregnant rats dosed during the period of organogenesis; however, larotrectinib was associated with fetal anasarca in rats from dams treated at twice-daily doses of 40 mg/kg [11 times the human exposure (AUC) at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily]. In pregnant rabbits, larotrectinib administration was associated with omphalocele at twice-daily doses of 15 mg/kg (0.7 times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of larotrectinib or its metabolites in human milk and no data on its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with larotrectinib and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating VITRAKVI [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
VITRAKVI can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Infertility
Females
Based on histopathological findings in the reproductive tracts of female rats in a 1-month repeated-dose study, VITRAKVI may reduce fertility [See Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of VITRAKVI in pediatric patients was established based upon data from three multicenter, open-label, single-arm clinical trials in adult or pediatric patients. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14)].
The efficacy of VITRAKVI was evaluated in 131 pediatric patients and is described in the Clinical Studies section [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The safety of VITRAKVI was evaluated in 154 pediatric patients who received VITRAKVI. Of these 154 patients, 31% were <1 month to < 2 years (n = 47), 49% were 2 years to < 12 years (n = 75), and 21% were 12 years to < 18 years (n = 32); 25% had metastatic disease, 44% had locally advanced disease, and 31% had primary CNS; and 82% had received prior treatment for their cancer, including surgery, radiotherapy, or systemic therapy, including radioactive iodine therapy (RAI). The most common cancers were infantile fibrosarcoma (32%), primary CNS tumors (31%), soft tissue sarcoma (27%), and thyroid cancer (4%). The median duration of exposure was 14.8 months (range: 0.4 months to 87.4 months).
Due to the small number of pediatric and adult patients, the single arm design of clinical studies of VITRAKVI, and confounding factors such as differences in susceptibility to infections between pediatric and adult patients, it is not possible to determine whether differences in the incidence of adverse reactions to VITRAKVI are related to patient age or other factors. Adverse reactions occurring more frequently (at least a 10% increase in per-patient incidence) in pediatric patients compared to adult patients were vomiting (51% versus 18%), pyrexia (47% versus 15%), cough (36% versus 23%), diarrhea (34% versus 21%), upper respiratory tract infection (33% versus 10%), headache (25% versus 13%), nasopharyngitis (20% versus 7%), nasal congestion (18% versus 7%), gastroenteritis (13% versus 2%), and rhinitis (12% versus 0%).
Laboratory abnormalities occurring more frequently (at least a 10% increase in per-patient incidence) in pediatric patients compared to adult patients were AST increased (75% versus 55% in adults), ALT increased (69% versus 57% in adults), neutrophil count decrease (59% versus 20% in adults), leukocyte count decrease (46% versus 32% in adults), hyperkalemia (39% versus 16%), glucose decrease (29% versus 13% in adults), and lymphocyte increase (25% versus 1%). Three of the 154 pediatric patients discontinued VITRAKVI due to an adverse reaction associated with a laboratory abnormality (1 patient with Grade 3 increased ALT and 2 patients with Grade 3 decreased neutrophil count).
The pharmacokinetics of VITRAKVI in the pediatric population were similar to those seen in adults [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Larotrectinib was administered in a juvenile toxicity study in rats at twice daily doses of 0.2, 2 and 7.5 mg/kg from postnatal day (PND) 7 to 27 and at twice daily doses of 0.6, 6 and 22.5mg/kg between PND 28 and 70. The dosing period was equivalent to human pediatric populations from newborn to adulthood. The doses of 2/6 mg/kg twice daily [approximately 0.7 times the human exposure (AUC) at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily] and 7.5/22.5 mg/kg twice daily (approximately 4 times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily) resulted in mortality between PND 9 to 99; a definitive cause of death was not identified in the majority of cases.
The main findings were transient central nervous system-related signs including head flick, tremor, and circling in both sexes. An increase in the number of errors in a maze swim test occurred in females at exposures of approximately 4 times the human exposure (AUC) at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily. Decreased growth and delays in sexual development occurred in the mid- and high-dose groups. Mating was normal in treated animals, but a reduction in pregnancy rate occurred at the high-dose of 7.5/22.5 mg/kg twice daily (approximately 4 times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 100 mg twice daily).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of 444 patients in the overall safety population who received VITRAKVI, 20% of patients were ≥ 65 years of age and 6% of patients were ≥ 75 years of age. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of VITRAKVI were observed between patients 65 years and older and younger adult patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A). Larotrectinib clearance was reduced in subjects with moderate (Child-Pugh B) to severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Reduce VITRAKVI dose as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment of any severity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11. Vitrakvi Description
Larotrectinib is a kinase inhibitor. VITRAKVI (larotrectinib) capsules and oral solution are formulated using larotrectinib sulfate. The molecular formula for larotrectinib sulfate is C21H24F2N6O6S and the molecular weight is 526.51 g/mol for the sulfate salt and 428.44 g/mol for the free base. The chemical name is (3S)-N-{5-[(2R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl}-3-hydroxy-1-pyrrolidinecarboxamide sulfate. Larotrectinib sulfate has the following chemical structure:

Larotrectinib sulfate is an off-white to pinkish yellow solid that is not hygroscopic. The aqueous solubility of larotrectinib at 37°C is pH dependent (very soluble at pH 1.0 and freely soluble at pH 6.8, according to USP descriptive terms of solubility).
