How to Take A Blood Pressure Reading
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
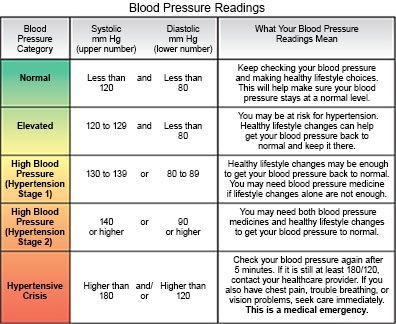
Blood pressure (BP) is the force of blood pushing on the walls of your arteries. Your BP results are written as 2 numbers. The first, or top, number is called systolic BP. This is the pressure caused by your heart pushing blood out to your body. The second, or bottom, number is called diastolic BP. This is the pressure when your heart relaxes and fills back up with blood. Ask your healthcare provider what your BP should be. For most people, a good BP goal is less than 120/80.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your doctor if:
- Your BP is higher or lower than you were told it should be.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Why you may need to take BP readings:
You may not have any signs or symptoms of high BP. You may need to take BP readings regularly to know how often your BP is high. High BP increases your risk for a stroke, heart attack, or kidney disease. You may need to take medicine to keep your BP at a normal level. Write down and keep a log of your BP readings. Your healthcare provider can use the results to see if your BP medicines are working.
Related medications
How often to take your BP readings:
Your healthcare provider may recommend that you take your BP readings 2 times a day. Take the readings at the same times each day, such as the morning and evening.
How to take BP readings:
You can take BP readings at home with a digital BP monitor. Read the instructions that came with your BP monitor. The monitor comes with an adjustable cuff. Ask your healthcare provider if your cuff is the correct size.
- Do not eat, drink, smoke, or exercise for 30 minutes before you take BP readings.
- Rest quietly for 5 minutes before you begin. Do not talk while you take BP readings.
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor and your back against a chair.
- Put your arm straight out and support it on a flat surface. Your arm should be at chest level. Do not move your arm while you take your BP readings.
- Make sure all of the air is out of the cuff. Place the BP cuff against your bare skin about 1 inch (2.5 cm) above your elbow. Wrap the cuff snugly around your arm. The BP reading may not be correct if the cuff is too loose.
- If you are using a wrist cuff, wrap the cuff snugly around your wrist. Hold your wrist at the same level as your heart.
- Turn on the BP monitor and follow the directions.
- Write down your BP, the date, the time, and which arm you used to take BP reading. Take 2 BP readings and write down both results. Use the same arm each time. These BP readings can be 1 minute apart.

What else you need to know:
- Do not take a BP reading in an arm that is injured or has an IV or shunt. The reading may not be accurate.
- Do not stop taking your medicines if your BP is at your goal. A BP at your goal means your medicine is working correctly. Take your BP medicines as directed.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Bring the log of your BP readings. Also bring the BP machine. Healthcare providers can check that you are using the machine correctly. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
