Kisqali: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: ribociclib
Dosage form: tablet, film coated
Drug class: CDK 4/6 inhibitors
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 10, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
KISQALI® (ribociclib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage for Kisqali
KISQALI is a kinase inhibitor indicated:
- in combination with an aromatase inhibitor for the adjuvant treatment of adults with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative stage II and III early breast cancer at high risk of recurrence. (1)
- for the treatment of adults with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer in combination with:
- an aromatase inhibitor as initial endocrine-based therapy; or
- fulvestrant as initial endocrine-based therapy or following disease progression on endocrine therapy. (1)
Kisqali Dosage and Administration
KISQALI tablets are taken orally with or without food in combination with an aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant. (2)
Early Breast Cancer
- Recommended starting dose: 400 mg orally (two 200 mg tablets) taken once daily with or without food for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off treatment. (2.1)
Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Recommended starting dose: 600 mg orally (three 200 mg tablets) taken once daily with or without food for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off treatment. (2.1)
Dose interruption, reduction, and/or discontinuation may be required based on individual safety and tolerability. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 200 mg (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis: Patients treated with CDK 4/6 inhibitors should be monitored for pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Interrupt and evaluate patients with new or worsening respiratory symptoms suspected to be due to ILD/pneumonitis. Permanently discontinue KISQALI in patients with recurrent symptomatic or severe ILD/pneumonitis. (2.2, 5.1)
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs): Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug-reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) can occur with KISQALI treatment. Permanently discontinue KISQALI in patients with SCARs or other life-threatening cutaneous reactions. (2.2, 5.2)
- QT Interval Prolongation: Monitor electrocardiograms (ECGs) and electrolytes prior to initiation of treatment with KISQALI. Repeat ECGs at approximately Day 14 of the first cycle, and as clinically indicated. Monitor electrolytes at the beginning of each cycle for 6 cycles, and as clinically indicated. Avoid using KISQALI with drugs known to prolong QT interval and/or strong CYP3A inhibitors. (2.2, 5.3, 7.1, 7.4)
- Increased QT Prolongation with Concomitant Use of Tamoxifen: KISQALI is not indicated for concomitant use with tamoxifen. (5.4)
- Hepatotoxicity: Increases in serum transaminase and bilirubin levels have been observed. Perform liver function tests (LFTs) before initiating treatment with KISQALI. Monitor LFTs every 2 weeks for the first 2 cycles, at the beginning of each subsequent 4 cycles, and as clinically indicated. (2.2, 5.5)
- Neutropenia: Perform complete blood count (CBC) before initiating therapy with KISQALI. Monitor CBC every 2 weeks for the first 2 cycles, at the beginning of each subsequent 4 cycles, and as clinically indicated. (2.2, 5.6)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception during therapy. (5.7, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- In patients with early breast cancer, the most common (incidence ≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are lymphocytes decreased, leukocytes decreased, neutrophils decreased, hemoglobin decreased, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, infections, creatinine increased, platelets decreased, headache, nausea, and fatigue. (6)
- In patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer, the most common (incidence ≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are leukocytes decreased, neutrophils decreased, hemoglobin decreased, lymphocytes decreased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, gamma glutamyl transferase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, infections, nausea, creatinine increased, fatigue, platelets decreased, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, constipation, alopecia, cough, rash, back pain, and glucose serum decreased. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use of KISQALI with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If strong inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce KISQALI dose. (2.2, 7.1)
- CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid concomitant use of KISQALI with strong CYP3A inducers. (7.2)
- CYP3A Substrates: The dose of CYP3A substrates may need to be reduced when given concurrently with KISQALI. (7.3)
- Drugs Known to Prolong QT Interval: Avoid concomitant use of drugs known to prolong QT interval, such as anti-arrhythmic medicines. (7.4)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 7/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Kisqali
1.1 Early Breast Cancer
KISQALI is indicated in combination with an aromatase inhibitor for the adjuvant treatment of adults with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative stage II and III early breast cancer at high risk of recurrence.
1.2 Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
KISQALI is indicated for the treatment of adults with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer in combination with:
- an aromatase inhibitor as initial endocrine-based therapy; or
- fulvestrant as initial endocrine-based therapy or following disease progression on endocrine therapy.
2. Kisqali Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Important Administration Instructions
KISQALI can be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Pre/perimenopausal women, or men, treated with the combination KISQALI plus an aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant, should be treated with a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist according to current clinical practice standards.
Patients should take their dose of KISQALI at approximately the same time each day, preferably in the morning.
If the patient vomits after taking the dose, or misses a dose, no additional dose should be taken that day. The next prescribed dose should be taken at the usual time. KISQALI tablets should be swallowed whole (tablets should not be chewed, crushed or split prior to swallowing). No tablet should be ingested if it is broken, cracked, or otherwise not intact.
Early Breast Cancer
The recommended dosage of KISQALI is 400 mg (two 200 mg film-coated tablets) taken orally, once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off in 28-day treatment cycles. KISQALI should be given in combination with an aromatase inhibitor. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for the recommended dosage of the aromatase inhibitor.
In patients with early breast cancer, treatment with KISQALI should continue for 3 years or until disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
The recommended dosage of KISQALI is 600 mg (three 200 mg film-coated tablets) taken orally, once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off in 28-day treatment cycles. KISQALI should be given in combination with endocrine therapy (fulvestrant or an aromatase inhibitor). Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for the recommended dose of endocrine therapy.
2.2 Dose Modifications
Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose modifications for adverse reactions are listed in Table 1.
| Level | KISQALI | |
| Dose | Number of tablets | |
| Early breast cancer | ||
| Starting dose | 400 mg/day | two 200 mg tablets |
| Dose reduction | 200 mg/day* | one 200 mg tablet |
| Advanced or metastatic breast cancer | ||
| Starting dose | 600 mg/day | three 200 mg tablets |
| First dose reduction | 400 mg/day | two 200 mg tablets |
| Second dose reduction | 200 mg/day* | one 200 mg tablet |
| *If dose reduction below 200 mg/day is required, discontinue KISQALI. | ||
Tables 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 summarize recommendations for dose interruption, reduction, or discontinuation of KISQALI in the management of specific adverse reactions. Dose modification of KISQALI is recommended based on individual patient safety and tolerability.
| Grade 1 (asymptomatic) | Grade 2 (symptomatic) | Grade 3 (severe symptomatic) or 4 (life-threatening) |
|
| ILD/Pneumonitis
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | No dose interruption or adjustment is required. Initiate appropriate medical therapy and monitor as clinically indicated. | Dose interruption until recovery to Grade ≤ 1 then consider resuming KISQALI at the next lower dose level*. If Grade 2 recurs, discontinue KISQALI. | Discontinue KISQALI. |
| Abbreviation: ILD, interstitial lung disease. Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. *An individualized benefit-risk assessment should be performed when considering resuming KISQALI. |
|||
| Grade 1
(< 10% body surface area (BSA) with active skin toxicity, no signs of systemic involvement) | Grade 2
(10%-30% BSA with active skin toxicity, no signs of systemic involvement) | Grade 3
(severe rash not responsive to medical management; > 30% BSA with active skin toxicity, signs of systemic involvement present; SJS*) | Grade 4
(any % BSA associated with extensive superinfection, with IV antibiotics indicated; life threatening consequences; TEN**) |
|
| Cutaneous adverse reactions, including SCARs
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | No dose adjustment is required.
Initiate appropriate medical therapy and monitor as clinically indicated. | Interrupt KISQALI until the etiology of the reaction has been determined. If the etiology is a SCAR, permanently discontinue KISQALI. If the etiology is not a SCAR, interrupt dose until recovery to Grade ≤ 1, then resume KISQALI at same dose level. If the cutaneous adverse reaction still recurs at Grade 3, resume KISQALI at the next lower dose level. | Permanently discontinue KISQALI. | |
| Abbreviations: BSA, body surface area; SCARs, severe cutaneous adverse reactions; SJS, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN, toxic epidermal necrolysis. *SJS (Grade 3 and 4) is defined as skin sloughing covering < 10% BSA and 10%-30% BSA, respectively, with associated signs (e.g., erythema, purpura, epidermal detachment, and mucous membrane detachment). **TEN (Grade 4) is defined as skin sloughing covering ≥ 30% BSA with associated symptoms (e.g., erythema, purpura, epidermal detachment, and mucous membrane detachment). Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. |
||||
| QTcF* prolongation | Early breast cancer | Advanced or metastatic breast cancer |
| > 480 ms and ≤ 500 ms | Interrupt KISQALI treatment and wait until QTcF resolves to ≤ 480 ms | |
| Resume at the same dose | Reduce to the next lower dose level | |
| If QTcF > 480 ms recurs, interrupt KISQALI treatment and wait until QTcF resolves to ≤ 480 ms, then resume at next lower dose level. | ||
| > 500 ms |
Interrupt KISQALI treatment and wait until QTcF resolves to ≤ 480 ms, then resume at next lower dose level. If QTcF > 500 ms recurs, discontinue KISQALI. |
|
| Permanently discontinue KISQALI if QTcF interval prolongation is either > 500 ms or > 60 ms change from baseline AND associated with any of the following: Torsades de Pointes, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, syncope, or signs/symptoms of serious arrhythmia. | ||
| Note: If dose reduction below 200 mg/day is required, discontinue KISQALI. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) should be assessed prior to initiation of treatment in all patients. Repeat ECGs at approximately Day 14 of the first cycle, and as clinically indicated. In case of QTcF prolongation at any given time during treatment, monitor ECG more frequently, and as clinically indicated *QTcF = QT interval corrected by Fridericia’s formula. |
||
| Grade 1
(> ULN – 3 x ULN) | Grade 2
(> 3 to 5 x ULN) | Grade 3
(> 5 to 20 x ULN) | Grade 4
(> 20 x ULN) |
|
| AST and/or ALT elevations from baseline*, WITHOUT increase in total bilirubin above 2 x ULN
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | No dose adjustment is required. | Baseline* at < Grade 2:
Dose interruption until recovery to ≤ baseline grade, then resume KISQALI at same dose level. If Grade 2 recurs, resume KISQALI at next lower dose level. ----------------------------- Baseline* at Grade 2: No dose interruption. | Dose interruption until recovery to ≤ baseline* grade, then resume at next lower dose level. If Grade 3 recurs, discontinue KISQALI. | Discontinue KISQALI. |
| Combined elevations in AST and/or ALT WITH total bilirubin increase, in the absence of cholestasis
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | If patients develop ALT and/or AST > 3 x ULN along with total bilirubin > 2 x ULN irrespective of baseline grade, discontinue KISQALI. | |||
| Perform Liver Function Tests (LFTs) before initiating treatment with KISQALI. Monitor LFTs every 2 weeks for the first 2 cycles, at the beginning of each subsequent 4 cycles, and as clinically indicated. If Grade ≥ 2 abnormalities are noted, monitor more frequently, and as clinically indicated. |
||||
| Abbreviations: AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ULN, upper limit of normal. *Baseline = prior to treatment initiation. Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. |
||||
| Grade 1 or 2
(ANC 1000/mm3 – < LLN) | Grade 3
(ANC 500 - < 1000/mm3) | Grade 3 febrile* neutropenia | Grade 4
(ANC < 500/mm3) |
|
| Neutropenia
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] | No dose adjustment is required. | Dose interruption until recovery to Grade ≤ 2. Resume KISQALI at the same dose level. If toxicity recurs at Grade 3, dose interruption until recovery, then resume KISQALI at the next lower dose level. | Dose interruption until recovery of neutropenia to Grade ≤ 2. Resume KISQALI at the next lower dose level. | Dose interruption until recovery to Grade ≤ 2. Resume KISQALI at the next lower dose level. |
| Perform complete blood counts (CBCs) before initiating treatment with KISQALI. Monitor CBC every 2 weeks for the first 2 cycles, at the beginning of each subsequent 4 cycles, and as clinically indicated. |
||||
| Abbreviations: ANC, absolute neutrophil count; LLN, lower limit of normal. *Grade 3 neutropenia with single episode of fever > 38.3°C (or) 38°C or above for more than one hour and/or concurrent infection. Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. |
||||
| Grade 1 or 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Other Toxicities | No dose adjustment is required. Initiate appropriate medical therapy and monitor as clinically indicated. | Dose interruption until recovery to Grade ≤ 1 then resume KISQALI at same dose level. If Grade 3 recurs, resume KISQALI at the next lower dose level. | Discontinue KISQALI. |
| *Excluding interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis, cutaneous adverse reactions, including severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs), QT interval prolongation, hepatobiliary toxicity, and neutropenia. Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. |
|||
Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for the coadministered aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant for dose modification guidelines in the event of toxicity and other relevant safety information.
