Anzupgo: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: delgocitinib
Dosage form: cream
Drug class: Miscellaneous topical agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 13, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
- Medication Guide
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ANZUPGO® (delgocitinib) cream, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025
Indications and Usage for Anzupgo
ANZUPGO is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor indicated for the topical treatment of moderate to severe chronic hand eczema (CHE) in adults who have had an inadequate response to, or for whom topical corticosteroids are not advisable. (1)
Limitations of Use: Use of ANZUPGO in combination with other JAK inhibitors or potent immunosuppressants is not recommended. (1)
Anzupgo Dosage and Administration
- See the full prescribing information for recommended immunizations prior to treatment. (2.1)
- Do not use more than 30 grams per 2 weeks or 60 grams per month.
- Apply twice daily to skin of the affected areas only on the hands and wrists. (2.2)
- For topical use only. Not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Cream: Each gram of ANZUPGO cream contains 20 mg of delgocitinib. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Serious Infections: ANZUPGO may increase the risk of infection. Eczema herpeticum was observed in a subject treated topically with ANZUPGO. Avoid use of ANZUPGO in patients with an active or serious infection. If a serious infection develops, discontinue ANZUPGO until the infection resolves. (5.1)
- Non-melanoma Skin Cancers: Non-melanoma skin cancers including basal cell carcinoma have been reported in subjects treated with ANZUPGO. Periodic skin examinations are recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer. (5.2)
- Immunizations: Avoid vaccination with live vaccines immediately prior to, during, and immediately after ANZUPGO treatment. (5.3)
- Potential Risks Related to JAK Inhibition: It is not known whether ANZUPGO may be associated with the observed or potential adverse reactions of JAK inhibition. Higher rates of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, major adverse cardiovascular events, overall thrombosis, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer) were observed in patients treated with a JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. ANZUPGO is not approved for use in RA. Treatment with oral and topical JAK inhibitors has been associated with increases in lipid parameters including total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adverse reactions that were reported in ≤ 1% of subjects were application site pain, paresthesia, pruritus, erythema, and bacterial skin infections including finger cellulitis, paronychia, other skin infections, leukopenia, and neutropenia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact LEO Pharma Inc. at 1-877-494-4536 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Anzupgo
ANZUPGO is indicated for the topical treatment of moderate to severe chronic hand eczema (CHE) in adults who have had an inadequate response to, or for whom topical corticosteroids are not advisable.
2. Anzupgo Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Immunizations Prior to Treatment Initiation
Complete any necessary immunizations, including herpes zoster vaccinations, according to current immunization guidelines prior to ANZUPGO treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
Do not use more than 30 grams per 2 weeks or 60 grams per month.
Prior to applying ANZUPGO, clean and dry affected areas.
Apply a thin layer of ANZUPGO, twice daily, to the affected areas only on the hands and wrists.
ANZUPGO is for topical use only. Not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
Avoid contact with eyes, mouth, or other mucous membranes. If contact with mucous membranes occurs, rinse thoroughly with water.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Cream, 2%: Each gram of ANZUPGO cream contains 20 mg of delgocitinib in a white to slightly brown cream.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Infections
ANZUPGO may increase the risk of infections. Eczema herpeticum was observed in a subject treated with ANZUPGO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Serious and sometimes fatal infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, or other opportunistic pathogens have been reported in patients receiving oral or topical JAK inhibitors [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Avoid use of ANZUPGO in patients with an active or serious infection.
Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating ANZUPGO in patients:
- with chronic or recurrent infection
- who have been exposed to tuberculosis
- with a history of a serious or an opportunistic infection
- with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection.
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with ANZUPGO. A patient who develops a new infection during treatment with ANZUPGO should undergo prompt and complete diagnostic testing; appropriate antimicrobial therapy should be initiated; and the patient should be closely monitored. Interrupt treatment with ANZUPGO if a patient develops a serious infection. Do not resume ANZUPGO until the infection resolves or is adequately treated.
Viral Reactivation
Viral reactivation, including cases of herpes virus reactivation (e.g., herpes zoster), were reported in clinical trials with ANZUPGO. If a patient develops herpes zoster, consider interrupting ANZUPGO treatment until the episode resolves.
The impact of ANZUPGO on chronic viral hepatitis reactivation is unknown. Patients with active hepatitis B or C infection were excluded from clinical trials with ANZUPGO. Consider viral hepatitis screening and monitoring for reactivation in accordance with clinical guidelines before starting therapy and during therapy with ANZUPGO. If signs of reactivation occur, consult a hepatitis specialist. ANZUPGO is not recommended for use in patients with active hepatitis B or hepatitis C.