VITRAKVI (larotrectinib) capsules and oral solution are for oral use. Each capsule contains 25 mg or 100 mg larotrectinib (30.7 mg and 123 mg larotrectinib sulfate, respectively) in a hard gelatin capsule. The capsule is composed of gelatin, titanium dioxide, and edible ink.
The oral solution packaged in one bottle containing 100 mL contains 20 mg/mL larotrectinib (24.6 mg/mL larotrectinib sulfate) and the following inactive ingredients: purified water, hydroxypropyl betadex, sucrose, glycerin, sorbitol, citric acid, sodium phosphate, sodium citrate dihydrate, propylene glycol and flavoring. Preserved with methylparaben and potassium sorbate.
The oral solution packaged in two bottles each containing 50 mL contains 20 mg/mL larotrectinib (24.6 mg/mL larotrectinib sulfate) and the following inactive ingredients: purified water, hydroxypropyl betadex, sucralose, sodium citrate, strawberry flavor, and citric acid. Preserved with sodium benzoate.
12. Vitrakvi - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Larotrectinib is an inhibitor of the tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK), TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC. In a broad panel of purified enzyme assays, larotrectinib inhibited TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC with IC50 values between 5-11 nM. One other kinase TNK2 was inhibited at approximately 100-fold higher concentration. TRKA, B, and C are encoded by the genes NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3. Chromosomal rearrangements involving in-frame fusions of these genes with various partners can result in constitutively-activated chimeric TRK fusion proteins that can act as an oncogenic driver, promoting cell proliferation and survival in tumor cell lines.
In in vitro and in vivo tumor models, larotrectinib demonstrated anti-tumor activity in cells with constitutive activation of TRK proteins resulting from gene fusions, deletion of a protein regulatory domain, or in cells with TRK protein overexpression. Larotrectinib had minimal activity in cell lines with point mutations in the TRKA kinase domain, including the clinically identified acquired resistance mutation, G595R. Point mutations in the TRKC kinase domain with clinically identified acquired resistance to larotrectinib include G623R, G696A, and F617L.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of larotrectinib were studied in healthy subjects and adult and pediatric patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors. In healthy subjects who received a single dose of VITRAKVI capsules, systemic exposure (Cmax and AUC) of larotrectinib was dose proportional over the dose range of 100 mg to 400 mg (1 to 4 times the recommended adult dose) and slightly greater than proportional at doses of 600 mg to 900 mg (6 to 9 times the recommended adult dose). In adult patients who received VITRAKVI capsules 100 mg twice daily in Study LOXO-TRK-14001, peak plasma levels (Cmax) of larotrectinib were achieved at approximately 1 hour after dosing and steady-state was reached within 3 days. Mean steady-state larotrectinib [coefficient of variation (CV%)] for Cmax was 788 (81%) ng/mL and AUC0-24hr was 4351 (97%) ng*h/mL.
Absorption
The mean absolute bioavailability of VITRAKVI capsules was 34% (range: 32% to 37%). In healthy subjects, the AUC of VITRAKVI oral solution was similar to that of the capsules and the Cmax was 36% higher with the oral solution.
Effect of Food
The AUC of larotrectinib was similar and the Cmax was reduced by 35% after oral administration of a single 100 mg capsule of VITRAKVI to healthy subjects taken with a high-fat meal (approximately 900 calories, 58 grams carbohydrate, 56 grams fat and 43 grams protein) compared to the Cmax and AUC in the fasted state.
Distribution
The mean (CV%) volume of distribution (Vss) of larotrectinib is 48 (38%) L following intravenous administration of larotrectinib in healthy subjects.
Larotrectinib is 70% bound to human plasma proteins in vitro and binding is independent of drug concentrations. The blood-to-plasma concentration ratio is 0.9.
Elimination
The mean (CV%) clearance (CL/F) of larotrectinib is 98 (44%) L/h and the half-life is 2.9 hours following oral administration of VITRAKVI in healthy subjects.
Metabolism
Larotrectinib is metabolized predominantly by CYP3A4. Following oral administration of a single [14C] radiolabeled 100 mg dose of larotrectinib to healthy subjects, unchanged larotrectinib constituted 19% and an O-linked glucuronide constituted 26% of the major circulating radioactive drug components in plasma.