Dose Modification for Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of KISQALI with strong CYP3A inhibitors and consider an alternative concomitant medication with less potential for CYP3A inhibition [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
If a strong CYP3A inhibitor must be coadministered, reduce the KISQALI dose as shown in Table 8.
| Indication | Co-administration with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors |
| Early breast cancer | Reduce the KISQALI dose to 200 mg once daily. |
| Advanced or metastatic breast cancer | Reduce the KISQALI dose to 400 mg once daily. |
If the strong inhibitor is discontinued, change the KISQALI dose (after at least 5 half-lives of the strong CYP3A inhibitor) to the dose used prior to the initiation of the strong CYP3A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Dose Modification for Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dose modifications for patients with hepatic impairment are shown in Table 9 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Indication | Mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A) | Moderate and severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C) |
| Early breast cancer | No dose adjustment is necessary | No dose adjustment is necessary |
| Advanced or metastatic breast cancer | No dose adjustment is necessary | KISQALI 400 mg once daily |
Review the Full Prescribing Information for the co-administered aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant for dose modifications related to hepatic impairment.
Dose Modification for Severe Renal Impairment
The recommended starting dose is 200 mg KISQALI once daily for patients with severe renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablet: 200 mg ribociclib (equivalent to 254.40 mg ribociclib succinate).
Film coated, light greyish violet, round, curved with beveled edges, debossed with “RIC” on one side and “NVR” on the other side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis
Severe, life-threatening, or fatal interstitial lung disease (ILD) and/or pneumonitis can occur in patients treated with KISQALI and other CDK 4/6 inhibitors.
In patients with early breast cancer (NATALEE) who received 400 mg KISQALI plus a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI), 1.5% of patients had ILD/pneumonitis (Grade 1-2).
In patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer (MONALEESA-2, MONALEESA-3, MONALEESA-7), 1.6% of patients had ILD/pneumonitis (any Grade, 0.4% had Grade 3-4, and 0.1% had a fatal outcome). Additional cases of ILD/pneumonitis have occurred in the postmarketing setting, some resulting in death [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis which may include hypoxia, cough, and dyspnea. In patients who have new or worsening respiratory symptoms suspected to be due to ILD or pneumonitis, interrupt KISQALI immediately and evaluate the patient. Permanently discontinue KISQALI in patients with severe ILD/pneumonitis or any recurrent symptomatic ILD/pneumonitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.2 Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs), including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DiHS)/drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) can occur in patients treated with KISQALI [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
If signs or symptoms of severe cutaneous reactions occur, interrupt KISQALI until the etiology of the reaction has been determined [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Early consultation with a dermatologist is recommended to ensure greater diagnostic accuracy and appropriate management.
If SJS, TEN, or DiHS/DRESS is confirmed, permanently discontinue KISQALI. Do not reintroduce KISQALI in patients who have experienced SCARs or other life-threatening cutaneous reactions during KISQALI treatment.
5.3 QT Interval Prolongation
KISQALI has been shown to prolong the QT interval in a concentration-dependent manner [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Avoid KISQALI in patients who are at significant risk of developing Torsades de Pointes (TdP), including those with:
- congenital long QT syndrome;
- uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease, recent myocardial infarction, heart failure, unstable angina, bradyarrhythmias, uncontrolled hypertension, high degree atrioventricular block, severe aortic stenosis, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism;
- electrolyte abnormalities;
- taking drugs known to prolong QT interval and/or strong CYP3A inhibitors as this may lead to prolongation of the QTcF interval.
Based on the observed QT prolongation during treatment, KISQALI may require dose interruption, reduction or discontinuation as described in Table 4 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Drug Interactions (7.4)].
In patients with early breast cancer (NATALEE) who received 400 mg KISQALI plus NSAI, 8 out of 2494 patients (0.3%) had > 500 ms post-baseline QTcF interval value and 50 out of 2494 patients (2%) had > 60 ms QTcF increase from baseline. QTcF prolongation was reversible with dose interruption. The majority of QTcF prolongation occurred within the first four weeks of KISQALI. There were no reported cases of Torsades de Pointes.
In patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer (MONALEESA-2, MONALEESA-3, and MONALEESA-7) who received 600 mg KISQALI plus NSAI or fulvestrant, 15 out of 1054 patients (1.4%) had a > 500 ms post-baseline QTcF value and 61 out of 1054 patients (6%) had a > 60 ms QTcF increase from baseline. QTcF prolongation was reversible with dose interruption. The majority of QTcF prolongation occurred within the first four weeks of KISQALI. There were no reported cases of Torsades de Pointes.
In MONALEESA-2, in the KISQALI plus letrozole treatment arm, there was one (0.3%) sudden death in a patient with Grade 3 hypokalemia and Grade 2 QT prolongation. No cases of sudden death were reported in MONALEESA-7 or MONALEESA-3 [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Perform ECG in all patients prior to starting KISQALI. Initiate treatment with KISQALI only in patients with QTcF values less than 450 ms. Repeat ECG at approximately Day 14 of the first cycle, and as clinically indicated.
Monitor serum electrolytes (including potassium, calcium, phosphorous and magnesium) prior to the initiation of KISQALI at the beginning of the first 6 cycles, and as clinically indicated. Correct any abnormality before starting KISQALI [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.4 Increased QT Prolongation with Concomitant Use of Tamoxifen
Avoid use of tamoxifen with KISQALI. In MONALEESA-7, the observed mean QTcF increase from baseline was > 10 ms higher in the tamoxifen plus placebo subgroup compared with the non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors (NSAIs) plus placebo subgroup. In the placebo arm, an increase of > 60 ms from baseline occurred in 6/90 (7%) of patients receiving tamoxifen, and in no patients receiving an NSAI. An increase of > 60 ms from baseline in the QTcF interval was observed in 14/87 (16%) of patients in the KISQALI and tamoxifen combination and in 18/245 (7%) of patients receiving KISQALI plus an NSAI [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5.5 Hepatotoxicity
In patients with early and advanced or metastatic breast cancer, drug-induced liver injury and increases in transaminases occurred with KISQALI.
In patients with early breast cancer (NATALEE) treated with KISQALI, drug-induced liver injury was reported in 9 patients (0.4%), of which 5 were Grade ≥ 3, and 8 had resolved as of the data cutoff. There were 8 (0.3%) clinically confirmed Hy’s Law cases (including 4 out of 9 drug-induced liver injury mentioned above), 6 of which had resolved within 303 days and 2 of which were improving, all after discontinuation of KISQALI. Grade 3 or 4 increases in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred in 8% and 4.7% respectively; including Grade 4 increases in ALT (1.5%) and AST (0.8%).
In patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer (MONALEESA-2, MONALEESA-7 and MONALEESA-3) treated with KISQALI Grade 3 or 4 increases in ALT and AST occurred in 11% and 8%, respectively. Among the patients who had Grade ≥ 3 ALT/AST elevation, the median time-to-onset was 92 days for the KISQALI plus aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant treatment arms. The median time to resolution to Grade ≤ 2 was 21 days in the KISQALI plus aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant treatment arms. In MONALEESA-2 and MONALEESA-3, concurrent elevations in ALT or AST greater than three times the ULN and total bilirubin greater than two times the ULN, with normal alkaline phosphatase, in the absence of cholestasis (Hy’s Law) occurred in 6 (1%) patients and all patients recovered after discontinuation of KISQALI.
Perform liver function tests (LFTs) in all patients before initiating KISQALI. Monitor LFTs every 2 weeks for first 2 cycles, at the beginning of each of the subsequent 4 cycles, and as clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Based on the severity of the transaminase elevations, KISQALI may require dose interruption, reduction, or discontinuation as described in Table 5 (Dose Modification and Management for Hepatobiliary Toxicity) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.6 Neutropenia
KISQALI causes concentration-dependent neutropenia.
In patients with early breast cancer (NATALEE) who received KISQALI plus NSAI, 94%, including 45% of Grade 3 or 4, had a decrease in neutrophil counts (based on laboratory findings), 63% had an adverse reaction of neutropenia, and 0.3% had febrile neutropenia. The median time to Grade ≥ 2 neutropenia was 18 days. The median time to resolution of Grade ≥ 3 neutropenia to Grade < 3 was 10 days. Treatment discontinuation due to neutropenia was required in 1.1% of patients.
In patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer (MONALEESA-2, MONALEESA-7, and MONALEESA-3) who received KISQALI plus NSAI or fulvestrant, 75% had neutropenia, 62% had Grade 3 or 4 decrease in neutrophil count (based on laboratory findings), and 1.7% had febrile neutropenia. The median time to Grade ≥ 2 neutropenia was 17 days. The median time to resolution of Grade ≥ 3 neutropenia to Grade < 3 was 12 days. Treatment discontinuation due to neutropenia was required in 1% of patients.
Perform a complete blood count (CBC) in all patients before initiating KISQALI. Monitor CBC every 2 weeks for the first 2 cycles, at the beginning of each subsequent 4 cycles, and as clinically indicated.
Based on the severity of the neutropenia, KISQALI may require dose interruption, reduction, or discontinuation as described in Table 6 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, KISQALI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of ribociclib to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis caused embryo-fetal toxicities at maternal exposures that were 0.6 and 1.5 times the human clinical exposure, respectively, based on area under the curve (AUC). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise women of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during therapy with KISQALI and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to KISQALI plus non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) in 2526 patients with early breast cancer (NATALEE), of whom 51% completed 36 months of KISQALI treatment. The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were lymphocytes decreased (97%), leukocytes decreased (95%), neutrophils decreased (94%), hemoglobin decreased (47%), alanine aminotransferase increased (45%), aspartate aminotransferase increased (44%), infections (37%), creatinine increased (33%), platelets decreased (28%), headache (23%), nausea (23%), and fatigue (22%).