5.2 Non-melanoma Skin Cancers
Non-melanoma skin cancers including basal cell carcinoma have been reported in subjects treated with ANZUPGO. Periodic skin examinations of the application sites are recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer. Advise patients to avoid sunlamps and minimize exposure to sunlight by wearing sun-protective clothing or using broad-spectrum sunscreen.
5.3 Immunizations
Prior to ANZUPGO treatment, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines, including herpes zoster vaccinations. Avoid vaccination with live vaccines immediately prior to, during, and immediately after ANZUPGO treatment.
5.4 Potential Risks Related to JAK Inhibition
It is not known whether ANZUPGO may be associated with the observed or potential adverse reactions of JAK inhibition.
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety trial of an oral JAK inhibitor in combination with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, higher rates of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), overall thrombosis, deep venous thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer) were observed in patients treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. ANZUPGO is not indicated for use in RA.
Treatment with oral and topical JAK inhibitors has been associated with increases in lipid parameters including total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of ANZUPGO was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, multicenter, vehicle-controlled clinical trials (TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2), in which 959 adults with moderate to severe CHE received ANZUPGO or vehicle cream topically twice daily for 16 weeks. A total of 638 subjects were treated with ANZUPGO [see Clinical Studies (14)].
In TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2, adverse reactions that were reported in ≤ 1% of subjects in the ANZUPGO group were application site pain, paresthesia, pruritus, erythema, and bacterial skin infections including finger cellulitis, paronychia, other skin infections, leukopenia, and neutropenia.
In an open label extension trial (TRIAL 3), 801 subjects were treated for up to an additional 36 weeks after completing TRIAL 1 or TRIAL 2. A total of 198 subjects received continuous treatment with ANZUPGO for 52 weeks. Eczema herpeticum was observed in one subject and herpes zoster was observed in two subjects treated with ANZUPGO.
Related/similar drugs
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The available data on the use of topical delgocitinib during pregnancy is insufficient to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of delgocitinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis did not result in adverse developmental effects at doses 120 or 193 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on AUC comparison (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, and other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In embryofetal development studies, delgocitinib was administered orally to pregnant rats or rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses of 3, 10 and 30 mg/kg/day in rats, and 1, 3 and 10 mg/kg/day in rabbits, respectively.
In rats, no significant maternal toxicity was noted at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (1446 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Decreases in fetal weight and skeletal variations were observed at doses ≥10 mg/kg/day (512 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). An increase in post-implantation loss was observed at 30 mg/kg/day (1446 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No embryofetal toxicity was noted at 3 mg/kg/day (120 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
In rabbits, no significant maternal toxicity was noted at doses up to 10 mg/kg/day (992 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). An increase in post-implantation loss, reduced number of live fetuses, and decrease in fetal weights were observed at 10 mg/kg/day (992 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No embryofetal toxicity was noted at 3 mg/kg/day (193 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
In a pre- and post-natal development study in pregnant rats, delgocitinib was orally administered at doses of 3, 10 and 30 mg/kg/day from gestation day 7 to lactation day 20. No significant maternal toxicity was noted at 30 mg/kg/day (1555 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Extended gestation period, a decrease in the birth index, and an increase in the number of dead newborns were observed at 30 mg/kg/day (1555 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Decreased fetal viability and reduced pup weights were noted during the early postnatal period at 30 mg/kg/day (1555 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
No developmental toxicity was noted at 10 mg/kg/day (378 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of delgocitinib in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. After oral administration, delgocitinib was present in the milk of lactating rats. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ANZUPGO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ANZUPGO or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of ANZUPGO have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 691 subjects exposed to ANZUPGO in clinical trials, 59 subjects (8.5%) were 65 years of age and older and 10 subjects (1.4%) were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between subjects 65 years of age and older and younger adult subjects.
11. Anzupgo Description
ANZUPGO (delgocitinib) cream is a white to slightly brown cream for topical use and contains delgocitinib as the active ingredient.
Delgocitinib is a white to almost white powder. Delgocitinib is slightly soluble in aqueous solutions at pH 5.0. The pKa of delgocitinib is 5.5.
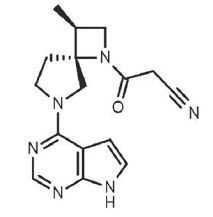
Delgocitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor [JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2)] with the chemical name 3-[(3S,4R)-3-Methyl- 6-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1,6-diazaspiro[3.4]octan-1-yl]-3- oxopropanenitrile.
