Menorrhagia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Menorrhagia
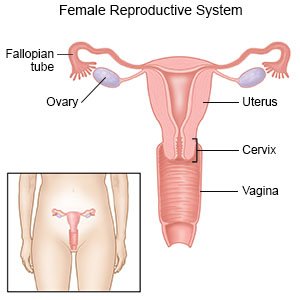
is heavy menstrual bleeding for more than 7 days or severe menstrual bleeding for less than 7 days. Your menstrual bleeding and cramping are so heavy that you have trouble doing your usual daily activities. Your monthly period may also occur more often, and you may bleed between periods. Menorrhagia is common in adolescence and around menopause.
 |
Common symptoms include the following:
- Soaking a pad or tampon every 1 to 2 hours
- Using both a pad and a tampon
- Waking up at night to change your pad or tampon
- Blood clots with your bleeding for more than 1 day
- Abdominal pain or cramps
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Your heart is fluttering or beating faster than usual for you.
Seek care immediately if:
- You feel dizzy when you stand.
- You feel confused.
- You have severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Your skin or the whites of your eyes turn yellow.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Call your doctor or gynecologist if:
- You need to change your pad or tampon more than 1 time per hour, for several hours in a row.
- You feel more weak and tired than usual.
- You have new coldness in your hands and feet.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Iron supplements may be given if your blood iron level decreases because of heavy bleeding.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Hormones help slow or stop your bleeding and make your monthly periods more regular. This medicine may be given as birth control pills or an intrauterine device (IUD).
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage your symptoms:
- Keep a supply of pads or tampons with you at all times. If possible, stay close to a bathroom.
- Apply heat on your abdomen to decrease pain and cramps. You can use a heating pad on a low setting. Apply heat for 20 to 30 minutes every 2 hours for as many days as directed.
Follow up with your doctor or gynecologist as directed:
You may need regular pelvic exams with Pap smears to monitor your condition. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Menorrhagia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