In addition, the pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to KISQALI in 1065 patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer (MONALEESA-2, MONALEESA-3, MONALEESA-7), of whom 76% were exposed for 6 months or longer, and 62% were exposed for greater than one year. The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were leukocytes decreased (95%), neutrophils decreased (93%), hemoglobin decreased (68%), lymphocytes decreased (66%), aspartate aminotransferase increased (55%), gamma-glutamyl transferase increased (53%), alanine aminotransferase increased (52%), infections (47%), nausea (47%), creatinine increased (42%), fatigue (35%), platelets decreased (34%), diarrhea (33%), vomiting (29%), headache (27%), constipation (25%), alopecia (25%), cough (24%), rash (24%), back pain (24%), and glucose serum decreased (20%).
NATALEE: KISQALI in Combination with a Non-steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor as Adjuvant Treatment
Adults with HR-positive, HER2-negative Stage II and III Early Breast Cancer at High Risk of Recurrence
The safety of KISQALI was evaluated in NATALEE, a clinical trial of 5101 patients who received KISQALI plus NSAI or NSAI alone, with or without goserelin [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The median duration of exposure to KISQALI was 33 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 14% of patients who received KISQALI. Serious adverse reactions in > 0.5% of patients who received KISQALI included COVID-19 (1.1%), pneumonia (0.8%), and pulmonary embolism (0.6%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 0.6% of patients who received KISQALI. Fatal adverse reactions in ≥ 0.1% of patients receiving KISQALI included COVID-19 or COVID-19 pneumonia (0.2%) and pulmonary embolism (0.1%).
Permanent discontinuation of KISQALI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 20% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of KISQALI in ≥ 2% of patients were alanine aminotransferase or aspartate aminotransferase increased (8%).
Dosage interruptions of both KISQALI plus NSAI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 73% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 5% of patients included neutropenia or neutrophil count decreased (43%), alanine aminotransferase or aspartate aminotransferase increased (11%), COVID-19 (10%), and hypomagnesemia (5%).
Dose reductions of KISQALI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 23% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in ≥ 2% of patients included neutropenia or neutrophil count decreased (14%) and liver function abnormal (2.3%).
The most common (≥ 20% on KISQALI plus NSAI and ≥ 2% higher than placebo) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were neutropenia, infections, nausea, headache, fatigue, leukopenia, and abnormal liver function tests.
Table 10 summarizes the adverse reactions in NATALEE.
| Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. 1Infections: urinary tract infections; respiratory tract infections. 2Only includes a Grade 3 adverse reaction. |
||||
| Adverse reaction | KISQALI + NSAI (n = 2526) | NSAI (n = 2441) |
||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Infections1 | 37 | 2.0 | 27 | 0.9 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Headache2 | 23 | 0.4 | 17 | 0.2 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea2 | 23 | 0.2 | 8 | 0.1 |
| Diarrhea2 | 15 | 0.6 | 6 | 0.1 |
| Constipation2 | 13 | 0.2 | 5 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain2 | 11 | 0.5 | 7 | 0.4 |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue2 | 22 | 0.8 | 13 | 0.2 |
| Asthenia2 | 17 | 0.6 | 12 | 0.1 |
| Pyrexia2 | 11 | 0.2 | 6 | 0.1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 15 | 0 | 4.6 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Cough2 | 13 | 0.1 | 8 | 0.1 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions reported in < 10% of patients who received KISQALI plus NSAI included rash (9%), dizziness (9%), vomiting (8%), peripheral edema (7%), pruritis (7%), dyspnea (7%), stomatitis (6%), oropharyngeal pain (6%), hypocalcemia (5%), hypokalemia (4.8%), decreased appetite (4.8%).
Table 11 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in NATALEE.
| Laboratory abnormality | KISQALI + NSAI (n = 2526) | NSAI (n = 2441) |
||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Hematology | ||||
| Lymphocytes decreased | 97 | 19 | 88 | 6 |
| Leukocytes decreased | 95 | 27 | 45 | 0.6 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 94 | 45 | 35 | 1.7 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 47 | 0.6 | 26 | 0.3 |
| Platelets decreased | 28 | 0.4 | 13 | 0.3 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 45 | 8 | 35 | 1 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 44 | 5 | 33 | 1 |
| Creatinine increased | 33 | 0.3 | 11 | 0 |
MONALEESA-2: KISQALI in Combination with Letrozole
Postmenopausal Women with HR-positive, HER2-negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer for Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy
The safety of KISQALI was evaluated in MONALEESA-2, a clinical trial of 668 postmenopausal women receiving KISQALI plus letrozole or placebo plus letrozole [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The median duration of exposure to KISQALI plus letrozole was 13 months with 58% of patients exposed for ≥ 12 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 21% of patients who received KISQALI plus letrozole. Serious adverse reactions in ≥1 % of patients receiving KISQALI plus letrozole included abdominal pain (1.5%), vomiting (1.5%), constipation (1.2%), nausea (1.2%), anemia (1.2%), febrile neutropenia (1.2%), dyspnea (1.2%), and alanine aminotransferase increased (1.2%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.8% of patients who received KISQALI. Fatal adverse reactions in ≥ 0.1% of patients receiving KISQALI included acute respiratory failure (0.6%), acute myocardial infarction, sudden death (with Grade 3 hypokalemia and Grade 2 QT prolongation), unknown cause, and pneumonia (0.3% each). Permanent discontinuation of both KISQALI and letrozole due to an adverse reaction occurred in 7% of patients. Permanent discontinuation of KISQALI alone occurred in 7% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of both KISQALI and letrozole in ≥ 2% of patients were alanine aminotransferase increased (5%), aspartate aminotransferase increased (3%), and vomiting (2%).
Dosage interruptions of both KISQALI and letrozole due to an adverse reaction occurred in 71% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 5% of patients included neutropenia (39%), neutrophils decreased (12%), vomiting (6%), nausea (5%), alanine aminotransferase increased (5%), and leukocytes decreased (5%).
Dose reductions of KISQALI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 45% of patients receiving KISQALI plus letrozole. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in ≥ 2% of patients included neutropenia (24%), neutrophils decreased (8%), and alanine aminotransferase increased (3%).
Antiemetics and antidiarrheal medications were used to manage symptoms as clinically indicated.
The most common (≥ 20% on the KISQALI arm and ≥ 2% higher than placebo) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were neutrophils decreased, leukocytes decreased, hemoglobin decreased, nausea, lymphocytes decreased, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, fatigue, diarrhea, alopecia, vomiting, platelets decreased, constipation, headache, and back pain.
Table 12 summarizes the adverse reactions in MONALEESA-2.
| Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. 1Only includes a Grade 3 adverse reaction. |
||||
| Adverse reaction | KISQALI + Letrozole (n = 334) | Placebo + Letrozole (n = 330) |
||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea1 | 52 | 2.4 | 29 | 0.6 |
| Diarrhea1 | 35 | 1.2 | 22 | 0.9 |
| Vomiting1 | 29 | 3.6 | 16 | 0.9 |
| Constipation1 | 25 | 1.2 | 19 | 0 |
| Stomatitis1 | 12 | 0.3 | 7 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain1 | 11 | 1.2 | 8 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue | 37 | 2.4 | 30 | 0.9 |
| Pyrexia1 | 13 | 0.3 | 6 | 0 |
| Peripheral edema1 | 12 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia1 | 33 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Rash1 | 17 | 0.6 | 8 | 0 |
| Pruritus1 | 14 | 0.6 | 6 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Headache1 | 22 | 0.3 | 19 | 0.3 |
| Insomnia1 | 12 | 0.3 | 9 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Back pain1 | 20 | 2.1 | 18 | 0.3 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite1 | 19 | 1.5 | 15 | 0.3 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Dyspnea1 | 12 | 1.2 | 9 | 0.6 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Urinary tract infections1 | 11 | 0.6 | 8 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients in MONALEESA-2 receiving KISQALI plus letrozole included interstitial lung disease (0.3%), lung infiltration (0.3%), pneumonitis (0.3%), and pulmonary fibrosis (0.6%). Table 13 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in MONALEESA-2.
| Laboratory abnormality | KISQALI + Letrozole (n = 334) | Placebo + Letrozole (n = 330) |
||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Hematology | ||||
| Leukocytes decreased | 93 | 34 | 29 | 1.5 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 93 | 60 | 24 | 1.2 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 57 | 1.8 | 26 | 1.2 |
| Lymphocytes decreased | 51 | 14 | 22 | 3.9 |
| Platelets decreased | 29 | 0.9 | 6 | 0.3 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 46 | 10 | 36 | 1.2 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 44 | 7 | 32 | 1.5 |
| Creatinine increased | 20 | 0.6 | 6 | 0 |
| Phosphorous decreased | 13 | 5 | 4 | 0.6 |
| Potassium decreased | 11 | 1.2 | 7 | 1.2 |
MONALEESA-7: KISQALI in Combination with a Non-Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor
Pre/perimenopausal Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer for Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy
The safety of KISQALI was evaluated in MONALEESA-7, a clinical trial of 672 pre/perimenopausal patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer receiving either KISQALI plus a NSAI or tamoxifen plus goserelin or placebo plus NSAI or tamoxifen plus goserelin [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The median duration of exposure in the KISQALI plus a NSAI arm was 15.2 months with 66% of patients exposed for ≥ 12 months. The safety data reported below are based on 495 pre/perimenopausal patients receiving KISQALI plus NSAI plus goserelin or placebo plus NSAI plus goserelin.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 17% of patients who received KISQALI plus NSAI plus goserelin. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 1% of patients receiving KISQALI plus NSAI plus goserelin included drug-induced liver injury (1.6%), abdominal pain (1.2%), dyspnea (1.2%), febrile neutropenia (1.2%), and back pain (1.2%).
Permanent discontinuation of both KISQALI and NSAI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 3% of patients. Permanent discontinuation of KISQALI alone occurred in 3% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of both KISQALI and NSAI in ≥ 2% of patients were alanine aminotransferase increased (2%), and aspartate aminotransferase increased (2%).
Dosage interruptions of KISQALI plus NSAI plus goserelin due to an adverse reaction occurred in 73% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 5% of patients included neutropenia (41%), neutrophils decreased (26%), and leukocytes decreased (6%).
Dose reductions of KISQALI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 33% of patients receiving KISQALI plus NSAI plus goserelin. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in ≥ 2 % of patients included neutropenia (17%), neutrophils decreased (5%), and alanine aminotransferase increased (2%).
The most common (≥ 20% on the KISQALI arm and ≥ 2% higher than placebo) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were leukocytes decreased, neutrophils decreased, hemoglobin decreased, lymphocytes decreased, gamma-glutamyl transferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, infections, arthralgia, alanine aminotransferase increased, nausea, platelets decreased, and alopecia.