The molecular formula is C16H18N6O and the molecular weight is 310.35 g/mol. Delgocitinib has the structural formula:
Each gram of ANZUPGO contains 20 mg of delgocitinib. Inactive ingredients include benzyl alcohol, butylated hydroxyanisole, cetostearyl alcohol, citric acid monohydrate, edetate disodium, hydrochloric acid, mineral oil, polyoxyl 20 cetostearyl ether, and purified water.
12. Anzupgo - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Delgocitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, inhibits the activity of JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2). JAK signaling involves recruitment of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) to cytokine receptors, and activation and subsequent localization of STATs to the nucleus, leading to the expression of cytokine-responsive genes to induce specific biological responses in target cells. The exact mechanism of action of delgocitinib in the treatment of moderate to severe CHE is currently not known.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of ANZUPGO were evaluated in a pharmacokinetic (PK) trial involving 15 adult subjects 22 to 69 years of age with moderate to severe CHE and in 313 subjects in TRIAL 2 [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Absorption
In the PK trial, subjects applied on average 0.87 g of ANZUPGO topically to the affected areas of the hands and wrists twice a day for 8 days.
The mean ± SD maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-curve from time 0 to 12 hours (AUC0-12) on Day 1 was 1.53 ng/mL ± 2.24 and 6.1 ng*h/mL ± 8.14, respectively. The lower limit of quantification was 0.005 ng/mL in the assay. The systemic exposure (AUC and Cmax) between Day 1 and Day 8 were similar. There was no evidence of accumulation with twice daily topical application of ANZUPGO.
In TRIAL 2, a single PK sample was assessed between 2-6 hours following twice daily application of ANZUPGO. The mean plasma concentration on Weeks 1, 4, and 16 were 0.42 ng/mL, 0.50 ng/mL, and 0.35 ng/mL, respectively.
Elimination
Following repeated topical application of ANZUPGO, the average half-life of delgocitinib was estimated to be 21 hours.
Metabolism
Delgocitinib does not undergo extensive metabolism and the main plasma component is unchanged delgocitinib. Following oral administration, four metabolites (formed via oxidation and glucuronide conjugation) were detected at < 2% of the average unchanged delgocitinib plasma concentrations. The limited metabolism of delgocitinib occurs primarily though CYP3A4/5 and to a lesser extent by CYP1A1, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6.
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies
Delgocitinib does not inhibit or induce cytochrome P450 enzymes or inhibit transporter systems such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp), breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), organic anion transporting proteins (OATP), organic anion transporters (OAT), organic cation transporters (OCT), or multidrug and toxin extrusion protein (MATE) at clinically relevant concentrations.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Delgocitinib was not carcinogenic when administered topically in a 2-year dermal carcinogenicity study in mice. No drug-related neoplastic findings were observed at strengths up to 5% delgocitinib ointment (approximately 600 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). In a 2-year oral carcinogenicity study in rats, delgocitinib was administered at doses of 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day. Benign thymoma was seen in female rats at 30 mg/kg/day (2274 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No drug-related neoplastic findings were observed in males at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (1869 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) or in females at 10 mg/kg/day (580 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
Delgocitinib was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a bacterial mutagenicity assay (the Ames test) or in vivo chromosomal aberration tests in rat bone marrow cells and human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Delgocitinib did not impair fertility in male rats at oral doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (1308 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). In female rats, delgocitinib resulted in a decrease in fertility index and corpora lutea, and an increase in implantation loss at 100 mg/kg/day (5897 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). An increase in post-implantation loss and a decrease in the number of live embryos were observed at 10 and 30 mg/kg/day, respectively (432 and 1087 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No adverse effects on fertility were noted at 30 mg/kg/day (1087 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) and no adverse effects on early embryonic development were noted at 3 mg/kg/day (110 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of ANZUPGO was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, 16-week trials (TRIAL 1 [NCT04871711] and TRIAL 2 [NCT04872101]) which enrolled a total of 960 adult subjects with moderate to severe CHE who had a history of inadequate response to, or for whom topical corticosteroids were not advisable. All subjects who completed TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2 were eligible to enroll into a long-term extension trial (TRIAL 3 [NCT04949841]).
