Subclavian Artery Stenosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is subclavian artery stenosis?
Subclavian artery stenosis is a condition where one of the arteries that supply blood to your arm becomes narrow and stiff. The subclavian arteries are big blood vessels located under your clavicle (collarbone) on each side of your body. Narrow and stiff arteries cause reduced blood flow to either arm.
What causes subclavian artery stenosis?
The cause of subclavian artery stenosis may include any of the following:
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) or fatty cholesterol deposits on artery walls
- A condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels such as Takayasu disease
- Radiation (cancer treatment) to the chest
- A condition that causes pressure on the subclavian arteries such as thoracic outlet syndrome
- Abnormal cell growth in the artery walls
- Trauma to the subclavian artery, such as from a motor vehicle accident, sharp object, or past surgery
- A condition you were born with where the subclavian artery is not well developed or absent, such as congenital atresia
What increases my risk for subclavian artery stenosis?
- A higher weight than recommended
- High cholesterol, diabetes, or high blood pressure
- Smoking cigarettes
- Not enough exercise or poor nutrition
What are the signs and symptoms of subclavian artery stenosis?
You may not have any symptoms if your subclavian artery stenosis is mild. You may have any of the following if it is more severe:
- Arm pain, muscle fatigue (tiredness), or muscle cramps that gets worse with activity
- Numbness or tingling in either arm
- Dizziness, vertigo (feeling that you are moving when you are not), or fainting
How is subclavian artery stenosis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms. Your provider will check for differences in blood pressure between your arms. Your provider will listen to your heart and check for a whooshing sound in your arteries. You may need any of the following tests:
- Ultrasound, CT, or MR angiography pictures may be used to check for blocked or narrow arteries. Contrast liquid may be given to help arteries show up better in pictures. Tell the provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- An angiogram is a procedure to check how blood flows through your arteries. A catheter (long thin tube) is inserted into your arm, neck, or groin and moved into your arteries. An x-ray may be used to guide the tube to the right place.
Related medications
How is subclavian artery stenosis treated?
You may need any of the following:
- Medicines may be given to prevent blood clots and improve blood flow. You may also need medicine to control your blood pressure, cholesterol, or blood sugar levels.
- Angioplasty with stenting may be done to open an artery blocked by plaque. A tube with a balloon on the end is put into the blocked artery. When the tube is in the artery, the balloon is inflated. As the balloon inflates, it presses the plaque against the artery wall to open the artery. A stent may be placed in your artery to keep it open.
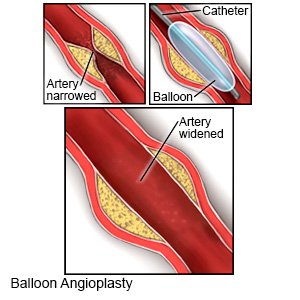
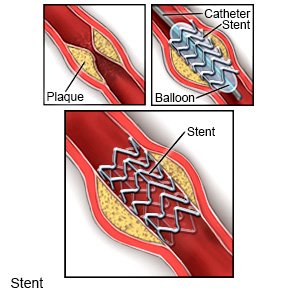
- Surgery may be used to bypass (send blood around) the blocked part of an artery.
How can I manage or prevent subclavian artery stenosis?
- Manage other health conditions. High blood pressure and high cholesterol levels can worsen subclavian artery stenosis. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on managing these or other health conditions.
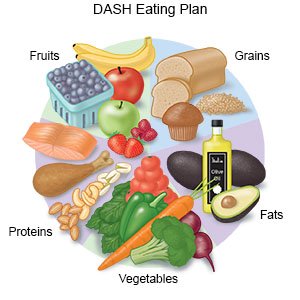
- Eat heart-healthy foods. Heart-healthy foods include salmon, tuna, walnuts, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, and oils such as olive or canola oil. A dietitian or your provider can give you more information on meal plans such as the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) eating plan. The DASH plan is low in sodium, processed sugar, unhealthy fats, and total fat. It is high in potassium, calcium, and fiber. These can be found in vegetables, fruit, and whole-grain foods.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Extra body weight can increase your risk for health problems that may cause subclavian artery stenosis. Ask your provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask your provider to help you create a weight loss plan, if needed.
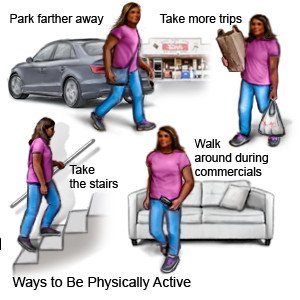
- Be physically active, as directed. Physical activity, such as exercise, helps improve blood flow in your arteries and can help you manage your weight. Activity can also help lower your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. Your provider can help you create an activity plan that works best for you.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause inflammation and damage to your artery walls. This increases your risk for fatty cholesterol deposits in your arteries. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone call if:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have sudden pain or weakness in your affected arm.
- Your affected arm feels cold or numb with tingling.
- You feel dizzy, faint, or have blurred vision.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have new or worsening symptoms.
- You have trouble taking your medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