Table 14 summarizes the adverse reactions in MONALEESA-7.
| Abbreviation: NSAI, non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor. Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. 1Infections: urinary tract infections; respiratory tract infections, gastroenteritis, sepsis (< 1%). 2Only includes a Grade 3 adverse reactions. |
||||
| Adverse reaction | KISQALI + NSAI + Goserelin (n = 248) | Placebo + NSAI + Goserelin (n = 247) |
||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Infections1;2 | 36 | 1.6 | 24 | 0.4 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Arthralgia2 | 34 | 0.8 | 29 | 1.2 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea2 | 32 | 0 | 20 | 0 |
| Constipation2 | 16 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Stomatitis2 | 10 | 0 | 8 | 0.4 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia2 | 21 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Rash2 | 17 | 0.4 | 9 | 0 |
| Pruritus2 | 11 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||||
| Pyrexia2 | 17 | 0.8 | 7 | 0 |
| Pain in extremity2 | 10 | 0 | 8 | 1.2 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Cough2 | 15 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients in MONALEESA-7 receiving KISQALI plus NSAI included thrombocytopenia (9%), dry skin (9%), oropharyngeal pain (7%), dyspepsia (5%), lacrimation increased (4%), dry eye (4%), vitiligo (3%), hypocalcemia, (2%), blood bilirubin increased (1%), syncope (0.4%), and pneumonitis (0.4%).
| Laboratory abnormality | KISQALI + NSAI + Goserelin (n = 248) | Placebo + NSAI + Goserelin (n = 247) |
||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Hematology | ||||
| Leukocytes decreased | 93 | 36 | 30 | 0.8 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 92 | 63 | 27 | 2.4 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 84 | 2.4 | 51 | 0.4 |
| Lymphocytes decreased | 55 | 14 | 18 | 2.8 |
| Platelets decreased | 26 | 0.4 | 9 | 0.4 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase increased | 42 | 7 | 42 | 9 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 37 | 4.8 | 35 | 1.6 |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 33 | 6 | 31 | 1.6 |
| Phosphorous decreased | 14 | 1.6 | 11 | 0.8 |
| Potassium decreased | 11 | 1.2 | 14 | 1.2 |
| Glucose serum decreased | 10 | 0.4 | 10 | 0.4 |
| Creatinine increased | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
MONALEESA-3: KISQALI in Combination with Fulvestrant
Postmenopausal Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer for Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy or After Disease Progression on Endocrine Therapy
The safety of KISQALI was evaluated in MONALEESA-3, a clinical trial of 724 postmenopausal women receiving KISQALI plus fulvestrant or placebo plus fulvestrant [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The median duration of exposure to KISQALI plus fulvestrant was 15.8 months with 58% of patients exposed for ≥ 12 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 29% of patients who received KISQALI plus fulvestrant. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 1% of patients receiving KISQALI plus fulvestrant included pneumonia (1.9%), nausea (1.4%), vomiting (1.4%), anemia (1.2%), dyspnea (1.2%), neutropenia (1.2%). One case (0.2%) of fatal adverse reaction (pneumonia) occurred in patients who received KISQALI plus fulvestrant.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.2% of patients who received KISQALI. Fatal adverse reactions in ≥ 0.1% of patients receiving KISQALI included cardiac failure, ventricular arrhythmia, pneumonia, acute respiratory distress, pulmonary embolism, and hemorrhagic shock (0.2% each). Permanent discontinuation of both KISQALI and fulvestrant due to an adverse reaction occurred in 8% of patients. Permanent discontinuation of KISQALI alone occurred in 9% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of both KISQALI and fulvestrant in ≥ 2% of patients were alanine aminotransferase increased (5%), and aspartate aminotransferase increased (3%).
Dosage interruptions of KISQALI plus fulvestrant due to an adverse reaction occurred in 72% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 5% of patients included neutropenia (40%), neutrophils decreased (13%), alanine aminotransferase increased (8%), aspartate aminotransferase increased (8%), and leukocytes decreased (5%).
Dose reductions of KISQALI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 32% of patients receiving KISQALI plus fulvestrant. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in ≥ 2% of patients included neutropenia (15%), and neutrophils decreased (3%).
The most common (≥ 20% on the KISQALI arm and ≥ 2% higher than placebo) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were leukocytes decreased, neutrophils decreased, lymphocytes decreased, creatinine increased, hemoglobin decreased, gamma-glutamyl transferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, nausea, alanine aminotransferase increased, infections, platelets decreased, diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, glucose serum decreased, cough, rash, and pruritus.
Table 16 summarizes the adverse reactions in MONALEESA-3.
| Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. 1Infections: urinary tract infections; respiratory tract infections; gastroenteritis; sepsis (1%). 2Only include Grade 3 adverse reactions. 3Includes the following fatal adverse reactions: pneumonia (n = 1). |
||||
| Adverse reaction | KISQALI + Fulvestrant (n = 483) | Placebo + Fulvestrant (n = 241) |
||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea2 | 45 | 1.4 | 28 | 0.8 |
| Diarrhea2 | 29 | 0.6 | 20 | 0.8 |
| Vomiting2 | 27 | 1.4 | 13 | 0 |
| Constipation2 | 25 | 0.8 | 12 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain2 | 17 | 1.4 | 13 | 0.8 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Infections1;2;3 | 42 | 4.6 | 30 | 1.7 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Rash2 | 23 | 0.8 | 8 | 0 |
| Pruritus2 | 20 | 0.2 | 7 | 0 |
| Alopecia2 | 19 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Cough2 | 22 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 15 | 1.4 | 12 | 1.7 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite2 | 16 | 0.2 | 13 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||||
| Peripheral edema2 | 15 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Pyrexia2 | 11 | 0.2 | 7 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Dizziness2 | 13 | 0.2 | 8 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients in MONALEESA-3 receiving KISQALI plus fulvestrant included thrombocytopenia (9%) dry skin (8%), dysgeusia (7%), dry mouth (5%), vertigo (5%), dry eye (5%), lacrimation increased (4%), erythema (4%), hypocalcemia (4%), blood bilirubin increased (1%), syncope (1%), interstitial lung disease (0.4%), pneumonitis (0.4%), hypersensitivity pneumonitis (0.2%), and acute respiratory distress syndrome (0.2%).
| Laboratory abnormality | KISQALI + Fulvestrant (n = 483) | Placebo + Fulvestrant (n = 241) |
||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Hematology | ||||
| Leukocytes decreased | 95 | 26 | 26 | 0.4 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 92 | 53 | 21 | 0.8 |
| Lymphocytes decreased | 69 | 16 | 35 | 4.1 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 60 | 4.3 | 35 | 2.9 |
| Platelets decreased | 33 | 1.9 | 11 | 0 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Creatinine increased | 65 | 1 | 33 | 0.4 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase increased | 52 | 8 | 49 | 10 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 50 | 7 | 43 | 2.9 |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 44 | 11 | 37 | 1.7 |
| Glucose serum decreased | 23 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Phosphorous decreased | 18 | 4.6 | 8 | 0.8 |
| Albumin decreased | 12 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
COMPLEEMENT-1: KISQALI in Combination with Letrozole and Goserelin or Leuprolide
Men with HR-positive, HER2-negative Advanced Breast Cancer for Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy
The safety of KISQALI in combination with letrozole was evaluated in men (n = 39) in an open-label, multicenter clinical trial for the treatment of adult patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer who received no prior hormonal therapy for advanced disease (COMPLEEMENT-1) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
The median duration of exposure to KISQALI was 20.8 months (range, 0.5 to 30.6 months).
Other adverse reactions occurring in men treated with KISQALI plus letrozole and goserelin or leuprolide were similar to those occurring in women treated with KISQALI plus endocrine therapy.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse events have been reported during post-approval use of KISQALI. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Respiratory Disorders: Interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DiHS)/drug reaction with eosinophilia, and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs That May Increase Ribociclib Plasma Concentrations
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Coadministration of strong CYP3A inhibitors increases ribociclib exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Increased ribociclib concentrations may increase the incidence and severity of adverse reactions, including QTcF prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with KISQALI and consider alternative concomitant medications with less potential for CYP3A inhibition.
In patients with early breast cancer, if coadministration of KISQALI with a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the dose of KISQALI to 200 mg once daily. In patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer, if coadministration of KISQALI with a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the dose of KISQALI to 400 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
7.2 Drugs That May Decrease Ribociclib Plasma Concentrations
CYP3A Inducers
Coadministration of strong CYP3A inducers decreases the plasma exposure of ribociclib [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers and consider an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal potential to induce CYP3A.
7.3 Effect of KISQALI on Other Drugs
CYP3A Substrates
Coadministration of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with multiple doses of KISQALI increases the substrate exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. For CYP3A substrates where minimal increases in the concentration may increase CYP3A substrate adverse reactions, monitor for increased adverse reactions of the CYP3A substrate during treatment with KISQALI. The dose of the sensitive CYP3A substrate may need to be reduced as KISQALI can increase its exposure.
7.4 Drugs That Prolong the QT Interval
Avoid coadministration of KISQALI with products with a known potential to prolong QT interval, such as antiarrhythmic drugs and other drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, monitor ECG when initiating, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, KISQALI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
There are no available human data informing the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of ribociclib to pregnant animals during organogenesis resulted in increased incidences of post implantation loss and reduced fetal weights in rats and increased incidences of fetal abnormalities in rabbits at exposures 0.6 or 1.5 times the exposure in humans, respectively, at the highest recommended dose of 600 mg/day based on AUC (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. However, the background risk of major birth defects is 2%-4% and of miscarriage is 15%-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies in the U.S. general population.
Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies in rats and rabbits, pregnant animals received oral doses of ribociclib up to 1000 mg/kg/day and 60 mg/kg/day, respectively, during the period of organogenesis.
In rats, 300 mg/kg/day resulted in reduced maternal body weight gain and reduced fetal weights accompanied by skeletal changes related to the lower fetal weights. There were no significant effects on embryo-fetal viability or fetal morphology at 50 or 300 mg/kg/day.
In rabbits at doses ≥ 30 mg/kg/day, there were adverse effects on embryo-fetal development, including increased incidences of fetal abnormalities (malformations and external, visceral, and skeletal variants) and fetal growth (lower fetal weights). These findings included reduced/small lung lobes, additional vessel on the descending aorta, additional vessel on the aortic arch, small eyes, diaphragmatic hernia, absent accessory lobe or (partly) fused lung lobes, reduced/small accessory lung lobe, extra/rudimentary 13th ribs, misshapen hyoid bone, bent hyoid bone alae, and reduced number of phalanges in the pollex. There was no evidence of increased incidence of embryo-fetal mortality. There was no maternal toxicity observed at 30 mg/kg/day.
At 300 mg/kg/day in rats and 30 mg/kg/day in rabbits, the maternal systemic exposures (AUC) were approximately 0.6 and 1.5 times, respectively, the exposure in patients at the highest recommended dose of 600 mg/day.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known if ribociclib is present in human milk. There are no data on the effects of ribociclib on the breastfed infant or on milk production. Ribociclib and its metabolites readily passed into the milk of lactating rats. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from KISQALI, advise lactating women not to breastfeed while taking KISQALI and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose.