Specific Populations
Age (range: 28 days to 82 years), sex, and body weight (range: 3.8 kg to 179 kg) had no clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of larotrectinib.
Pediatric Patients
In pediatric patients, the larotrectinib geometric mean (%CV) AUC0-24hr by age subgroup was: 3348 (66%) ng*h/mL in patients 1 month to < 2 years (n = 9), 4135 (36%) ng*h/mL in patients 2 to < 12 years (n = 15), and 3108 (69%) ng*h/mL and in patients 12 to < 18 years (n = 9).
Patients with Renal Impairment
Following oral administration of a single 100 mg dose of VITRAKVI capsules in subjects with end-stage renal disease (e.g., subjects who required dialysis), the AUC0-INF of larotrectinib increased 1.5-fold and Cmax increased 1.3-fold as compared to that in subjects with normal renal function (creatinine clearance ≥ 90 mL/min as estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). The pharmacokinetics of VITRAKVI in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 60 mL/min) have not been studied.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following oral administration of a single 100 mg dose of VITRAKVI capsules, the AUC0-INF of larotrectinib increased 1.3-fold in subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A), 2-fold in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) and 3.2-fold in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) as compared to that in subjects with normal hepatic function. The Cmax was similar in subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment and the Cmax of larotrectinib increased 1.5-fold in subjects with severe hepatic impairment as compared to that in subjects with normal hepatic function [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Effect of CYP3A Inhibitors: Coadministration of a single 100 mg dose of VITRAKVI capsules with itraconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) increased the AUC0-INF of larotrectinib by 4.3-fold and the Cmax by 2.8-fold as compared to VITRAKVI administered alone [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Coadministration of VITRAKVI with fluconazole (moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) is predicted to increase VITRAKVI steady state AUC by 2.7-fold and Cmax by 1.9-fold.
Effect of CYP3A Inducers: Coadministration of a single 100 mg dose of VITRAKVI capsules with rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) decreased the AUC0-INF of larotrectinib by 81% and the Cmax by 71% as compared to VITRAKVI administered alone [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Coadministration of VITRAKVI with efavirenz (moderate CYP3A4 inducer) is predicted to decrease steady state AUC of VITRAKVI by approximately 72% and Cmax by 60% compared to VITRAKVI administered alone [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Effect of Strong P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibitors: Coadministration of a single 100 mg dose of VITRAKVI capsules with a P-gp inhibitor (rifampin) increased the AUC0-INF of larotrectinib by 1.7-fold and the Cmax by 1.8-fold as compared to VITRAKVI administered alone.
Effect of Larotrectinib on CYP3A4 Substrates: Coadministration of VITRAKVI capsules 100 mg twice daily with a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate (midazolam) increased both the AUC0-INF and Cmax of midazolam by 1.7-fold as compared to midazolam administered alone. The AUC0-INF and Cmax of 1-hydroxymidazolam, the main metabolite of midazolam, were both increased 1.4-fold as compared to when midazolam was administered alone [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
In Vitro Studies
Effect of Transporter on Larotrectinib: Larotrectinib is a substrate for P-gp and BCRP. Larotrectinib is not a substrate of OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, OATP1B1, or OATP1B3.
Effect of Larotrectinib on Transporters: Larotrectinib is not an inhibitor of BCRP, P-gp, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, BSEP, MATE1 and MATE2-K at clinically relevant concentrations.
Effect of Larotrectinib on CYP Substrates: Larotrectinib is not an inhibitor or inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP2D6 at clinically relevant concentrations.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with larotrectinib. Larotrectinib was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assays, with or without metabolic activation, or in the in vitro mammalian mutagenesis assays, with or without metabolic activation. In vivo, larotrectinib was negative in the mouse micronucleus test.
Fertility studies with larotrectinib have not been conducted. In a 3-month repeat-dose toxicity study in the rat, larotrectinib had no effects on spermatogenesis at 75 mg/kg/day (approximately 7 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily dose). Additionally, larotrectinib had no histological effects on the male reproductive tract in rats or monkeys at doses resulting in exposures up to 10 times the human exposure (AUC0-24hr) at the 100 mg twice daily clinical dose.
