Trigeminal Neuralgia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
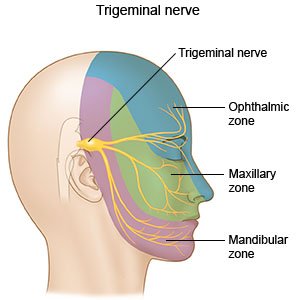
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a nerve disorder that causes sudden attacks of severe facial pain. You have a trigeminal nerve on each side of your face. The nerves allow you to feel pain, touch, and temperature changes in different areas of your face.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
An IV
is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
Related medications
Tests:
Contrast liquid may be given before some of the following tests to help the area show up better in pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- Blood tests may be used to find the cause of your TN.
- CT scan pictures may be used to look at bones, muscles, and blood vessels.
- MRI pictures may be used to examine your trigeminal nerve. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- MRA pictures may be used to examine the blood vessels in your brain. Healthcare providers will look for the location of the blood vessel that is pressing on your trigeminal nerve. An MRA may be done with an MRI to help your healthcare provider better plan your TN treatment.
Treatment:
TN may go away on its own without treatment. If your TN is caused by another condition, your healthcare provider will also treat that condition. Any of the following may be used to treat TN:
- Medicines:
- Anticonvulsants may be used to help prevent pain attacks and decrease other symptoms.
- Antidepressants decrease pain and help prevent depression.
- Muscle relaxers may be used to help relax your facial muscles. This helps lower the risk for pain attacks.
- Pain medicines may be given if your facial pain is severe.
- Procedures or surgery may be needed if TN does not get better with medicines or if you cannot take the medicines.
- A nerve block is an injection of medicine that makes you lose feeling in an area of your body.
- Microvascular decompression is surgery to separate your trigeminal nerve from the blood vessel pressing on it.
- Percutaneous procedures help control your pain by destroying an area deep in your skull where nerve branches come together. Healthcare providers will insert a needle and tube through the base of your skull to reach this area.
- Peripheral techniques are done to block the nerve impulses that cause your pain attacks. Your healthcare provider may destroy the nerve with alcohol (medicine) injections, or freeze the nerve. He or she may also remove part of the nerve.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (or Gamma Knife surgery) is used to remove a blood vessel that is pressing on the nerve. You may have some pain relief right away after radiosurgery. It may take at least 1 month before you have decreased pain.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
- Medicines used to treat TN can cause organ damage. Medicines may not help your TN. Over time, some medicines may stop working. Procedures and surgeries to treat TN can cause facial pain or damage. You may have changes in your vision, hearing, memory, speech, or sense of smell or taste. You may have trouble chewing or get mouth sores. You may get an infection, or have brain and nerve damage, seizures, a stroke, or even death. After treatment with a procedure or surgery, your TN may come back, or you may have new TN pain.
- If TN is not treated, pain attacks may get worse and occur more often. You may begin to have a dull, constant ache in areas of your face. Your TN pain, and fear of an attack, may be so bad that you stop brushing your teeth, eating, and drinking. This may lead to dental problems, poor nutrition, weight loss, and dehydration. You may feel tired, anxious, or depressed.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Trigeminal Neuralgia
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