Data
In lactating rats administered a single dose of 50 mg/kg, exposure to ribociclib was 3.56-fold higher in milk compared to maternal plasma.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on animal studies and mechanism of action, KISQALI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to starting treatment with KISQALI.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception (methods that result in less than 1% pregnancy rates) during treatment with KISQALI and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Males
Based on animal studies, KISQALI may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of KISQALI in pediatric patients has not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 2549 adults with early breast cancer who received KISQALI in NATALEE, 407 patients (16%) were ≥ 65 years of age and 123 patients (2.4%) were ≥ 75 years of age. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of KISQALI were observed between older and younger adults with early breast cancer.
Of 334 patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer who received KISQALI in MONALEESA-2, 150 patients (45%) were ≥ 65 years of age and 35 patients (11%) were ≥ 75 years of age. Of 484 patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer who received KISQALI in MONALEESA-3, 226 patients (47%) were ≥ 65 years of age and 65 patients (14%) were ≥ 75 years of age. Of 248 patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer who received KISQALI in MONALEESA-7, no patients were ≥ 65 years of age. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of KISQALI were observed between older and younger adults with advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with breast cancer who have mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. A reduced starting dose of 400 mg is recommended in patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have moderate (Child-Pugh class B) and severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with breast cancer who have mild to moderate (30 mL/min to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2 ≤ estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)) renal impairment. A reduced starting dose of 200 mg is recommended in patients with breast cancer who have severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11. Kisqali Description
KISQALI (ribociclib) is a kinase inhibitor.
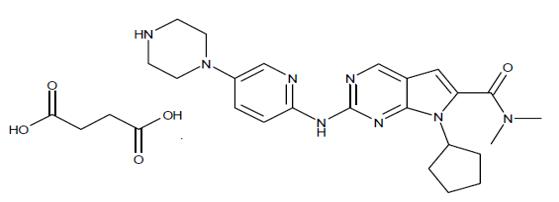
The chemical name of ribociclib succinate is: Butanedioic acid—7-cyclopentyl-N,N-dimethyl-2-{[5-(piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-2-yl]amino}-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide (1/1).
Ribociclib succinate is a light yellow to yellowish brown crystalline powder. The molecular formula for ribociclib succinate is C23H30N8O·C4H6O4 and the molecular weight is 552.64 g/mol (Free base: 434.55 g/mol).
The chemical structure of ribociclib is shown below:
KISQALI film-coated tablets are supplied for oral use and contain 200 mg of ribociclib free base (equivalent to 254.40 mg ribociclib succinate). The tablets also contain colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hydroxypropylcellulose, magnesium stearate and microcrystalline cellulose. The film-coating contains iron oxide black, iron oxide red, lecithin (soya), polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolysed), talc, titanium dioxide, and xanthan gum as inactive ingredients.
12. Kisqali - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ribociclib is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4 and 6. These kinases are activated upon binding to D-cyclins and are downstream of signaling pathways which lead to cell cycle progression and cellular proliferation. The cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex regulates cell cycle progression through phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRb).
In vitro, ribociclib decreased pRb phosphorylation, resulting in arrest in the G1 phase of the cell cycle and reduced proliferation in breast cancer-derived models. In vivo, treatment with single agent ribociclib in a rat xenograft model with human tumor cells led to decreased tumor volumes, which correlated with inhibition of pRb phosphorylation. In studies using patient-derived estrogen receptor positive breast cancer xenograft models, combination of ribociclib and antiestrogen (e.g., letrozole) therapies resulted in increased tumor growth inhibition compared to each drug alone. Additionally, the combination of ribociclib and fulvestrant resulted in tumor growth inhibition in an estrogen receptor positive breast cancer xenograft model.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of KISQALI have not been fully characterized in patients.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
A concentration-QT analysis of the data in patients with breast cancer treated with KISQALI at doses ranging from 50 to 1200 mg (0.083 to 2 times of the approved recommended high dose) suggested that ribociclib causes concentration-dependent increases in QTcF interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)].
In patients with early breast cancer, the estimated mean QTcF interval change from baseline for the KISQALI 400 mg in combination with non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) was 10.0 ms (90% CI: 8.0, 11.9) at the mean steady-state Cmax [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)].
In patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer the estimated mean QTcF interval change from baseline for the KISQALI 600 mg in combination with aromatase inhibitors or fulvestrant was 22.0 ms (90% CI: 20.6, 23.4) and 23.7 ms (90% CI: 22.3, 25.1), respectively, and was 34.7 ms (90% CI: 31.6, 37.8) in combination with tamoxifen at the mean steady-state Cmax [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Ribociclib exhibited over-proportional increases in exposure (Cmax and AUC) across the dose range of 50 mg to 1200 mg (0.083 to 2 times of the approved recommended high dose) following both single dose and repeated doses of KISQALI. Following repeated 600 mg once daily administration, steady-state was generally achieved after 8 days and ribociclib accumulated with a mean accumulation ratio of 2.5 (range, 0.97 to 6.4), and mean (coefficient of variation (CV%)) steady-state ribociclib Cmax was 1820 (62%) ng/mL and AUC was 23800 (66%) ng*h/mL.
Absorption
The Tmax following KISQALI administration was between 1 and 4 hours. The mean absolute bioavailability of ribociclib after a single oral dose of 600 mg was 65.8%.
Food Effect: Compared to the fasted state, oral administration of a single 600 mg dose of KISQALI tablet with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (approximately 800 to 1000 calories with ~50% calories from fat, ~35% calories from carbohydrates, and ~15% calories from protein) had no clinically meaningful differences in ribociclib Cmax or AUCinf.
Distribution
Ribociclib protein binding in vitro was approximately 70% and independent of concentration (10 to 10,000 ng/mL). The mean in vivo blood-to-plasma ratio was 1.04. The apparent volume of distribution at steady-state (Vss/F) was 1090 L.
Metabolism
Ribociclib undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism mainly via CYP3A4 in humans. Following oral administration of a single 600 mg dose of radio-labeled ribociclib to humans, the primary metabolic pathways for ribociclib involved oxidation (dealkylation, C and/or N-oxygenation, oxidation (-2H)) and combinations thereof. Ribociclib was the major circulating drug-derived entity in plasma (44%). The major circulating metabolites included metabolite M13 (CCI284, N-hydroxylation), M4 (LEQ803, N-demethylation), and M1 (secondary glucuronide), each representing an estimated 9%, 9%, and 8% of total radioactivity, and 22%, 20%, and 18% of ribociclib exposure. Clinical activity of ribociclib was due primarily to parent drug, with negligible contribution from circulating metabolites.
Ribociclib was extensively metabolized with unchanged drug accounting for 17% and 12% in feces and urine, respectively. Metabolite LEQ803 represented approximately 14% and 4% of the administered dose in feces and urine, respectively.
Elimination
The mean plasma effective half-life (CV%) was 32.0 hours (63%) and the mean apparent oral clearance (CL/F) was 25.5 L/hr (66%) at steady-state following 600 mg dose of KISQALI in patients with advanced cancer. The steady state mean CL/F was 38.4 L/hr following the 400 mg dose of KISQALI in patients with early breast cancer.
The mean apparent plasma terminal half-life of ribociclib ranged from 29.7 to 54.7 hours and mean CL/F of ribociclib ranged from 39.9 to 77.5 L/hr at 600 mg across studies in healthy adults.
Following a single oral dose of radio-labeled ribociclib in healthy adults, 92% of the total administered radioactive dose was recovered within 22 days; 69% in feces and 23% in urine.
Specific Populations
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Compared to adults with normal hepatic function, mild (Child-Pugh class A) hepatic impairment had no effect on the exposure of ribociclib; while in adults with moderate (Child-Pugh class B) hepatic impairment, the mean ratio was 1.44 for Cmax and 1.28 for AUCinf; and in adults with severe (Child-Pugh class C) hepatic impairment, the mean ratio was 1.32 for Cmax and 1.29 for AUCinf.
Patients with Renal Impairment
In adults with severe renal impairment and end stage renal disease, ribociclib AUCinf increased 2.4-fold and 3.8-fold, and Cmax increased 2.1-fold and 2.7-fold relative to the exposure in adults with normal renal function.
Mild or moderate renal impairment had no effect on the exposure of ribociclib. A sub-group analysis of data from studies following oral administration of KISQALI in patients with advanced cancer or early breast cancer who have mild to moderate renal impairment, AUC and Cmax were comparable to those in patients with normal renal function, suggesting no clinically meaningful effect of mild or moderate renal impairment on ribociclib exposure.
Effect of Age, Weight, Gender, and Race
No clinically relevant effects of age, body weight, gender, or race on the systemic exposure of ribociclib were identified.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Drugs That Affect Ribociclib Plasma Concentrations
CYP3A Inhibitors: Following a single 400 mg dose of KISQALI with ritonavir (a strong CYP3A inhibitor), ritonavir (100 mg twice a day for 14 days) increased ribociclib Cmax and AUCinf by 1.7-fold and 3.2-fold, respectively, compared to ribociclib alone. Cmax and AUC for LEQ803 (a prominent metabolite of ribociclib, accounting for less than 10% of parent exposure) decreased by 96% and 98%, respectively. A moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor (erythromycin) is predicted to increase ribociclib steady-state Cmax and AUC by 1.1-fold and 1.2-fold, respectively, following KISQALI 400 mg once daily, and 1.1-fold and 1.1-fold, respectively, following KISQALI 600 mg once daily.
CYP3A Inducers: Following a single 600 mg dose of KISQALI with rifampicin (a strong CYP3A4 inducer) at 600 mg daily for 14 days, ribociclib Cmax decreased by 81% and AUCinf decreased by 89%, while LEQ803 Cmax increased 1.7-fold and AUCinf decreased by 27% compared to ribociclib alone. A moderate CYP3A inducer (efavirenz) is predicted to decrease ribociclib steady-state Cmax by 55% and AUC by 74%, following KISQALI 400 mg once daily, and by 52% and 71%, respectively, following KISQALI 600 mg once daily.
Drugs That are Affected by KISQALI
CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 Substrates: In a cocktail study with midazolam (sensitive CYP3A4 substrate) multiple doses of ribociclib (400 mg once daily for 8 days) increased midazolam Cmax by 2.1-fold and increased AUCinf by 3.8-fold compared to midazolam alone. Administration of KISQALI 600 mg once daily is predicted to increase midazolam Cmax and AUC by 2.4-fold and 5.2-fold, respectively. The effect of multiple doses of 400 mg ribociclib on caffeine (sensitive CYP1A2 substrate) was minimal, with Cmax decreased by 10% and AUCinf increased by 20%. Only weak inhibitory effects on CYP1A2 substrates are predicted at KISQALI 600 mg once daily dose.
Gastric pH-Elevating Agents: Coadministration of ribociclib with drugs that elevate the gastric pH is not predicted to alter ribociclib absorption.
Letrozole: Data from a clinical trial in patients with breast cancer indicated no drug interaction between ribociclib and letrozole following coadministration of the drugs.
Anastrozole: Data from a clinical trial in patients with breast cancer indicated no clinically relevant drug interaction between ribociclib and anastrozole following coadministration of the drugs.
Exemestane: Data from a clinical trial in patients with breast cancer indicated no clinically relevant drug interaction between ribociclib and exemestane following coadministration of the drugs.