Disease severity of enrolled subjects was defined using the Investigator's Global Assessment for chronic hand eczema (IGA-CHE) score and the Hand Eczema Symptom Diary (HESD) itch score (weekly average). The IGA-CHE is the investigator's overall assessment of chronic hand eczema at a given time point on a scale ranging from 0 (clear) to 4 (severe). The HESD itch score assesses disease severity of pruritus using a scale ranging from 0 (no symptoms) to 10 (severe symptoms). Subjects enrolled in these three trials had an IGA-CHE score of 3 or 4 (moderate or severe, respectively) and a HESD itch score (weekly average) of ≥ 4 points at baseline.
Across all treatment groups in TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2, the mean age of enrolled subjects was 44.1 years, and 8% of subjects were 65 years of age or older, 64% were female, 90% were White, 4% were Asian, and 1% were Black. For ethnicity, 94% of subjects identified as not Hispanic or Latino and 3% of subjects identified as Hispanic or Latino. The primary classifications of CHE by subtype were atopic hand eczema (35.9%), hyperkeratotic eczema (21.5%), irritant contact dermatitis (19.6%), allergic contact dermatitis (13.9%), vesicular hand eczema (9.1%), and contact urticaria/protein contact dermatitis (0.1%). Across all trial arms, 28% of subjects were diagnosed with two or more overlapping CHE subtypes.
The HESD itch score is a weekly average of daily itch severity on an 11-point scale from 0-10 that assesses the maximal intensity of pruritus in the last 24 hours with 0 being no pruritus and 10 being the worst pruritus. The HESD pain score is a weekly average of daily pain severity on an 11-point scale from 0-10 that assesses the maximal intensity of pain in the last 24 hours with 0 being no pain and 10 being the worst pain. In these trials, 28% of subjects had a baseline IGA-CHE score of 4 (severe CHE). The mean baseline HESD itch and pain scores were 7.1 and 6.7, respectively.
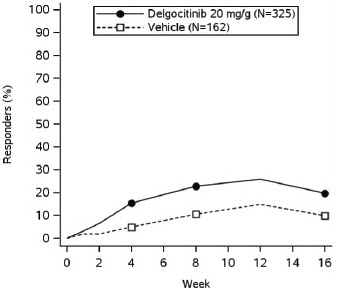
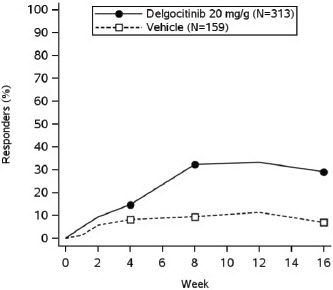
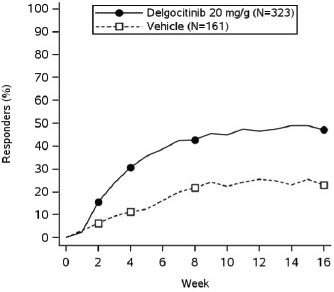
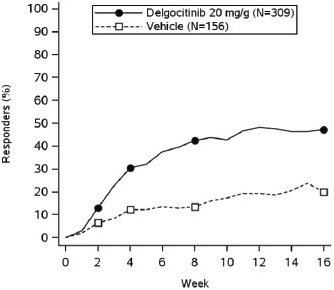
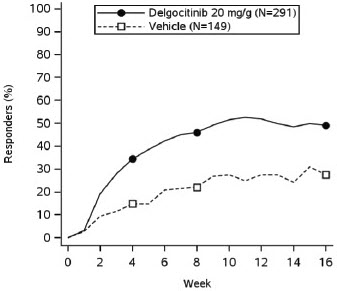
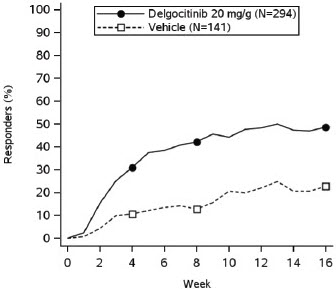
In both trials, subjects applied either topical ANZUPGO or vehicle twice daily to affected areas on the hands and wrists for 16 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of subjects who achieved IGA-CHE treatment success (IGA-CHE TS) at Week 16, defined as a score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least a 2-point improvement from baseline. Table 2 describes the efficacy results at Week 16 in TRIAL 2. Figure 1 describes the proportion of subjects who achieve IGA-CHE TS during the 16-week treatment period in TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2. Figures 2 and 3 describe the proportion of subjects who achieved HESD itch ≥ 4-point improvement and HESD pain ≥ 4-point improvement during the 16-week treatment period in TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2.
