Vaginal Hysterectomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
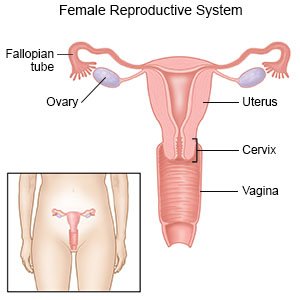
A vaginal hysterectomy is surgery to remove your uterus through your vagina. Other organs, such as your ovaries and fallopian tubes, may also have been removed. You will have pain and vaginal bleeding for the first few days after surgery.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
Contact your healthcare provider or gynecologist if:
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- You have increasing abdominal or pelvic pain.
- You have heavy vaginal bleeding that fills 1 or more sanitary pads in 1 hour.
- You have a fever.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You feel pain or burning when you urinate, or you have trouble urinating.
- You have pus or a foul-smelling odor coming from your vagina.
- You feel pressure in your rectum.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Stool softeners help treat or prevent constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Related medications
Activity:
- Wear an abdominal binder as directed. An abdominal binder will decrease pain when you move or cough.
- Rest as needed. Get up and move around as directed to help prevent blood clots. Start with short walks and slowly increase the distance every day. Limit the number of times you climb stairs to 2 times each day. Plan most of your daily activities on one level of your home.
- Do not lift objects heavier than 10 pounds for 6 weeks. Avoid strenuous activity for 2 weeks.
- Do not strain during bowel movements. High-fiber foods and extra liquids can help you prevent constipation. Examples of high-fiber foods are fruit and bran. Prune juice and water are good liquids to drink.
- Do not have sex, use tampons, or douche for up to 8 weeks. Ask your healthcare provider if it is okay to take a tub bath.
- Do not go in pools or hot tubs for 6 weeks or as directed.
- Ask when it is safe for you to drive, return to work, and return to other regular activities.
Deep breathing:
Take deep breaths and cough 10 times each hour. This will decrease your risk for a lung infection. Take a deep breath and hold it for as long as you can. Let the air out and then cough strongly. Deep breaths help open your airway. You may be given an incentive spirometer to help you take deep breaths. Put the plastic piece in your mouth and take a slow, deep breath, then let the air out and cough. Repeat these steps 10 times every hour.
Get support:
This surgery may be life-changing for you and your family. You will no longer be able to get pregnant. Sudden changes in the levels of your hormones may occur and cause mood swings and depression. You may feel angry, sad, or frightened, or cry frequently and unexpectedly. These feelings are normal. Talk to your healthcare provider about where you can get support. You can also ask if hormone replacement medicine is right for you.
Follow up with your healthcare provider or gynecologist as directed:
You may need to return for other tests. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