Fulvestrant: Data from a clinical trial in patients with breast cancer indicated no clinically relevant effect of fulvestrant on ribociclib exposure following coadministration of the drugs.
Tamoxifen: KISQALI is not indicated for concomitant use with tamoxifen. Data from a clinical trial in patients with breast cancer indicated that tamoxifen Cmax and AUC increased approximately 2-fold following coadministration of KISQALI 600 mg.
In vitro Studies
Effect of Ribociclib on CYP Enzymes: In vitro, ribociclib was a reversible inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4/5 and a time-dependent inhibitor of CYP3A4/5, at clinically relevant concentrations. In vitro evaluations indicated that ribociclib has no potential to inhibit the activities of CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6 at clinically relevant concentrations. It has no potential for time-dependent inhibition of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2D6, and no induction of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, and CYP3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Effect of Ribociclib on Transporters: In vitro evaluations indicated that ribociclib has a low potential to inhibit the activities of drug transporters P-gp, OATP1B1/B3, OCT1, MATEK2 at clinically relevant concentrations. Ribociclib may inhibit BCRP, OCT2, MATE1, and human BSEP at clinically relevant concentrations.
Effect of Transporters on Ribociclib: Based on in vitro data, P-gp and BCRP mediated transport are unlikely to affect the extent of oral absorption of ribociclib at therapeutic doses. Ribociclib is not a substrate for hepatic uptake transporters OATP1B1/1B3 or OCT1 in vitro.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study with oral administration of ribociclib daily in cycles of 3 weeks on/1 week off, ribociclib was not carcinogenic at doses up to 50 mg/kg in male rats and 600 mg/kg in female rats. Systemic exposure in male and female rats were 1.3 and 1.8 times, respectively, the human exposure at the highest recommended dose of 600 mg/day based on AUC.
Ribociclib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or clastogenic in an in vitro human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration assay or an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
In a fertility and early embryonic development study, female rats received oral doses of ribociclib for 14 days prior to mating through the first week of pregnancy. Ribociclib did not affect reproductive function, fertility or early embryonic development at doses up to 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 times the clinical exposure in patients at the highest recommended dose of 600 mg/day based on AUC).
A fertility study in male rats has not been performed with ribociclib. In repeat-dose toxicity studies with oral administration of ribociclib daily for 3 weeks on/1 week off in rats up to 26 weeks duration and dogs up to 39 weeks duration, atrophic changes in testes were reported. Findings included degeneration of seminiferous tubular epithelia in the testes and hypospermia and luminal cellular debris in the epididymides of rats and dogs and vacuolation of epithelia in the epididymides of rats. These findings were observed at doses ≥ 75 mg/kg in rats and ≥ 1 mg/kg in dogs which resulted in systemic exposures that were 1.4 and 0.03 times the human exposure at the highest recommended daily dose of 600 mg/day based on AUC, respectively. These effects can be linked to a direct anti-proliferative effect on the testicular germ cells resulting in atrophy of the seminiferous tubules and showed a trend towards reversibility in rats and dogs after a four-week non-dosing period.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In vivo cardiac safety studies in dogs demonstrated dose and concentration related QTc interval prolongation at an exposure similar to patients receiving the recommended dose of 600 mg. There is a potential to induce incidences of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) at elevated exposures (approximately 5-fold the anticipated clinical Cmax).
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Early Breast Cancer
NATALEE: KISQALI in Combination with a Non-steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor (NSAI) with or without Goserelin
Adults with HR-positive, HER2-negative Stage II and III Early Breast Cancer at High Risk of Recurrence
NATALEE (NCT03701334) was a randomized (1:1), open-label, multicenter study in adults (N = 5101) with HR-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer that was:
- Anatomic Stage Group IIB-III, or
- Anatomic Stage Group IIA that is either:
- Node positive or
- Node negative, with:
- Histologic Grade 3, or
- Histologic Grade 2, with any of the following criteria:
- Ki67 ≥ 20%
- High risk by gene signature testing
Applying TNM criteria, NATALEE included patients with any lymph node involvement, or if no nodal involvement either tumor size > 5 cm, or tumor size 2 to 5 cm with either Grade 2 (and high genomic risk or Ki67 ≥ 20%) or Grade 3.
Participants were randomized to receive KISQALI 400 mg plus a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI, letrozole or anastrozole) or NSAI only, and goserelin as indicated. Randomization was stratified by Anatomic Stage, prior treatment (neoadjuvant versus adjuvant chemotherapy), menopausal status (premenopausal and males versus postmenopausal) and region (North America/Western Europe/Oceania versus rest of the world).
The main efficacy outcome measure was invasive disease-free survival (iDFS). iDFS was defined as the time from randomization to the first occurrence of: local invasive breast recurrence, regional invasive recurrence, distant recurrence, death (any cause), contralateral invasive breast cancer, or second primary non-breast invasive cancer (excluding basal and squamous cell carcinomas of the skin). Overall survival (OS) was an additional outcome measure.
KISQALI was given orally at a dose of 400 mg once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off treatment in combination with letrozole 2.5 mg or anastrozole 1 mg orally once daily for 28 days; goserelin 3.6 mg was administered on Day 1 of each 28-day cycle. KISQALI was administered for up to 36 months in the absence of recurrence or unacceptable toxicity. NSAI was administered for at least 5 years.
The median age was 52 years (range, 24 to 90); > 99% women (n = 19 men); 73% White, 13% Asian, 1.7% Black or African American, < 0.1% Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, < 0.1% American Indian or Alaskan Native; 8.5% Hispanic or Latino; 99% ECOG 0-1; 88% node positive disease; 88% received prior (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy.
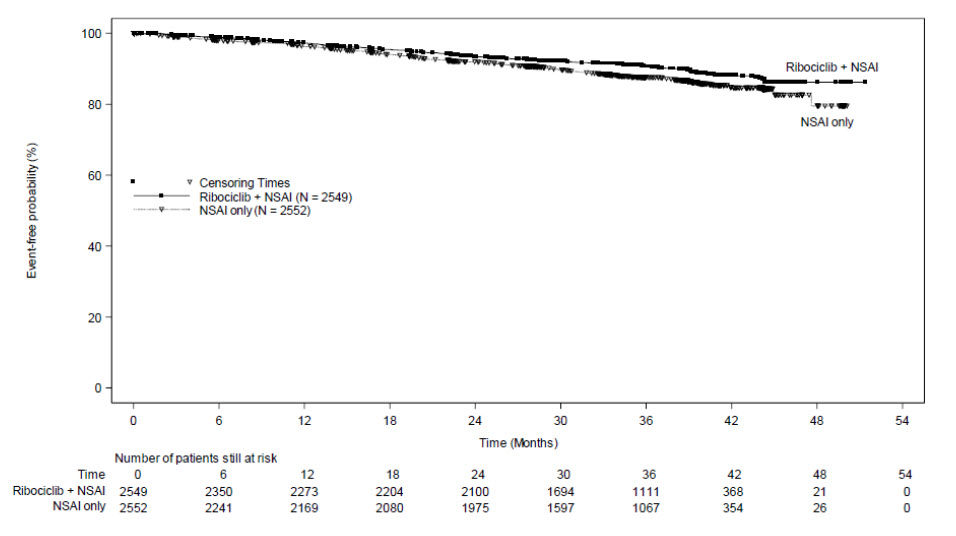
A statistically significant improvement in iDFS was observed in the intent-to-treat (ITT) population at an interim analysis. The efficacy results at the time of the final iDFS analysis are summarized in Table 18 and Figure 1. At the time of the iDFS final analysis, OS was immature, and a total of 172 (3.5%) of patients had died across both study arms.
| KISQALI + NSAI +/- Goserelin | NSAI +/- Goserelin | |
| Invasive Disease-Free Survival (iDFS)a | N = 2549 | N = 2552 |
| Events (n, %) | 226 (8.9) | 283 (11.1) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.749 (0.628, 0.892) | |
| iDFS at 36 months (%, 95% CI) | 90.7 (89.3, 91.8) | 87.6 (86.1, 88.9) |
|
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; iDFS, invasive disease-free survival. aiDFS was statistically significant at an interim analysis based on a one-sided stratified log-rank p-value of 0.0014. |
||
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Plot of iDFS – NATALEE (Investigator Assessment, Intent-to-Treat Population)
14.2 Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
MONALEESA-2: KISQALI in Combination with Letrozole
Postmenopausal Women with HR-positive, HER2-negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer for Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy
MONALEESA-2 (NCT01958021) was a randomized (1:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical study of KISQALI plus letrozole vs. placebo plus letrozole conducted in postmenopausal women (N = 668) with HR-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer who received no prior therapy for advanced disease.
Participants were randomized to receive either KISQALI plus letrozole or placebo plus letrozole, stratified according to the presence of liver and/or lung metastases. Letrozole 2.5 mg was given orally once daily for 28 days, with either KISQALI 600 mg or placebo orally once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measure for the study was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1.
The median age was 62 years (range, 23 to 91) and 45% of patients were older than 65. The majority of patients were White (82%), and all patients had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. A total of 47% of patients had received chemotherapy and 51% had received antihormonal therapy in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting. Thirty-four percent (34%) of patients had de novo metastatic disease, 21% had bone only disease, and 59% had visceral disease.
The efficacy results are summarized in Table 19, Figure 2 and Figure 3. The PFS assessment based on a blinded independent central radiological review was consistent with investigator assessment. Consistent results were observed across patient subgroups of prior adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy or hormonal therapies, liver and/or lung involvement, and bone-only metastatic disease.