In a 1-month repeat-dose study in the rat, decreased uterine weight and uterine atrophy were seen at 200 mg/kg/day [approximately 45 times the human exposure (AUC) at the 100 mg twice daily dose]. Fewer corpora lutea and increased incidence of anestrus were also noted at doses ≥ 60 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily dose). Decreased fertility occurred in a juvenile animal study [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. There were no findings in female reproductive organs in repeat-dose studies in monkeys at exposures up to 22 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily dose.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In general toxicology studies conducted in rats and monkeys and in reproductive toxicology studies conducted in rats and rabbits, administration of larotrectinib led to increased food consumption and increased body weight at doses resulting in exposures 0.6 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily clinical dose. Obesity has also been one phenotypic outcome of some human syndromes resulting from congenital mutations in NTRK2 resulting in altered TRK signaling.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of VITRAKVI was evaluated in pediatric and adult patients with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with a NTRK gene fusion enrolled in one of three multicenter, open-label, single-arm clinical trials: Study LOXO-TRK-14001 (NCT02122913), SCOUT (NCT02637687), and NAVIGATE (NCT02576431). All patients were required to have progressed following systemic therapy for their disease, if available, or would have required surgery with significant morbidity for locally advanced disease.
Adult patients received VITRAKVI 100 mg orally twice daily and pediatric patients (18 years or younger) received VITRAKVI 100 mg/m2 up to a maximum dose of 100 mg orally twice daily until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. Identification of positive NTRK gene fusion status was prospectively determined in local laboratories using next generation sequencing (NGS) (89%), fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) or reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). NTRK gene fusions were inferred in 14 patients who had a documented ETV6 or NTRK 3 translocation identified by FISH. The major efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR), as determined by a blinded independent review committee (BIRC) according to RECIST v1.1.
The assessment of efficacy was based on 339 patients with solid tumors with an NTRK gene fusion enrolled across the three clinical trials. Baseline characteristics were: median age 38 years (range: 18 days to 90 years); 39% <18 years of age; 51% female; 57% White, 28% Asian, 2.4% Black or African American; 6% Hispanic or Latino and ECOG performance status (PS) 0-1 (88%) or 2 (10%). Sixty-three percent of patients had metastatic disease, including patients with brain metastases, and 22% had locally advanced, unresectable disease. Ninety-two percent of patients had received prior treatment for their cancer, including surgery, radiotherapy, or systemic therapy, including RAI. Seventy percent of all patients had received prior systemic therapy in the unresectable or metastatic setting excluding RAI; 30% were treatment naive, 33% had received 1 prior therapy and 37% percent had received 2 or more prior therapies with a median of one prior systemic regimen.
Efficacy results are summarized in Tables 5, 6, and 7.
| Efficacy Parameter | VITRAKVI N = 339 |
|---|---|
| + Denotes ongoing response. | |
|
|
| Overall response rate (95% CI) | 60% (55%, 65%) |
| Complete response rate | 24%* |
| Partial response rate | 36% |
| Duration of response (DOR) | N = 204 |
| Median (months) (95% CI) | 43.3† (32.5, NE‡) |
| Range (months) | 0.0+, 73.7+ |
| % with Observed DOR> 12 months | 64% |
| % with Observed DOR> 24 months | 45% |
| Tumor Type | Patients (N=339) | ORR | DOR Range (months) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 95% CI | |||
| NA = not applicable due to small numbers or lack of response; NE = not evaluable; SD = stable disease; PD = progressive disease. + Denotes ongoing response. |
||||
| Soft tissue sarcoma | 70 | 70% | (58%, 80%) | 0.0+, 72.7+ |
| Infantile fibrosarcoma | 49 | 94% | (83%, 99%) | 1.6+, 73.7+ |
| Primary CNS | 49 | 27% | (15%, 41%) | 1.9+, 57.5+ |
| Lung | 30 | 70% | (51%, 85%) | 1.9+, 56.2+ |
| Thyroid | 30 | 63% | (44%, 80%) | 3.7, 72.4+ |
| Differentiated | 23 | 78% | (56%, 93%) | 4.9, 72.4+ |
| Non-differentiated | 7 | 14% | (0%, 58%) | 3.7* |
| Salivary gland | 25 | 84% | (64%, 95%) | 7.4, 65.2+ |
| MASC | 14 | 79% | (49%, 95%) | 7.7, 59.1 |
| Colorectal† | 24 | 46% | (26%, 67%) | 3.9, 45.2+ |
| Breast | 14 | 57% | (29%, 82%) | 7.4, 58.2+ |
| Secretory | 6 | 83% | (36%, 100%) | 11.1, 58.2+ |
| Non-secretory | 8 | 38% | (9%, 76%) | 7.4, 12.5+ |
| Melanoma | 11 | 45% | (17%, 77%) | 1.9+, 23.2+ |
| Pancreas | 7 | 14% | (0%, 58%) | 5.8* |
| Gastrointestinal stromal tumor | 5 | 80% | (28%, 99%) | 9.5, 50.4+ |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | 4 | 2 SD, 2 NE | NA | NA |
| Bone sarcoma | 3 | 33% | (1%, 91%) | 9.5* |
| Gastric | 3 | 2 PD, NE | NA | NA |
| Cancer of unknown primary | 2 | 100% | (16%, 100%) | 5.6, 7.4 |
| Congenital mesoblastic nephroma | 2 | 100% | (16%, 100%) | 32.9, 44.5 |
| Prostate | 2 | SD, PD | NA | NA |
| Appendix | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| Cervix | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| Duodenal | 1 | PD | NA | NA |
| Esophageal | 1 | PD | NA | NA |
| External auditory canal | 1 | 100% | (3%, 100%) | 33.8+* |
| Hepatic | 1 | NE | NA | NA |
| Thymus | 1 | PD | NA | NA |
| Urothelial | 1 | PD | NA | NA |
| Uterus | 1 | NE | NA | NA |
The ORR for patients with NTRK1 fusions (n=142) was 59% (95% CI: 51, 67), NTRK2 fusions (n=44) was 32% (95% CI: 19, 48) and NTRK3 fusions (n=142) was 67% (95% CI: 59, 75).