| TRIAL 1 | TRIAL 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANZUPGO (N=325) | Vehicle (N=162) | ANZUPGO (N=313) | Vehicle (N=159) |
|
| Abbreviations: N=number of subjects in the full analysis set (all subjects randomized and dosed); | ||||
|
||||
| IGA-CHE TS, % responders*, † | 20% (64/325) | 10% (16/162) | 29% (91/313) | 7% (11/159) |
| Difference from Vehicle (95% CI) | 10% (4%, 16%) | 22% (16%, 29%) | ||
| HESD itch ≥ 4-point improvement, % responders*, ‡ | 47% (152/323) | 23% (37/161) | 47% (146/309) | 20% (31/156) |
| Difference from Vehicle (95% CI) | 24% (16%, 33%) | 27% (19%, 36%) | ||
| HESD pain ≥ 4-point improvement, % responders*, ‡ | 49% (143/291) | 28% (41/149) | 49% (143/294) | 23% (32/141) |
| Difference from Vehicle (95% CI) | 22% (12%, 31%) | 26% (17%, 35%) | ||
Figure 1: Proportion of Adult Subjects with Moderate to Severe CHE who Achieved IGA-CHE Treatment Success (0 or 1 with ≥2-point improvement from baseline) Over Time in TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2
| TRIAL 1 | TRIAL 2 |
|
|
|
Point symbols are the multiplicity controlled timepoints.
Figure 2: Proportion of Adult Subjects with Moderate to Severe CHE who Achieved HESD Itch ≥ 4-point Improvement Over Time in TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2
| TRIAL 1 | TRIAL 2 |
|
|
|
Based on the number of subjects whose weekly average baseline value was ≥ 4 (scale from 0-10).
Point symbols are the multiplicity controlled timepoints.
Figure 3: Proportion of Adult Subjects with Moderate to Severe CHE who Achieved HESD Pain ≥ 4-point Improvement Over Time in TRIAL 1 and TRIAL 2
| TRIAL 1 | TRIAL 2 |
|
|
|
Based on the number of subjects whose weekly average baseline value was ≥ 4 (scale from 0-10).
Point symbols are the multiplicity controlled timepoints.
16. How is Anzupgo supplied
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Administration Instructions
Advise patients that ANZUPGO is for topical use only and is not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Advise patients to limit treatment to 30 grams per 2 weeks or 60 grams per month. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Instruct patients to clean and dry affected areas prior to applying ANZUPGO. Instruct patients to apply ANZUPGO, twice daily, to affected areas only on the hands and wrists, and avoid contact with eyes, mouth, or other mucous membranes [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Serious Infections
Inform patients that ANZUPGO may lower the ability of their immune system to fight infections and to contact their healthcare provider immediately if they develop any signs or symptoms of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Non-melanoma Skin Cancers
Inform patients that ANZUPGO may increase the risk of developing non-melanoma skin cancers. Inform patients that periodic skin examinations should be performed while using ANZUPGO. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they have ever had any type of cancer. Advise patients to avoid sunlamps and minimize exposure to sunlight by wearing sun-protective clothing or using broad-spectrum sunscreen [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Immunizations
Advise patients treated with ANZUPGO to avoid use of live vaccines immediately prior to, during, and immediately after treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Lactation
Advise breastfeeding women to avoid direct contact with the nipple and surrounding area immediately after applying ANZUPGO to the hands and/ or wrists to minimize infant exposure [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Manufactured by:
LEO Laboratories Ltd.
285 Cashel Road
Dublin 12, Ireland
Distributed by:
LEO Pharma Inc.
Madison, NJ 07940, USA
ANZUPGO® is a registered trademark of LEO Pharma A/S.
© 2025 LEO Pharma Inc. All rights reserved.
Medication Guide
Important: ANZUPGO is for use on the skin (topical use) only. Do not use ANZUPGO in or on your eyes, mouth, or vagina.
What is the most important information I should know about ANZUPGO?
ANZUPGO may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Serious Infections. ANZUPGO may increase your risk of infections. ANZUPGO contains delgocitinib. Delgocitinib belongs to a class of medicines called Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. JAK inhibitors are medicines that affect your immune system. JAK inhibitors can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. Some people have had serious infections while taking JAK inhibitors by mouth or applying on the skin, including tuberculosis (TB), and infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses that can spread throughout the body. Some people have been hospitalized or died from these infections.
- ANZUPGO should not be used in people with an active, serious infection. You should not start using ANZUPGO if you have any kind of infection unless your healthcare provider tells you it is okay. You may be at a higher risk of developing shingles (herpes zoster) or eczema herpeticum (a blistery, painful skin rash) during treatment with ANZUPGO.