|
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; NR, not reached. ap-value estimated from one-sided log-rank test. |
||
| KISQALI + Letrozole | Placebo + Letrozole | |
| Progression-Free Survival | N = 334 | N = 334 |
| Events (n, %) | 93 (27.8) | 150 (44.9) |
| Median (months, 95% CI) | NR (19.3 – NR) | 14.7 (13.0 – 16.5) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.556 (0.429, 0.720) | |
| p-value | < 0.0001a | |
| Overall Survival | N = 334 | N = 334 |
| Events (n, %) | 181 (54.2) | 219 (65.6) |
| Median (months, 95% CI) | 63.9 (52.4, 71.0) | 51.4 (47.2, 59.7) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.765 (0.628, 0.932) | |
| p-value | 0.004a | |
| Overall Response Rate for patients with measurable disease | N = 256 | N = 245 |
| Overall Response Rate (95% CI) | 52.7 (46.6, 58.9) | 37.1 (31.1, 43.2) |
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Progression-Free Survival – MONALEESA-2 (Investigator Assessment, Intent-to-Treat Population)
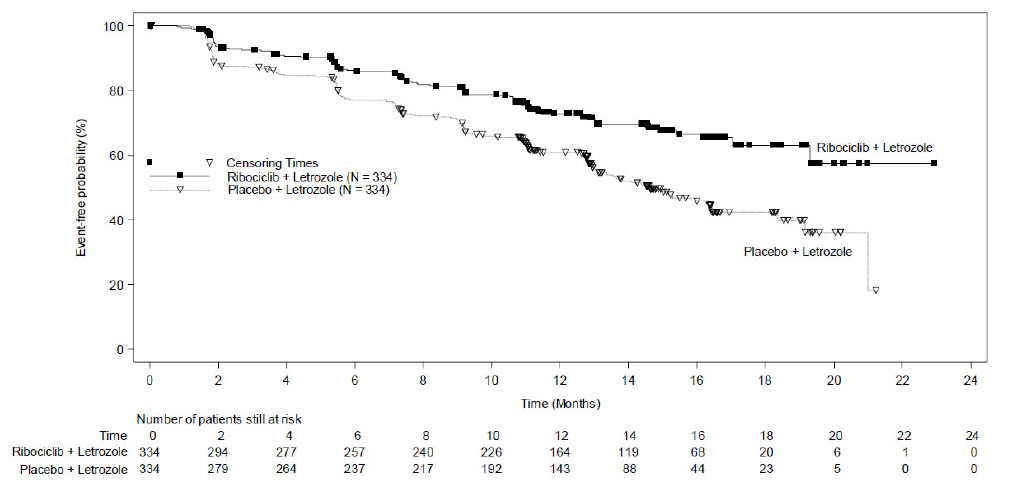
Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival – MONALEESA-2 (Investigator Assessment, Intent-to-Treat Population)
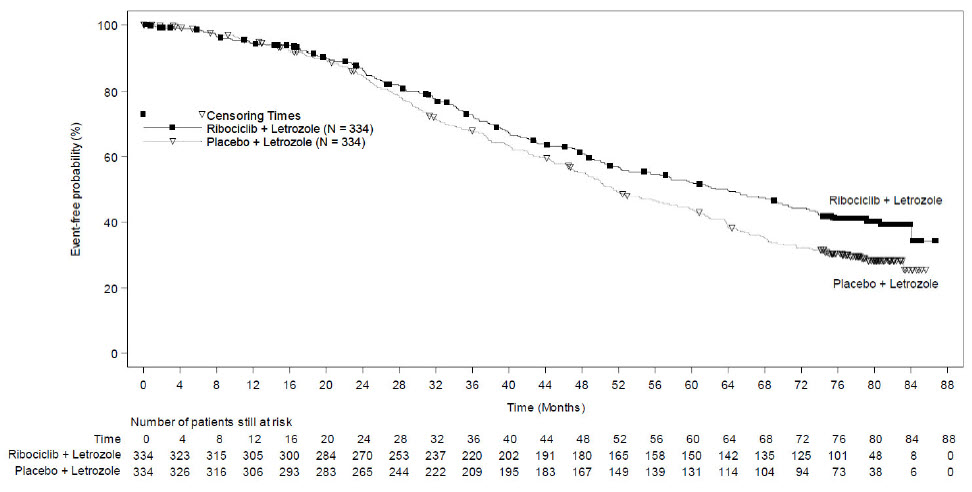
MONALEESA-7: KISQALI in Combination with a Non-Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor with or without Goserelin
Pre/perimenopausal Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer for Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy
MONALEESA-7 (NCT02278120) was a randomized (1:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled study of KISQALI plus either a NSAI or tamoxifen and goserelin vs. placebo plus either a NSAI or tamoxifen and goserelin conducted in pre/perimenopausal women (N = 672) with HR-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer who received no prior endocrine therapy for advanced disease.
Participants were randomized to receive KISQALI plus NSAI or tamoxifen plus goserelin or placebo plus NSAI or tamoxifen plus goserelin, stratified according to the presence of liver and/or lung metastases, prior chemotherapy for advanced disease and endocrine combination partner (tamoxifen and goserelin vs. NSAI and goserelin). NSAI (letrozole 2.5 mg or anastrozole 1 mg) or tamoxifen 20 mg were given orally once daily on a continuous daily schedule, goserelin was administered as a sub-cutaneous injection on Day 1 of each 28-day cycle, with either KISQALI 600 mg or placebo orally once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measure for the study was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1.
The median age was 44 years (range, 25 to 58). Patients were primarily White (58%), Asian (29%), or Black (3%). Nearly all patients (99%) had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. Of the 672 patients, 33% had received chemotherapy in the adjuvant vs. 18% in the neoadjuvant setting and 40% had received endocrine therapy in the adjuvant vs. 0.7% in the neoadjuvant setting prior to study entry. Forty percent (40%) of patients had de novo metastatic disease, 24% had bone only disease, and 57% had visceral disease. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were balanced and comparable between study arms, and endocrine combination partner.
The efficacy results from a pre-specified subgroup analysis of 495 patients who had received KISQALI or placebo with NSAI plus goserelin are summarized in Table 20, Figure 4, and Figure 5. Consistent results were observed in stratification factor subgroups of disease site and prior chemotherapy for advanced disease.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; NR, not reached; NSAI, non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors. *Based on confirmed responses. 1Investigator Assessment. |
||
| KISQALI + NSAI + Goserelin | Placebo + NSAI + Goserelin | |
| Progression-Free Survival1 | N = 248 | N = 247 |
| Events (n, %) | 92 (37.1) | 132 (53.4) |
| Median (months, 95% CI) | 27.5 (19.1, NR) | 13.8 (12.6, 17.4) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.569 (0.436, 0.743) | |
| Overall Survival | N = 248 | N = 247 |
| Events (n, %) | 61 (24.6) | 80 (32.4) |
| Median (months, 95% CI) | NR (NR, NR) | 40.7 (37.4, NR) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.699 (0.501, 0.976) | |
| Overall Response Rate for patients with measurable disease*,1 | N = 192 | N = 199 |
| Overall Response Rate (95% CI) | 50.5 (43.4, 57.6) | 36.2 (29.5, 42.9) |
Figure 4: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Progression-Free Survival – MONALEESA-7 (NSAI, Investigator Assessment)
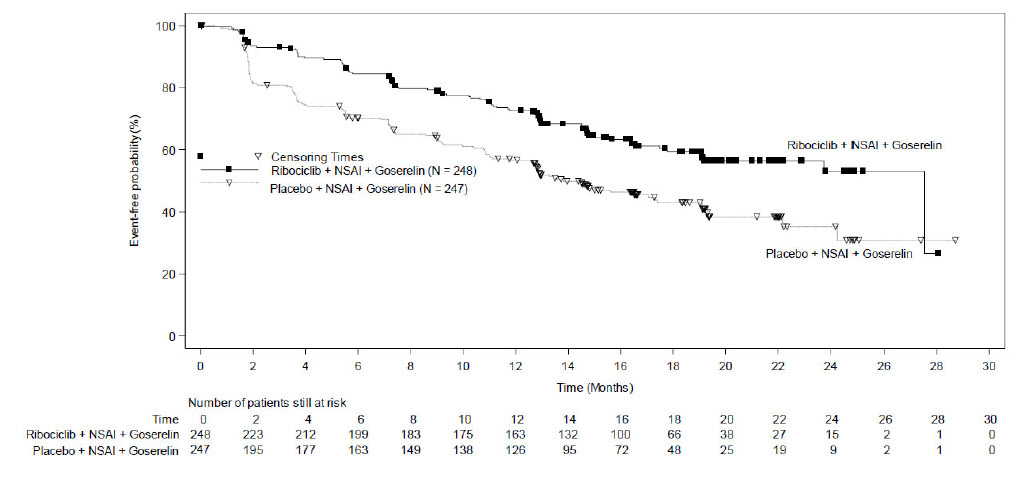
Figure 5: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival – MONALEESA-7 (NSAI, Investigator Assessment)
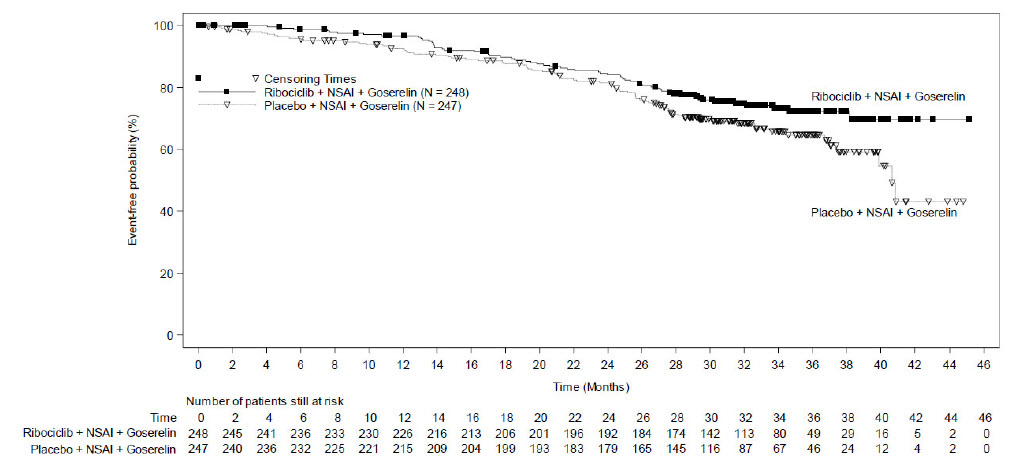
MONALEESA-3: KISQALI in Combination with Fulvestrant
Postmenopausal Women with HR-positive, HER2-negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer for Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy or After Disease Progression on Endocrine Therapy
MONALEESA-3 (NCT06129786) was a randomized (2:1) double-blind, placebo-controlled study of ribociclib in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of postmenopausal women (N = 726) with hormone receptor positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer who have received no or only one line of prior endocrine treatment.
Participants were randomized to receive KISQALI 600 mg and fulvestrant or placebo and fulvestrant, stratified according to the presence of liver and/or lung metastases and prior endocrine therapy for advanced or metastatic disease. Fulvestrant 500 mg was administered intramuscularly on Days 1, 15, 29, and once monthly thereafter, with either KISQALI 600 mg or placebo given orally once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measure for the study was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1.
The median age was 63 years (range, 31 to 89). Of the patients enrolled, 47% were 65 years and older, including 14% age 75 years and older. The patients enrolled were primarily White (85%), Asian (9%), and Black (0.7%). Nearly all patients (99.7%) had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. Patients enrolled in this study were treated in the first- or second-line setting, and 19% had de novo metastatic disease. Forty-three percent (43%) of patients had received chemotherapy in the adjuvant vs. 13% in the neoadjuvant setting, and 59% had received endocrine therapy in the adjuvant vs. 1% in the neoadjuvant setting prior to study entry. Twenty-one percent (21%) of patients had bone only disease, and 61% had visceral disease. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were balanced and comparable between study arms.