| NTRK Partner* | Patients (N=339) | ORR | DOR Range (months) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 95% CI | |||
| PD = progressive disease; SD = stable disease; NA = not applicable. + Denotes ongoing response. |
||||
| ETV6-NTRK3 | 102 | 80% | (71%, 88%) | 0.0+, 66.7+ |
| TPM3-NTRK1 | 63 | 67% | (54%, 78%) | 0.8+, 73.7+ |
| LMNA-NTRK1 | 29 | 69% | (49%, 85%) | 3.4, 70.7+ |
| Inferred ETV6-NTRK3 | 14 | 93% | (66%, 100%) | 1.6+, 73.4+ |
| TPR-NTRK1 | 10 | 60% | (26%, 88%) | 3.0+, 38.7+ |
| EML4-NTRK3 | 6 | 50% | (12%, 88%) | 7.9, 40.7+ |
| IRF2BP2-NTRK1 | 4 | 100% | (40%, 100%) | 3.7, 47.8+ |
| BCR-NTRK2 | 3 | 67% | (9%, 99%) | 9.2+, 11.0 |
| GKAP1-NTRK2 | 3 | 2 SD, 1 PD | NA | NA |
| NACC2-NTRK2 | 3 | 33% | (1%, 91%) | 3.7† |
| RBPMS-NTRK3 | 3 | 67% | (9%, 99%) | 3.3+, 23.0 |
| SQSTM1-NTRK1 | 3 | 67% | (9%, 99%) | 9.9, 12.9+ |
16. How is Vitrakvi supplied
Capsules
25 mg: Hard gelatin opaque white capsule size #2 with blue printing of "BAYER" cross and "25 mg" on the body of the capsule.
| NDC# 50419-390-01 |
100 mg: Hard gelatin opaque white capsule size #0 with blue printing of "BAYER" cross and "100 mg" on the body of the capsule.
| NDC# 50419-391-01 |
Store capsules at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); temperature excursions between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F) are permitted [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Central Nervous System Effects
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they experience new or worsening neurotoxicity. Advise patients not to drive or operate hazardous machinery if they are experiencing neurologic adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Skeletal Fractures
Inform patients that bone fractures can occur in patients taking VITRAKVI. Advise patients to report symptoms such as pain, changes in mobility, or deformity to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients that they will need to undergo laboratory tests to monitor liver function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise males and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy and to use effective contraception during the treatment with VITRAKVI and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with VITRAKVI and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with VITRAKVI and for 1 week following the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females of reproductive potential that VITRAKVI may impair fertility [See Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients and caregivers to inform their healthcare provider of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products. Inform patients to avoid St. John's wort, grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking VITRAKVI [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 4/2025 | |||
| PATIENT INFORMATION | ||||
| VITRAKVI (vi trak vee) (larotrectinib) capsules | VITRAKVI (vi trak vee) (larotrectinib) oral solution |
|||
| What is VITRAKVI?
VITRAKVI is a prescription medicine that is used to treat adults and children with solid tumors (cancer) that:
|
||||
| Before taking VITRAKVI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | ||||
|
||||
Taking VITRAKVI with certain other medicines may affect the amount of VITRAKVI or other medicines in your blood and may cause side effects or affect the way that VITRAKVI works. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
||||
How should I take VITRAKVI?
|
||||
What should I avoid while taking VITRAKVI?
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of VITRAKVI?
VITRAKVI may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
|
|
|||
| Your healthcare provider may decrease your dose, temporarily stop or permanently stop your treatment with VITRAKVI if you develop serious side effects. The most common side effects of VITRAKVI include: |
||||
|
|
|||
| VITRAKVI may affect fertility in females and may affect your ability to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you. These are not all the possible side effects with VITRAKVI. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||
How should I store VITRAKVI?
|
||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of VITRAKVI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use VITRAKVI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give VITRAKVI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about VITRAKVI that is written for health professionals. |
||||
| What are the ingredients in VITRAKVI?
