Tdap and Td Vaccines for Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Tdap and Td
are shots given to protect your child from tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (whooping cough). These are severe infections caused by bacteria. Tetanus bacteria are found in dirt, manure, and dust. The bacteria enter the body through open skin, such as puncture wounds and burns. Diphtheria and pertussis bacteria are spread from person to person. Children are usually given a series of 5 DTaP shots by age 7. By age 11, the DTaP vaccine starts to wear off. Booster shots are then given to continue the protection.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has signs of a severe allergic reaction, such as trouble breathing, hives, or wheezing.
- Your child begins to have seizures (staring or jerking).
- Your child has a fever of 105º F (40.5º C).
Seek immediate care if:
- Your child's face is red or swollen.
- Your child has hives that spread over his or her body.
- Your child feels weak or dizzy.
Call your child's doctor if:
- Your child has a headache, body aches, or joint pain.
- Your child has nausea or diarrhea, or he or she is vomiting.
- You have questions or concerns about the vaccine.
When the Tdap vaccine is given:
The Tdap vaccine is usually given to prevent a tetanus, diphtheria, or pertussis infection. It can also be given after a severe wound or burn to prevent tetanus. Your healthcare provider will tell you when to bring your child in for a Tdap vaccine:
- At 11 to 12 years, 1 dose of the Tdap vaccine is given routinely.
- From 7 to 18 years, 1 dose may be given as part of a catch-up series if your child missed any DTaP doses.
- From 13 to 18 years, 1 dose may be given if your child did not receive Tdap at 11 or 12 years of age.
- For pregnant adolescents, a Tdap shot is given at 27 to 36 weeks of each pregnancy. The shot can also be given immediately after your adolescent gives birth if it was not given during the pregnancy.
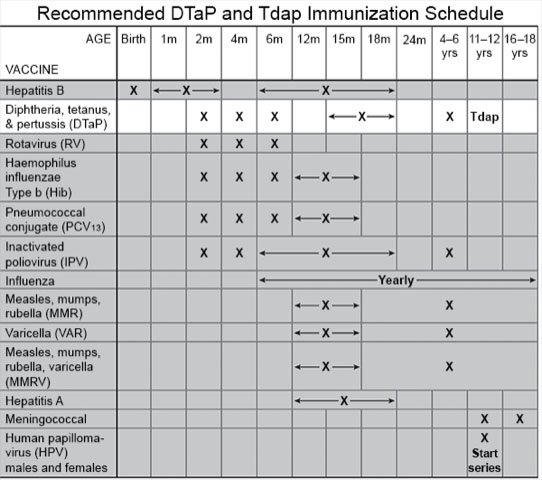 |
When the Td vaccine is given:
The Td vaccine is usually given as a booster dose every 10 years. This can start when your child is an adolescent. Td can also be given after 5 years if your child has a severe wound or burn. One dose can also be given as part of the catch-up DTaP series, after a catch-up Tdap dose.
Related medications
What to tell your child's healthcare provider before the Tdap or Td vaccine is given:
- Your child has a seizure disorder or a problem with his or her nervous system.
- Your child had severe pain or swelling after a dose of DTaP.
- Your child has any severe allergy.
- Your child has a history of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Your child had a period of crying for more than 3 hours within the first 2 days of a DTaP dose.
- Your child had a fever of 105ºF (40.5ºC) after a DTaP dose.
Do not have your child get the Tdap vaccine if:
- Your child is allergic to any part of the vaccine.
- Your child had a severe allergic reaction to DTaP.
- Your child had seizures or a coma within 7 days of receiving DTaP, caused by the vaccine. Your child can still safely get the Td vaccine in this case.
Do not have your child get the Td vaccine if:
- Your child had an allergic reaction to DTaP, Tdap, or Td.
- Your child is allergic to any part of the Td vaccine.
When your child should wait to get the Tdap or Td vaccine:
Tell the provider if your child has a fever or illness on the day of the vaccine appointment. The provider may wait to give the vaccine until the fever or illness is gone.
Risks of the Tdap and Td vaccines:
The area where the vaccine was given may be painful, red, tender, or swollen. This should get better in 1 to 2 days. Rarely, your child may develop severe shoulder pain that lasts longer than 2 days. Your child may develop a fever, headache, or feel more tired than usual. Your child may have nausea, diarrhea, or a stomachache. Your child may have an allergic reaction to the vaccine that can become life-threatening.
Apply a warm compress
to the injection area as directed to decrease pain and swelling.
Follow up with your child's doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your child's visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