The efficacy results from MONALEESA-3 are summarized in Table 21, Figure 6, and Figure 7. Consistent results were observed in stratification factor subgroups of disease site and prior endocrine treatment for advanced disease.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; NR, not reached. ap-value is obtained from the one-sided log-rank. *Based on confirmed responses. 1Investigator Assessment. |
||
| KISQALI + Fulvestrant | Placebo + Fulvestrant | |
| Progression-Free Survivala,1 | N = 484 | N = 242 |
| Events (n, %) | 210 (43.4) | 151 (62.4) |
| Median (months, 95% CI) | 20.5 (18.5, 23.5) | 12.8 (10.9, 16.3) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.593 (0.480, 0.732) | |
| p-valuea | < 0.0001 | |
| Overall Survival | N = 484 | N = 242 |
| Events (n, %) | 167 (34.5) | 108 (44.6) |
| Median (months, 95% CI) | NR (42.5, NR) | 40.0 (37.0, NR) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.724 (0.568, 0.924) | |
| p-valuea | 0.00455 | |
| Overall Response Rate for patients with measurable disease*,1 | N = 379 | N = 181 |
| Overall Response Rate (95% CI) | 40.9 (35.9, 45.8) | 28.7 (22.1, 35.3) |
Figure 6: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Progression-Free Survival – MONALEESA-3 (Investigator Assessment, Intent-to-Treat Population)
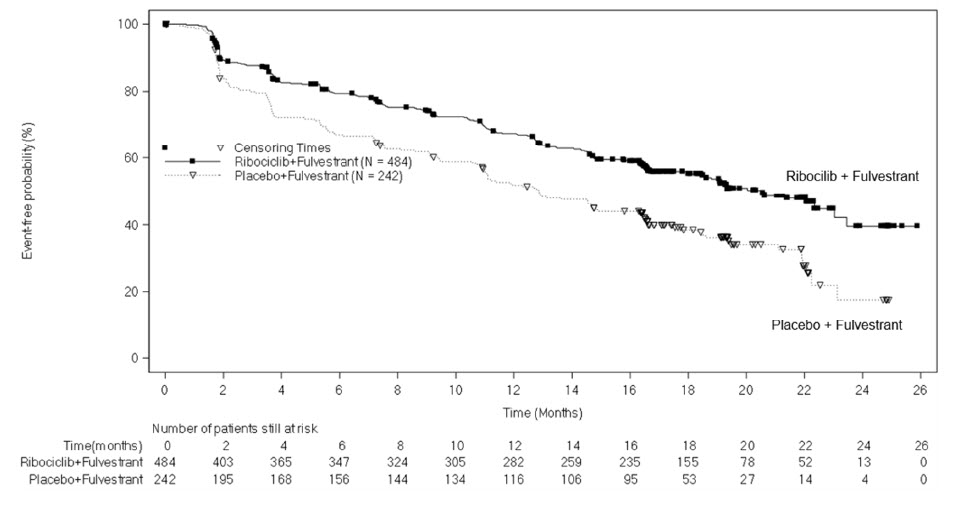
Figure 7: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival – MONALEESA-3 (Investigator Assessment, Intent-to-Treat Population)
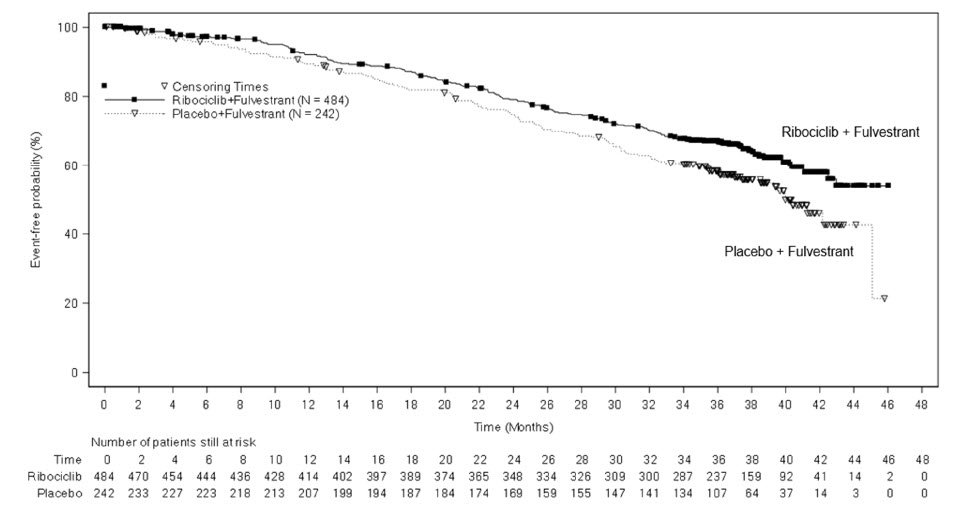
COMPLEEMENT-1: KISQALI in combination with Letrozole with or without Goserelin or Leuprolide
Men with HR-positive, HER2-negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer for Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy
COMPLEEMENT-1 (NCT 02941926) was an open-label, multicenter clinical study of ribociclib in combination with letrozole and goserelin or leuprolide for the treatment of adults with HR-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer who received no prior hormonal therapy for advanced disease.
The study included 39 male patients who received KISQALI 600 mg orally once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off; and letrozole 2.5 mg orally once daily for 28 days; and goserelin 3.6 mg as injectable subcutaneous implant or leuprolide 7.5 mg as intramuscular injection administered on Day 1 of each 28-day cycle. Patients were treated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
Male patients enrolled in this study had a median age of 62 years (range, 33 to 80). Of these patients, 39% were 65 years and older, including 10% aged 75 years and older. The male patients enrolled were White (72%), Asian (8%), and Black (3%), with 17% unknown. Nearly all male patients (97%) had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. The majority of male patients (97%) had 4 or less metastatic sites, which were primarily bone and visceral (69% each). Table 22 summarizes the efficacy results in male patients from COMPLEEMENT-1.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval, NR, not reached. *Based on confirmed responses. 1Patients with measurable disease. 2Investigator Assessment. 3Proportion of patients with complete response or partial response. |
|
| KISQALI + Letrozole + Goserelin or Leuprolide | |
| Overall Response Rate for patients with measurable disease*,2 | N = 32 |
| Overall Response Rate (95% CI) | 46.9 (29.1, 65.3) |
| Duration of Response (DoR)3 | N = 15 |
| Median (months, 95% CI) | NR (21.3, NR) |
| Patients with DoR ≥ 12 months, n (%) | 12 (80.0) |
16. How is Kisqali supplied
KISQALI (ribociclib) Tablets
Each film-coated tablet contains 200 mg of ribociclib free base.
Light greyish violet, round, curved with beveled edge, debossed with “RIC” on one side and “NVR” on the other side; available in:
Carton of 3 blister packs (63 tablets total) – each blister pack contains a 7-day supply of 21 tablets (200 mg per tablet)
(600 mg daily dose). NDC 0078-0874-63
Carton of 3 blister packs (42 tablets total) – each blister pack contains a 7-day supply of 14 tablets (200 mg per tablet)
(400 mg daily dose). NDC 0078-0867-42
Carton of 1 blister pack (21 tablets total) – each blister pack contains a 21-day supply of 21 tablets (200 mg per tablet)
(200 mg daily dose). NDC 0078-0860-01
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Excursions permitted between 2°C and 15°C (36°F and 59°F).
After dispensing, patients may store at room temperature at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 2 months.
Store tablets in the original blister pack.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis
Advise patients to immediately report new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions (e.g., skin pain/burning, rapidly-spreading skin rash, and/or mucosal lesions accompanied by fever or flu-like symptoms). Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if they develop signs and symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
QT Prolongation
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of QT prolongation. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of QT prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)].
Hepatobiliary Toxicity
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of hepatobiliary toxicity. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of hepatobiliary toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Neutropenia
Advise patients of the possibility of developing neutropenia and to immediately contact their healthcare provider should they develop a fever, particularly in association with any suggestion of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during KISQALI therapy and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose [Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment with KISQALI and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Drug Interactions
- Inform patients to avoid strong CYP3A inhibitors, strong CYP3A inducers, and drugs known to prolong the QT interval [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2, 7.4)].
Dosing
- Instruct patients to take the doses of KISQALI at approximately the same time every day and to swallow whole (do not chew, crush, or split them prior to swallowing) [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- If patient vomits or misses a dose, advise the patient to take the next prescribed dose at the usual time [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- Advise the patient that KISQALI may be taken with or without food [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Storage
- After dispensing, advise patients to store at room temperature at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 2 months.
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
© Novartis
T2025-43
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: July 2025 | ||
| PATIENT INFORMATION KISQALI® (kis kah' lee) (ribociclib) tablets |
|||
|
What is the most important information I should know about KISQALI? KISQALI may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
|
o yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes (jaundice) |
o loss of appetite |
||
See “What are the possible side effects of KISQALI?” for more information about side effects. |
|||
| What is KISQALI?
KISQALI is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer:
|
|||
|
Before taking KISQALI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. KISQALI and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|||
How should I take KISQALI?
|
|||
| What are the possible side effects of KISQALI?
KISQALI may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
| • decreased white blood cell counts • decreased red blood cell counts • increased liver function tests • infections • increased kidney function test | • decreased platelet counts • nausea • headache • tiredness | ||
| The most common side effects of KISQALI in people with advanced or metastatic breast cancer include: | |||
| • decreased white blood cell counts • decreased red blood cell counts • increased liver function tests • infections | • nausea • increased kidney function test • tiredness • decreased platelet counts | • diarrhea • vomiting • headache • constipation • hair loss | • cough • rash • back pain • low blood sugar level |
|
KISQALI may cause fertility problems in males, which may affect your ability to father a child. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a problem for you. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of KISQALI. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||
|
How should I store KISQALI?
Keep KISQALI and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of KISQALI. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use KISQALI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give KISQALI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for more information about KISQALI that is written for health professionals. |
|||
|
What are the ingredients in KISQALI? Active ingredient: ribociclib Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hydroxypropylcellulose, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The film-coating contains iron oxide black, iron oxide red, lecithin (soya), polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolyzed), talc, titanium dioxide, and xanthan gum. |
|||
|
Distributed by: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, New Jersey 07936 © Novartis For more information, go to www.KISQALI.com or call 1-888-669-6682. |
|||
T2025-44
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0860-01
Rx only
Kisqali®
(ribociclib)
tablets
200 mg daily dose
(one 200 mg tablet)
21 Film-coated tablets
Contents: 1 individual monthly blister pack. Blister pack contains 21 tablets (200 mg per tablet).
Storage: Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Excursions permitted between 2°C and 15°C (36°F and 59°F). After dispensing, patients may store at room temperature at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 2 months.
NOVARTIS
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0867-42
Rx only
Kisqali®
(ribociclib)
tablets
400 mg daily dose
(two 200 mg tablets)
42 Film-coated tablets
Contents: 3 individual weekly blister packs. Each blister pack contains 14 tablets (200 mg per tablet).
Storage: Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Excursions permitted between 2°C and 15°C (36°F and 59°F). After dispensing, patients may store at room temperature at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 2 months.
NOVARTIS
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0874-63
Rx only
Kisqali®
(ribociclib)
tablets
600 mg daily dose
(three 200 mg tablets)
63 Film-coated tablets
Contents: 3 individual weekly blister packs. Each blister pack contains 21 tablets (200 mg per tablet).
Storage: Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Excursions permitted between 2°C and 15°C (36°F and 59°F). After dispensing, patients may store at room temperature at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 2 months.
NOVARTIS
| KISQALI
ribociclib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KISQALI
ribociclib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KISQALI
ribociclib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |
Frequently asked questions
- Does Kisqali improve survival / life expectancy for mBC?
- What are the benefits of taking Kisqali and Femara together?
- How do you take Kisqali?
More about Kisqali (ribociclib)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (35)
- Imprints, shape & color data
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: CDK 4/6 inhibitors
- Breastfeeding
- En español