Active ingredient: larotrectinib Inactive ingredients: Capsule: gelatin, titanium dioxide and edible ink Oral Solution Packaged in One Bottle Containing 100 mL: purified water, hydroxypropyl betadex, sucrose, glycerin, sorbitol, citric acid, sodium phosphate, sodium citrate dihydrate, propylene glycol and flavoring. Preserved with methylparaben and potassium sorbate. Oral Solution Packaged in Two Bottles Each Containing 50 mL: purified water, hydroxypropyl betadex, sucralose, sodium citrate, strawberry flavor, and citric acid. Preserved with sodium benzoate. Manufactured for Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ 07981 For more information, go to www.VITRAKVI.com or call 1-888-842-2937 |
||||
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE VITRAKVI (vi trak vee) (larotrectinib) oral solution |
|
|---|---|
|
Read this Instructions for Use before you take or give a dose of VITRAKVI oral solution for the first time and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. Your healthcare provider should show you how to correctly measure the prescribed dose of VITRAKVI oral solution before you take or give a dose for the first time. Important information about measuring VITRAKVI oral solution:
|
|
|
Supplies needed to take or give a dose of VITRAKVI oral solution |
|
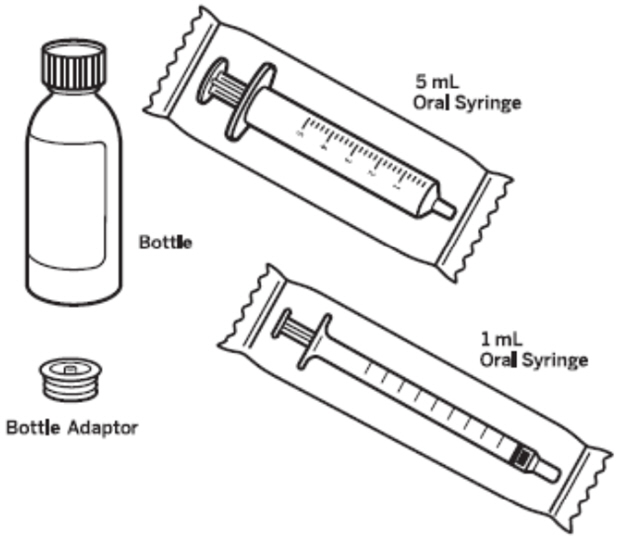 |
|
|
How to prepare a dose of VITRAKVI oral solution: |
|
|
Step 1: Remove the VITRAKVI oral solution bottle from the box. Place the bottle on a flat work surface. Open the bottle by pushing down firmly on the child-resistant cap and turning it in the direction of the arrow (counter-clockwise) See Figure B. Do not throw away the child-resistant cap. |
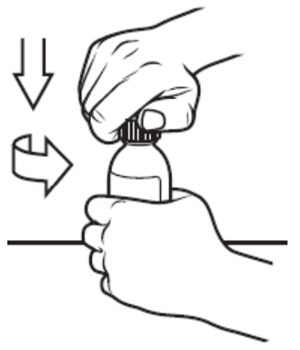 |
|
Step 2: Insert the bottle adaptor by pressing it into the bottle neck and make sure it is secure. See Figure C. Do not remove the bottle adaptor. If the bottle adaptor is missing, talk to your healthcare provider. |
 |
|
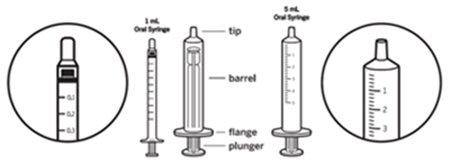
Step 3: Remove the oral syringe from the wrapper. Throw the wrapper away in your household trash. Look at the markings on the barrel of the oral syringe and find the marking that matches the VITRAKVI oral solution dose in mL prescribed by your healthcare provider. See Figure D. |
 |
|
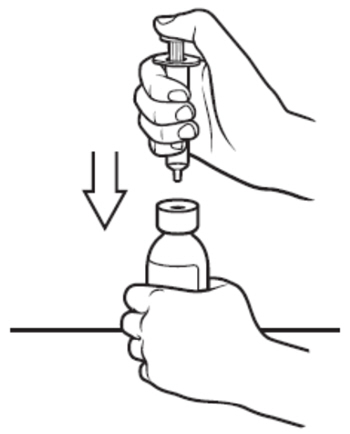
Step 4: With the bottle on your flat work surface, use 1 hand to hold the bottle upright. Using your other hand, push the air out of the oral syringe by pushing the plunger down. Then, insert the tip of the oral syringe into the bottle adaptor at the top of the bottle. See Figure E. The tip of the oral syringe should fit snugly into the hole of the bottle adaptor. |
 |
|
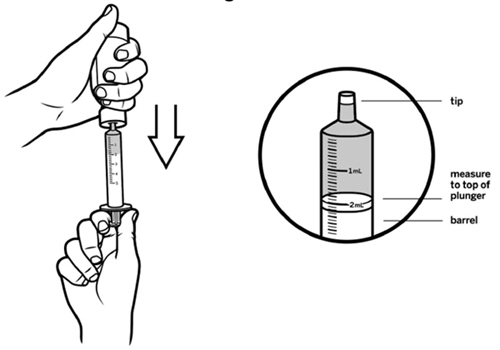