- are being treated for an infection
- have an infection that does not go away or that keeps coming back
- have TB or have been in close contact with someone with TB
- have had shingles (herpes zoster)
- have had hepatitis B or C
- think you have an infection or have symptoms of an infection such as:
- fever, sweating, or chills
- muscle aches
- cough or shortness of breath
- blood in your phlegm
- weight loss
- warm, red, or painful skin or sores on your body
- diarrhea or stomach pain
- burning when you urinate or
- urinating more often than usual
- feeling very tired
ANZUPGO can make you more likely to get infections or make worse any infections that you have. If you get a serious infection, your healthcare provider may stop your treatment with ANZUPGO until your infection is controlled. -
Non-melanoma skin cancer. ANZUPGO may increase your risk of certain non-melanoma skin cancers. Your healthcare provider will regularly check your skin during your treatment with ANZUPGO.
- Avoid sunlamps and limit the amount of time you spend in the sunlight. Wear protective clothing when you are in the sun or use a broad-spectrum sunscreen.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had any type of cancer.
- Potential risks from Janus kinase (JAK) inhibition. It is not known whether using ANZUPGO has the same risks as taking other oral or topical JAK inhibitors. Increased risk of death (all causes) has happened in people who were 50 years of age and older with at least 1 heart disease (cardiovascular) risk factor who were taking a JAK inhibitor used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared to people taking another medicine in a class of medicines called TNF blockers. ANZUPGO is not for use in people with RA. Other oral or topical JAK inhibitors have also caused increased cholesterol.
See "What are the possible side effects of ANZUPGO?" for more information about side effects.
What is ANZUPGO?
ANZUPGO is a prescription medicine used on the skin (topical) to treat moderate to severe chronic hand eczema in adults who are not well-controlled with, or cannot use topical corticosteroids.
The use of ANZUPGO along with other JAK inhibitors or strong immunosuppressants is not recommended.
It is not known if ANZUPGO is safe and effective in children.
Before using ANZUPGO, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- See "What is the most important information I should know about ANZUPGO?"
- have an infection
- have recently received or are scheduled to receive a vaccine. People who use ANZUPGO should not receive live vaccines right before starting, during treatment, or right after treatment with ANZUPGO.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if ANZUPGO will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if ANZUPGO passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with ANZUPGO.
If you use ANZUPGO while breastfeeding, avoid touching the nipple and surrounding area right away after applying ANZUPGO to your hands and wrists.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I use ANZUPGO?
- ANZUPGO is for use on the skin of your hands and wrists only. Do not use ANZUPGO in or on your eyes, mouth, vagina or other mucous membranes. If contact with mucous membranes happens, rinse well with water.
- Use ANZUPGO exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Clean and dry skin of the affected areas before applying ANZUPGO.
- Apply a thin layer of ANZUPGO 2 times each day to affected areas on your hands and wrists. Do not use more than 30 grams in 2 weeks or 60 grams in a month.
- If someone else applies ANZUPGO for you, they should wash their hands after applying ANZUPGO.
What are the possible side effects of ANZUPGO?
ANZUPGO may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects of ANZUPGO include:
- application site reactions, including pain, tingling, itching, and redness
- bacterial skin infections, including finger cellulitis, and nail infections
- low white blood cells
These are not all of the possible side effects of ANZUPGO.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ANZUPGO?
- Store ANZUPGO at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not freeze ANZUPGO.
Keep ANZUPGO and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of ANZUPGO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use ANZUPGO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ANZUPGO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ANZUPGO that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in ANZUPGO?
Active ingredient: delgocitinib
Inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol, butylated hydroxyanisole, cetostearyl alcohol, citric acid monohydrate, edetate disodium, hydrochloric acid, mineral oil, polyoxyl 20 cetostearyl ether, and purified water.
Manufactured by:
LEO Laboratories Ltd., 285 Cashel Road, Dublin 12, Ireland
Distributed by:
LEO Pharma Inc., Madison, NJ 07940, USA
ANZUPGO® is a registered trademark of LEO Pharma A/S.
© 2025 LEO Pharma Inc. All rights reserved.
For more information about ANZUPGO, go to www.ANZUPGO.com or call 1-877-494-4536.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: 7/2025
LEO®
075997
| ANZUPGO
delgocitinib cream |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - LEO Pharma, Inc (832692615) |
| Registrant - LEO Laboratories Ltd. (219532322) |
More about Anzupgo (delgocitinib topical)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: miscellaneous topical agents
- En español