Noncardiac Chest Pain
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Noncardiac chest pain is pain or discomfort in your chest not caused by a heart problem. Possible causes include acid reflux, nerve or muscle problems, emotions, or chest wall or rib pain.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have severe chest pain.
Call your doctor if:
- Your chest pain does not get better, even with treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Medicines:
- Medicines may be given to treat the cause of your chest pain. You may be given medicines to decrease pain, relieve anxiety, decrease acid reflux, or relax muscles in your esophagus.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Healthy living tips:
If the cause of your chest pain is known, your healthcare provider will give you specific guidelines to follow. The following are general healthy guidelines:
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause lung and heart damage. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
- Choose a variety of healthy foods as often as possible. Include fresh, frozen, or canned fruits and vegetables. Also include low-fat dairy products, fish, chicken (without skin), and lean meats. Your provider or a dietitian can help you create meal plans. You may need to avoid certain foods or drinks if your pain is caused by a digestion problem.

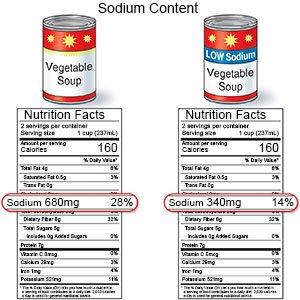
- Lower your sodium (salt) intake. Limit foods that are high in sodium, such as canned foods, salty snacks, and cold cuts. If you add salt when you cook food, do not add more at the table. Choose low-sodium canned foods as much as possible.
- Drink plenty of water every day. Water helps your body to control your temperature and blood pressure. Ask your provider how much water you should drink every day.
- Ask about activity. Your provider will tell you which activities to limit or avoid. Ask when you can drive, return to work, and have sex. Ask about the best exercise plan for you.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask your provider to help you create a safe weight loss plan if you are overweight.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. Certain vaccines help prevent diseases that can become serious for a person with a heart condition. Your provider can tell you if you also need vaccines not listed below, and when to get them:
- Ask your healthcare provider about the flu and pneumonia vaccines. All adults should get the flu (influenza) vaccine as soon as recommended each year, usually in September or October. The pneumonia vaccine is recommended for all adults aged 50 or older to prevent pneumococcal disease, such as pneumonia. Adults aged 19 to 49 years who are at high risk for pneumococcal disease should also receive the vaccine. You may need 1 dose or 2. The number depends on the vaccine used and your risk factors.
- COVID-19 vaccines are given to adults as a shot. At least 1 dose of an updated vaccine is recommended for all adults. COVID-19 vaccines are updated throughout the year. Adults 65 or older need a second dose of updated vaccine at least 4 months after the first dose. Your healthcare provider can help you schedule all needed doses as updated vaccines become available.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Noncardiac Chest Pain
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