Step 5: Use 1 hand to hold the oral syringe in place. With the other hand, turn the bottle upside down. Pull back on the plunger until the top of the plunger lines up with the marking on the barrel of the oral syringe that matches the dose of VITRAKVI oral solution prescribed by your healthcare provider. See Figure F. Your dose may be different than the dose shown in Figure F. |
 |
|
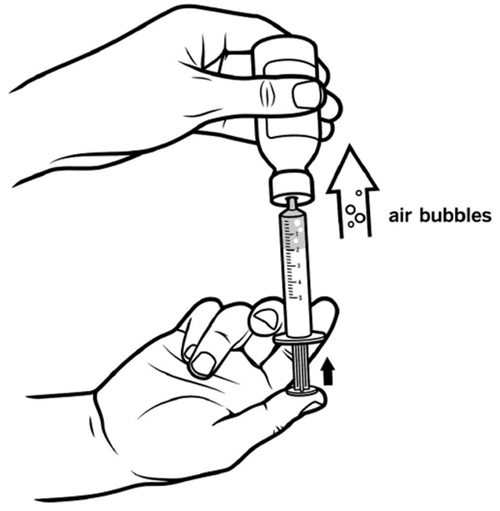
Step 6: Check for air bubbles in the oral syringe. If you see air bubbles, push up gently on the plunger to push any large air bubbles back into the bottle. Then, pull back on the plunger to the prescribed dose. See Figure G. |
 |
|
Step 7: Turn the bottle upright again and place it on your work surface. Remove the oral syringe from the bottle adaptor by gently pulling up on the syringe barrel. See Figure H. Do not push on the plunger during this step. The bottle adaptor should stay attached to the bottle. |
 |
|
Giving a dose of VITRAKVI oral solution by mouth: |
|
|
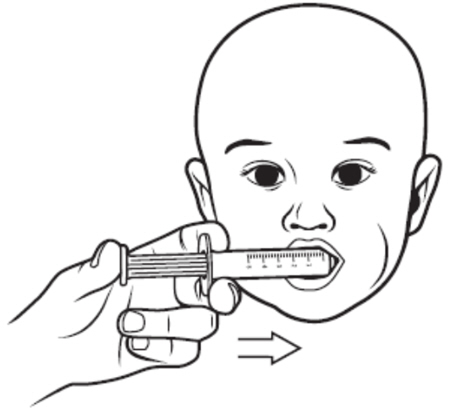
Step 8: Place the tip of the oral syringe into the child's mouth against the inside of the cheek. Slowly squirt VITRAKVI oral solution into the mouth by pressing down on the plunger and allow the child to swallow. See Figure I.
|
 |
|
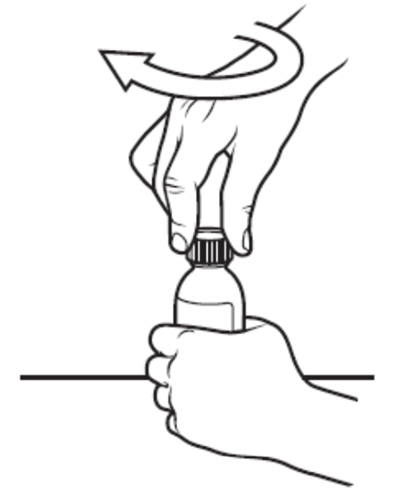
Step 9: Replace the child-resistant cap on the bottle of VITRAKVI oral solution. Do not remove the bottle adaptor. Close the bottle by turning the bottle cap in the direction of the arrow (clockwise). See Figure J. |
 |
|
Cleaning instructions for oral syringes |
|
|
Follow the instructions below for cleaning the oral syringe (Step 10 through Step 16). After 7 days of use, throw away the oral syringe in your household trash. Use a new oral syringe for the next 7 days. |
|
|
Step 10: Remove plunger from the barrel of the oral syringe. See Figure K. |
 |
|
Step 11: Rinse the barrel and plunger in warm running water to help make sure that all of the medicine has been removed from the oral syringe. See Figure L. Do not boil the oral syringe. |
 |
|
Step 12: Re-insert the plunger into the barrel of the oral syringe. See Figure M. |
 |
|
Step 13: Draw warm water several times into the oral syringe and squirt out again until all of the medicine has been removed from the oral syringe. See Figure N. |
 |
|
Step 14: Repeat steps 10 and 11 to rinse the barrel and plunger again with warm water. See Figure O. |
 |
|
Step 15: Shake off excess water or wipe off the outside. See Figure P. Place the barrel and plunger on a clean, dry paper towel to dry. |
 |
|
Step 16: Repeat step 12 to assemble the oral syringe and store in a clean place until the next use. Replace the oral syringe after 7 days of use, or if:
|
|
|
How should I store VITRAKVI oral solution? |
|
Keep VITRAKVI oral solution and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
 |
Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions about how to use VITRAKVI oral solution.
