Robot Assisted Laparoscopic Ureter Reimplantation
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
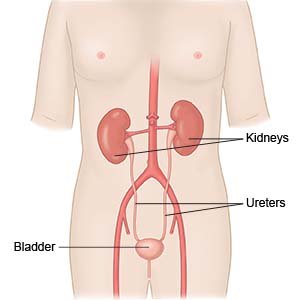
Robot assisted laparoscopic ureter reimplantation (RALUR) is surgery to fix the position of the ureters through small incisions in your child's abdomen. RALUR is done with a machine that is controlled by your child's surgeon. The machine has mechanical arms that use small tools to help perform the surgery.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child urinates less than usual or not at all.
- Your child's stitches come apart.
- Blood soaks through your child's bandage.
- Your child's incision sites are red, swollen, and draining pus.
Call your child's doctor if:
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child has nausea or vomits.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Related medications
Medicines:
Your child may need any of the following:
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to give your child and how often to give it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines your child uses to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your child's doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- Do not give aspirin to children younger than 18 years. Your child could develop Reye syndrome if he or she has the flu or a fever and takes aspirin. Reye syndrome can cause life-threatening brain and liver damage. Check your child's medicine labels for aspirin or salicylates.
- Give your child's medicine as directed. Contact your child's healthcare provider if you think the medicine is not working as expected. Tell the provider if your child is allergic to any medicine. Keep a current list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs your child takes. Include the amounts, and when, how, and why they are taken. Bring the list or the medicines in their containers to follow-up visits. Carry your child's medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for the incision sites as directed:
Do not let the sites get wet until the surgeon says it is okay. When it is okay to bathe your child, do not scrub the sites. Just let water run over the sites. Gently pat-dry the sites and put on new, clean bandages as directed. Change your child's bandages when they get wet or dirty. Do not put powders or lotions over your child's incision sites. Check the sites every day for signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, or pus.
Follow up with your child's surgeon as directed:
Follow up within 1 week if your child has a urinary catheter. Your child will need to return in 4 to 6 weeks to check if his or her ureters are working properly. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