For more information, go to www.VITRAKVI.com or call 1-888-842-2937.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ 07981
Revised: 12/2022
Package Label - 25 mg - 60 Capsules
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71777-390-01
VITRAKVI®
(larotrectinib) capsules
25 mg
Usual Dosage: See prescribing information. Rx only.
60 capsules. Keep out of reach of children.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
Excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
Manufactured for Loxo Omcology, Inc. Stamford, CT 06901 86579626
(01)10371777390012
Bayer
LOXO
Each capsule contains
25 mg larotrectinib
(equivalent to 30.7 mg
larotrectinib sulfate).
Package Label - 100 mg - 60 Capsules
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71777-391-01
VITRAKVI®
(larotrectinib) capsules
100 mg
Usual Dosage: See prescribing information.
Rx only. 60 capsules. Keep out of reach of children.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
Excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
Manufactured for Loxo Omcology, Inc. Stamford, CT 06901 86579634
(01)10371777391019
Bayer
LOXO
Each capsule
contains 100 mg
larotrectinib
(equivalent to
123 mg
larotrectinib
sulfate).
Package Label - 20 mg/mL - 100 mL Oral Solution
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71777-392-01
VITRAKVI®
(larotrectinib) oral solution
20 mg/mL
Usual Dosage: See prescribing information. Keep refrigerated. Store at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Rx only.
Date of first opening ____/____/____. Discard unused portion 90 days after first opening.
100 mL oral solution. Keep out of reach of children.
Manufactured for Loxo Omcology, Inc. Stamford, CT 06901 86659069
(01)10371777392016
Bayer
LOXO
Each bottle contains
100 ml of 20 mg/mL
larotrectinib (equivalent
to 24.6 mg/mL
larotrectinib sulfate).
Package/Label Display Panel
Package Label - 20 mg/mL - 50 mL Oral Solution
NDC 50419-393-02
VITRAKVI®
(larotrectinib) oral solution
20 mg/mL
RECOMMENDED DOSAGE: See prescribing information. Keep refrigerated. Store at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Rx only.
Date of first opening ____/____/____. Discard unused portion 31 days after first opening.
50 mL oral solution. For Oral Administration Only.Keep out of reach of children.
Manufactured for Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ 07981 88735951
(01)10350419393024
Bayer
Each bottle contains
50 mL of 20 mg/mL
larotrectinib (equivalent
to 24.6 mg/mL
larotrectinib sulfate).
| VITRAKVI
larotrectinib capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| VITRAKVI
larotrectinib capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| VITRAKVI
larotrectinib solution, concentrate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VITRAKVI
larotrectinib solution, concentrate |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. (005436809) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penn Pharmaceutical Services Ltd | 226277259 | MANUFACTURE(50419-393, 50419-390, 50419-391, 50419-392) , ANALYSIS(50419-393, 50419-390, 50419-391, 50419-392) , PACK(50419-393, 50419-390, 50419-391, 50419-392) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| W. R. Grace & Co.-Conn. | 788779192 | API MANUFACTURE(50419-393, 50419-390, 50419-391, 50419-392) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharp Corporation | 143696495 | PACK(50419-390, 50419-391) , LABEL(50419-390, 50419-391, 50419-392) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orion Corporation, Orion Pharma | 539763727 | ANALYSIS(50419-393, 50419-390, 50419-391, 50419-392) , PACK(50419-393) , LABEL(50419-393) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEXTPHARMA PLOERMEL | 493010524 | MANUFACTURE(50419-390, 50419-391) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wickham Micro Limited | 228216353 | ANALYSIS(50419-392) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Butterworth Laboratories Ltd | 225081538 | ANALYSIS(50419-392) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Currenta GmbH & Co. OHG | 331575303 | ANALYSIS(50419-392) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orion Corporation, Orion Pharma | 368380223 | LABEL(50419-392, 50419-390, 50419-391) , PACK(50419-390, 50419-391) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avista Pharma Solutions, Inc. dba Cambrex | 144616641 | ANALYSIS(50419-390, 50419-391) | |
Frequently asked questions
More about Vitrakvi (larotrectinib)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (1)
- Drug images
- Latest FDA alerts (1)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: multikinase inhibitors
- Breastfeeding
- En español





